The finds unearthed during the construction of local metro facilities in Thessaloniki, a Greek port city on the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea and also Greece’s 2nd largest city, are quite impressive.
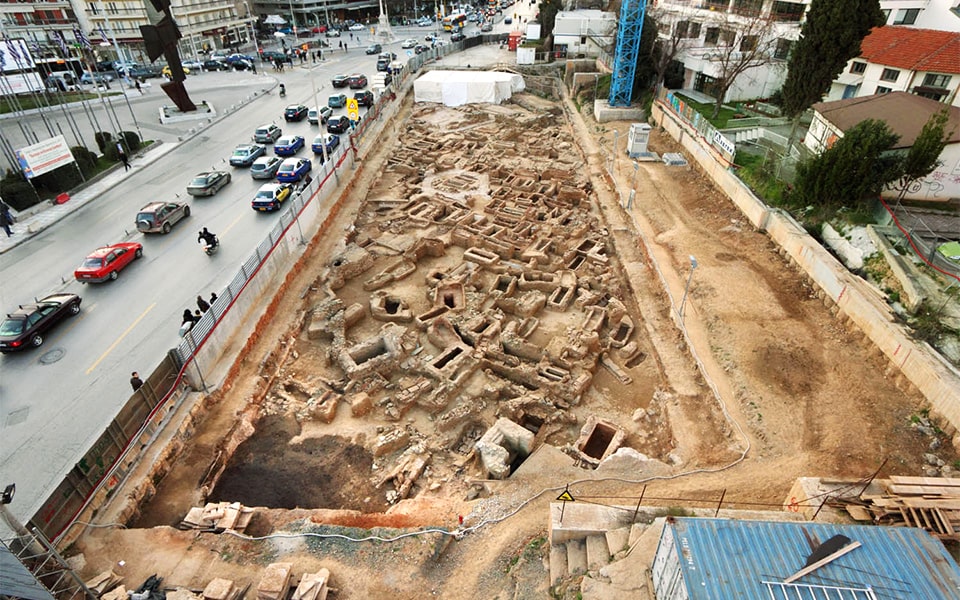
Attiko Metro SA has released a series of stunning photographs that provide a rare glimpse of the ancient city of Thessaloniki. Thessaloniki is hosting the largest archaeological excavation in Northern Greece, covering an area of 20,000 square meters, and the findings are extraordinary and of great historical significance.
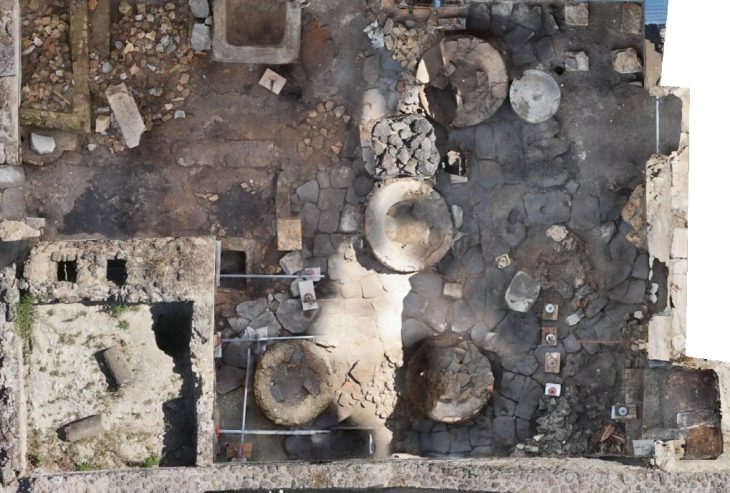
A pre-Cassandrian small town from the 4th century BC was discovered in Pylaia in 2012 during excavations at the “Amaksostasio” of the main line of the Metro. A 31-acre area was investigated, and part of the city was laid out according to the Hippodamian (grid plan) urban planning system and adhered to the standards of the great cities of Macedonia, Olynthos, and Pella—was revealed.
The numerous find suggests a thriving community with a robust economy and established sociopolitical structures. The second half of the fourth century is thought to have seen its greatest development. However, it was cut short when Kassandros founded the city of Thessaloniki, which was later abandoned, in 315 BC.
