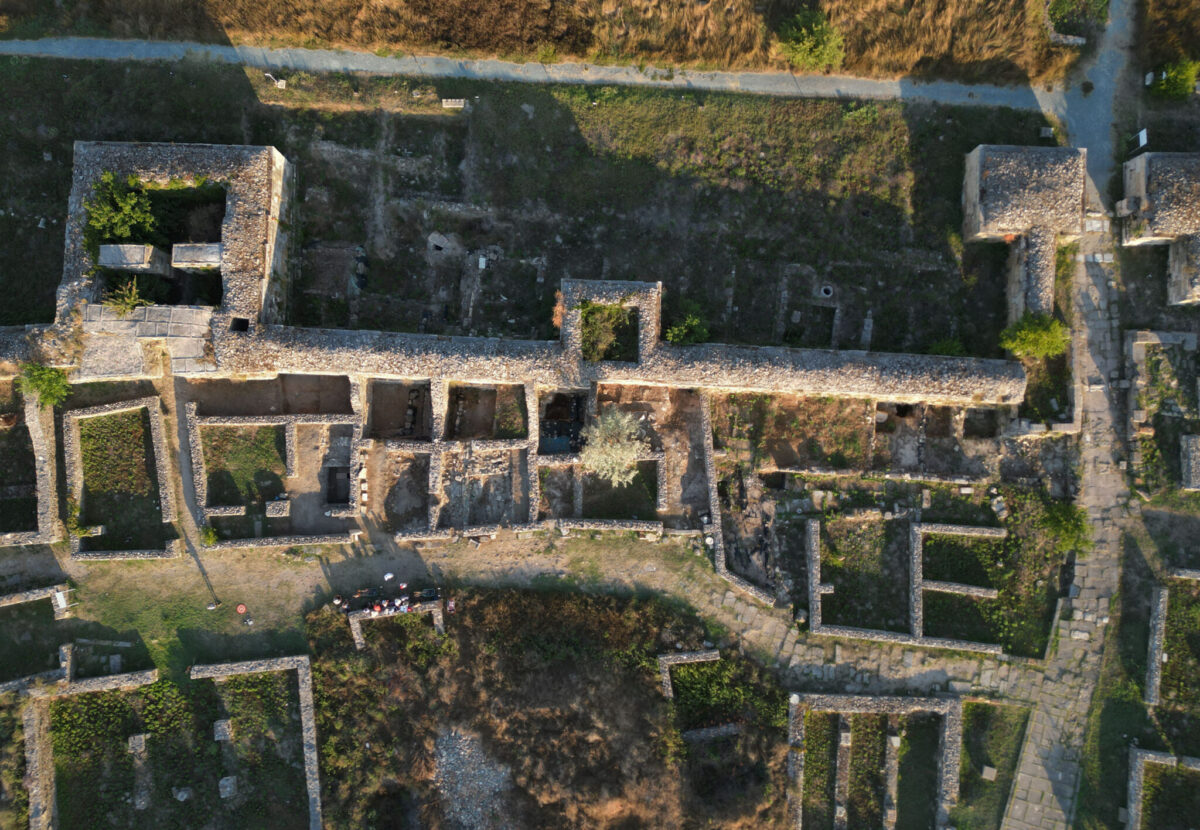
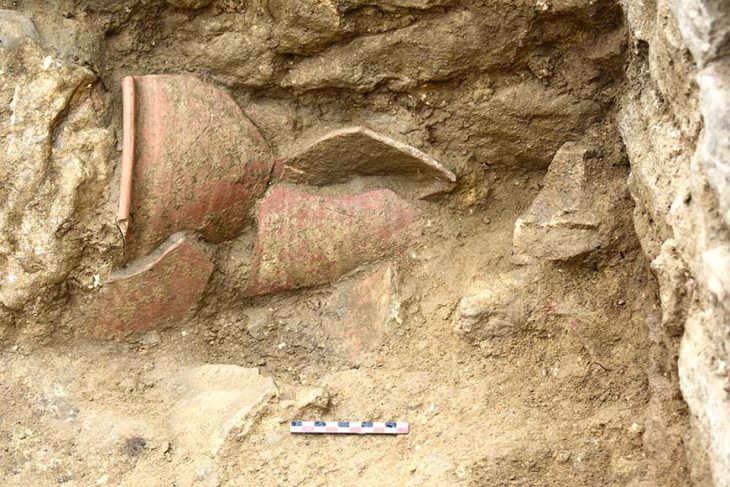
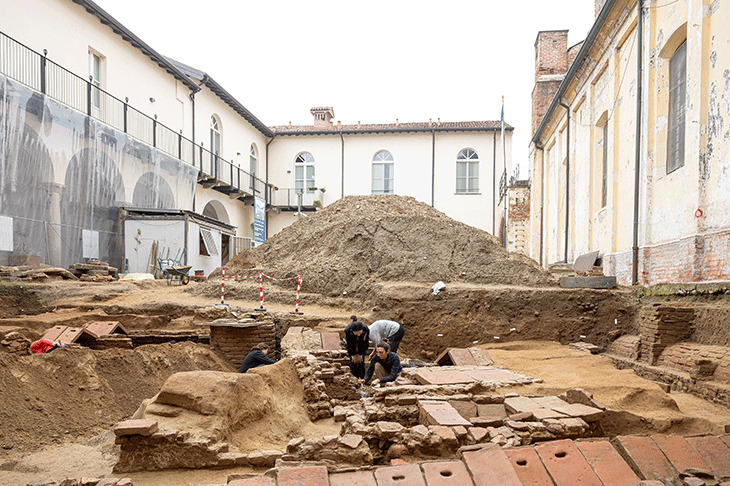
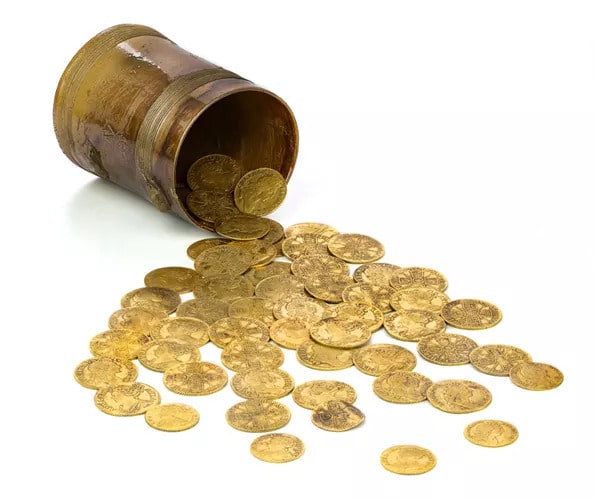
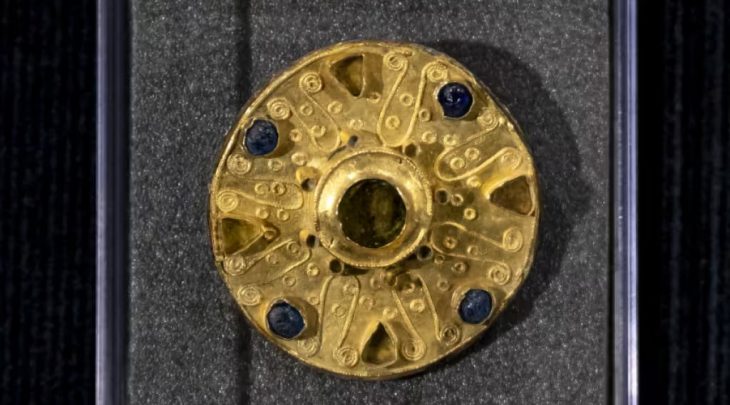
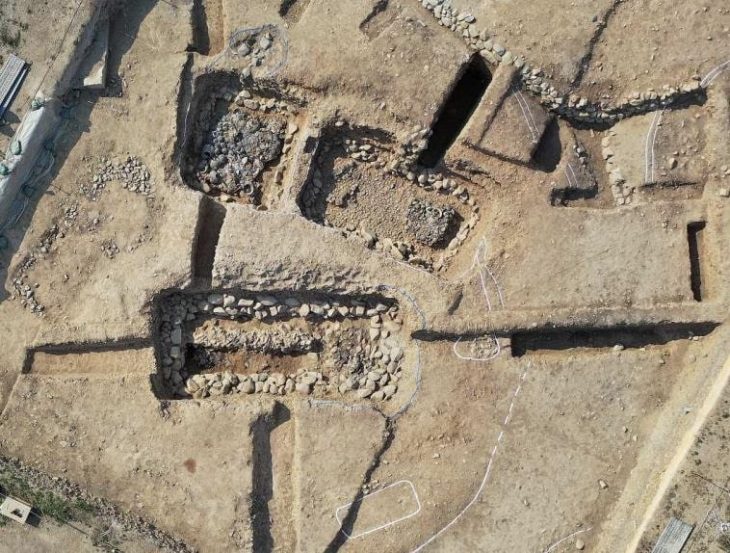
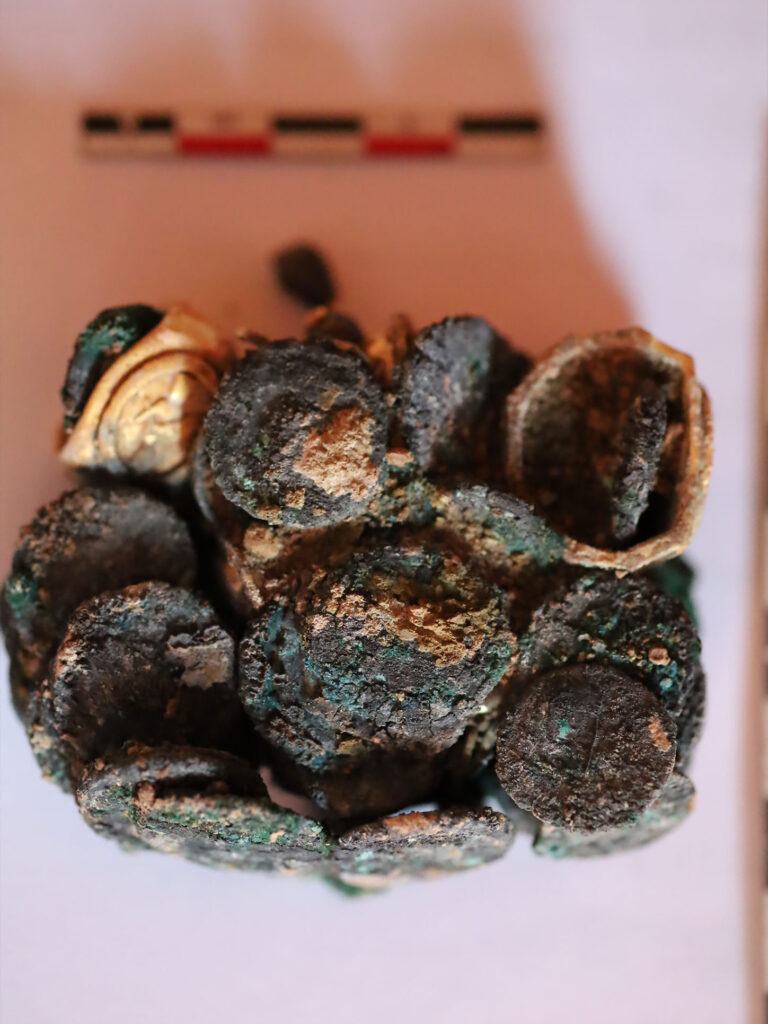
The National Museum of Romanian History (MNIR) has announced groundbreaking archaeological findings at the ancient site of Histria, one of the most significant historical settlements on the western coast of the Black Sea. During the museum’s ongoing annual excavation campaign, archaeologists uncovered a remarkable treasure consisting of more than 40 Roman coins and several exquisite pieces of jewelry crafted from precious metals.
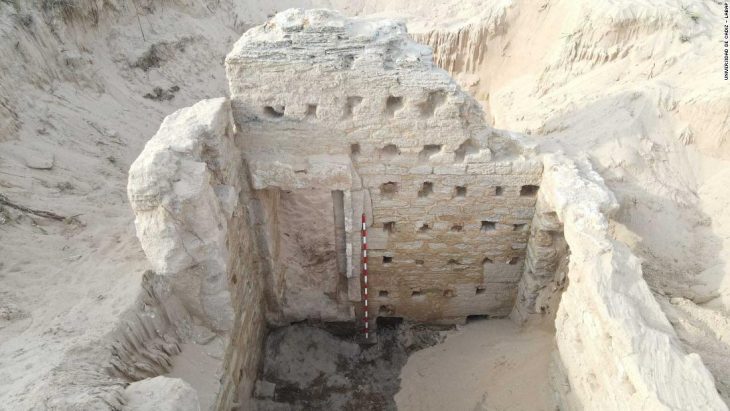
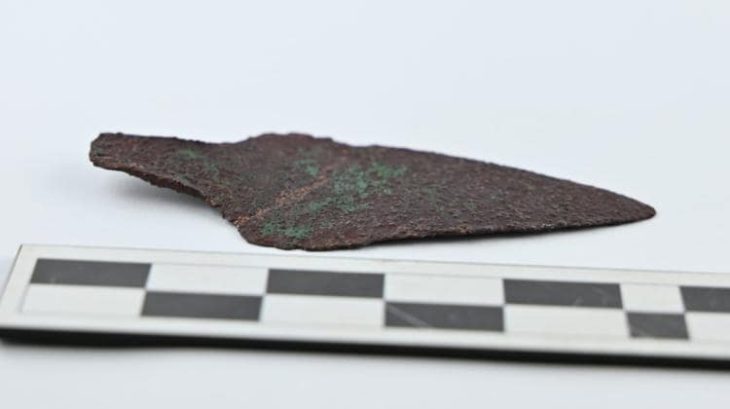
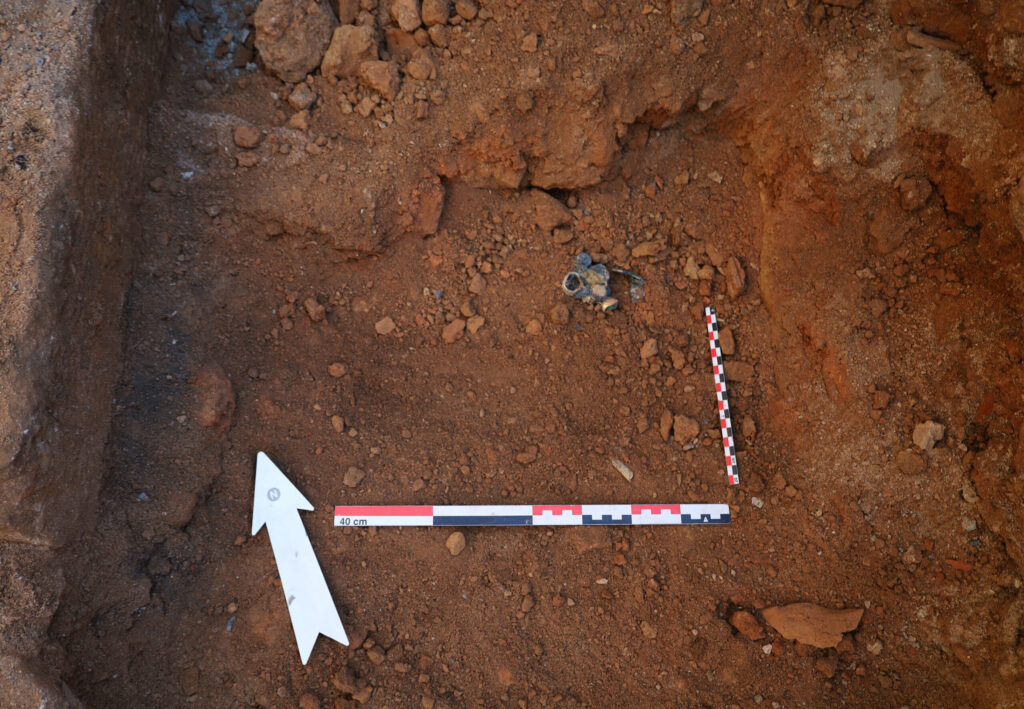
This exceptional discovery was made in the research sector known as Poarta Mare – Turnul Mare (The Great Gate – The Great Tower), coordinated by MNIR. The artifacts were found within the remains of a Roman dwelling that was destroyed by fire nearly 1,800 years ago. Alongside the treasure, researchers documented numerous other items, including inscriptions, ceramic vessels, glassware, and tools made of bronze, iron, and stone.
A Treasure Preserved by Fire
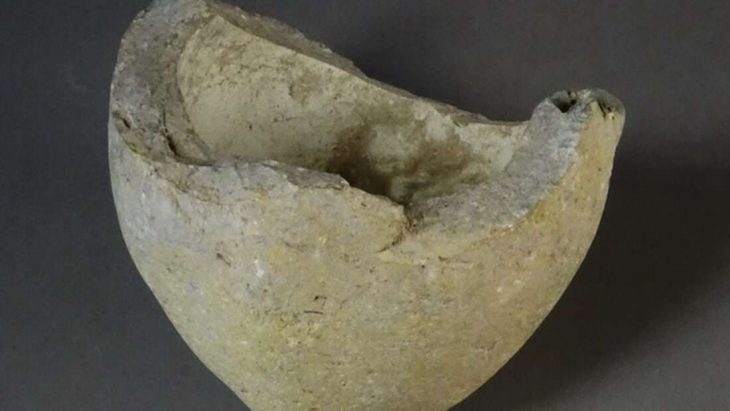
Preliminary analysis suggests that the jewelry and coins were once stored in a wooden chest. When the house was engulfed by flames during the 2nd–3rd century AD, the box was destroyed, but the heat caused the items to fuse together, preserving the outline of their container.
Archaeologists believe the house belonged to a prominent Roman family. Its decorative limestone pavements and painted plastered walls indicate wealth and social status. The treasure was likely safeguarded in a special location, but the sudden blaze made it impossible for its owners to recover their valuables.
The artifacts offer a vivid glimpse into daily life in Histria during the Principate, a period of Roman imperial rule marked by economic prosperity and cultural integration.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
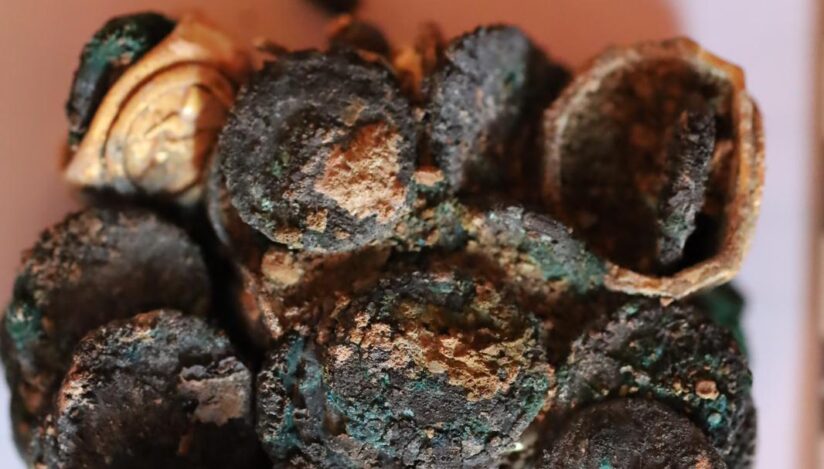
Over a Century of Archaeological Research
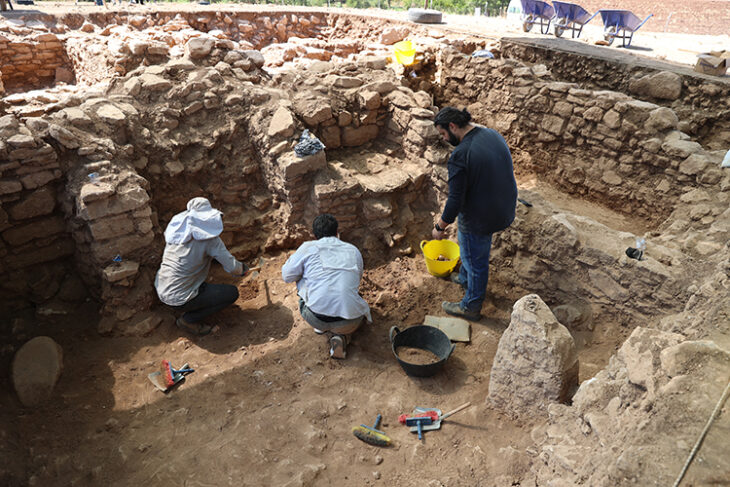
Excavations at Histria began in 1914 and continue to this day, overseen by the Vasile Pârvan Institute of Archaeology in Bucharest. The project brings together experts from the National History and Archaeology Museum of Constanța, MNIR, the University of Bucharest’s Faculty of History, and Ovidius University of Constanța.
Since 2000, MNIR has operated a dedicated research sector at the site, led by a team of archaeologists including Adela Bâltâc, Paul Damian, Virgil Apostol, and Eugen Paraschiv-Grigore. Their focus has been the study of early Roman phases of Histria, with excavations funded directly by the museum.
25 Years of Discoveries
Over the past quarter-century, MNIR’s work has yielded some of the most important archaeological results at Histria. Excavations have uncovered structures dating from the late Hellenistic period (1st century BC) through the late Roman era (4th–6th centuries AD).
Highlights include:
Newly revealed sections of two ancient streets previously known only from earlier research.
An entirely new street alignment unknown until MNIR’s investigations.
Three monumental Roman buildings connected to these streets.
Water management infrastructure, including drainage channels, pipelines, and a well.
Domestic and luxury objects such as amphorae, fine ceramics, bronze tools, glass vessels, iron implements, and carved bone artifacts.
Numerous coins, inscriptions, and architectural fragments.
These findings allow scholars to reconstruct the urban layout and daily life of Histria across centuries, painting a detailed picture of its development from a Greek colony to a flourishing Roman settlement.

The Treasure’s Future
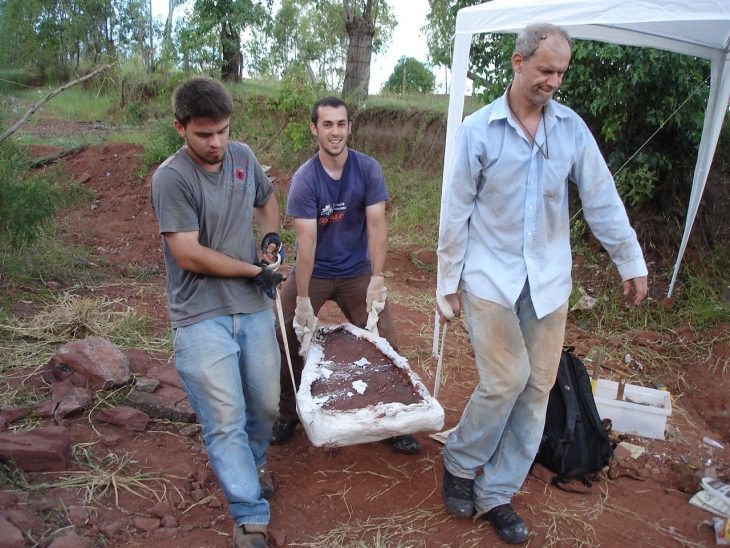
The recently uncovered hoard—over 40 Roman coins and a set of ancient ornaments—will be classified as part of Romania’s National Cultural Heritage Treasury due to its historical and artistic significance.
The artifacts were transferred this week to MNIR’s restoration laboratories in Bucharest. Specialists will conduct thorough scientific investigations, followed by conservation and restoration work. This process will ensure the long-term preservation of the objects and prepare them for eventual public display.
The museum has announced that an official presentation of the treasure will be organized in the near future, allowing both the public and the media to view these extraordinary finds.
Why Histria Matters
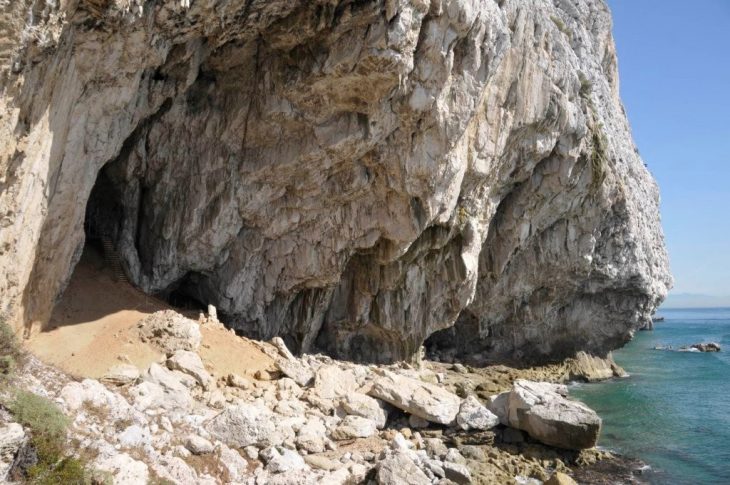
Founded in the 7th century BC by Greek settlers from Miletus, Histria is often called “the oldest city in Romania.” It flourished as a major economic and cultural hub, first under Greek influence and later as part of the Roman Empire. Its strategic location on the Black Sea made it a vital center for trade, religion, and military defense.
The latest discovery reinforces Histria’s importance as a living archive of ancient history. Each artifact recovered adds a new piece to the puzzle of life along the western Black Sea coast during antiquity.

A Step Closer to the Ancient World
According to MNIR representatives, archaeological research at Histria remains one of the museum’s highest priorities. Beyond enriching Romania’s national heritage collections, these discoveries provide fresh insights into the interconnected histories of the Greek and Roman worlds.
The newly uncovered treasure is more than a collection of ancient valuables—it is a powerful testament to human resilience, memory, and cultural continuity. With each excavation season, Histria continues to reveal secrets buried for millennia, offering the modern world a rare opportunity to walk in the footsteps of its ancient inhabitants.