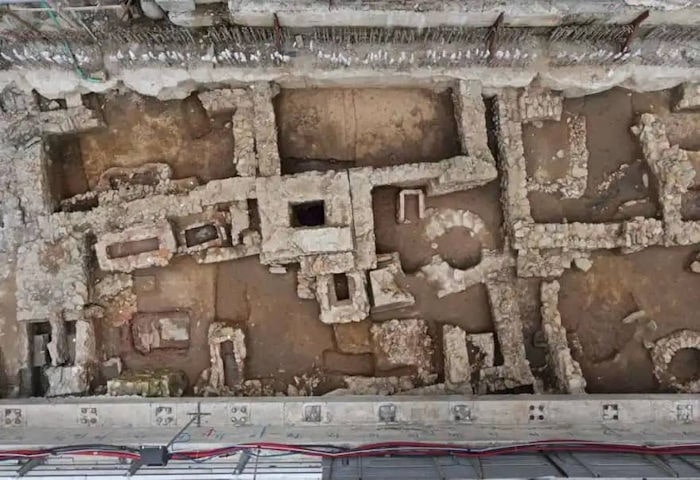

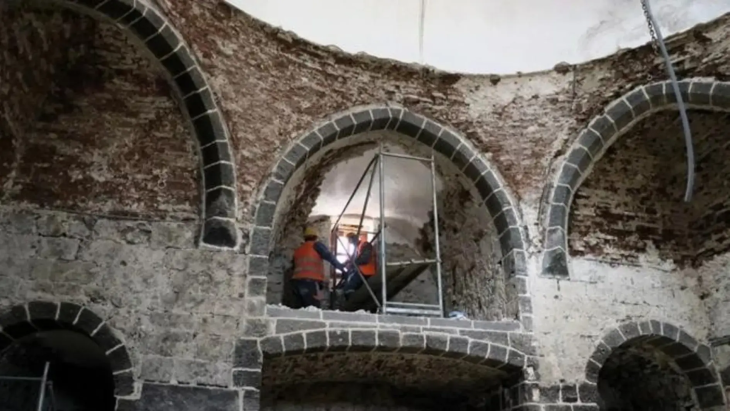
According to Attiko Metro SA, the most significant archaeological excavations occurred during the project’s first construction phase in four Historical Center stations: Syntagma, Kerameikos, Monastiraki, and Acropolis. However, Hagia Sophia and Fleming stations should also be included in these stations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The statue of Aphrodite, found in 2018, was discovered at the site of the Hagia Sophia station (named after the Hagia Sophia of Thessaloniki, one of the oldest churches in the city). The sculpture was identified near the very area which revealed an entire fountain complex.
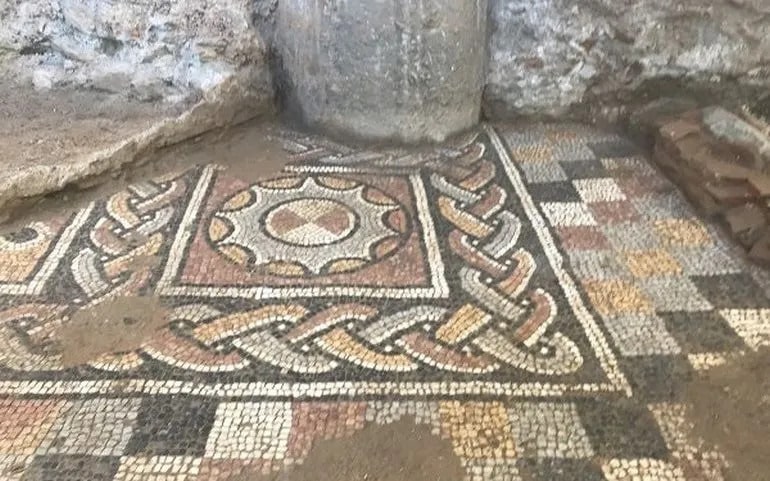
Other than this sculpture, the archaeologists excavating the area (near the southern entrance of the Hagia Sophia station) were pleasantly surprised by the well-preserved state of the 4th-century mosaics. Showcasing their geometric patterns, these multicolored mosaics were possibly a part of a public building complex or at the very least bedecked the floors of an urban villa.

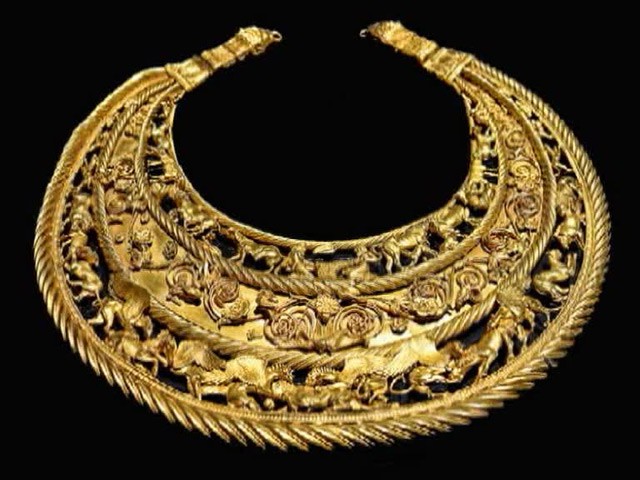
The Roman cemetery (2nd–4th century AD) that was discovered within the boundaries of Fleming Station and revealed to us details of a previously unidentified settlement on the outskirts of ancient Thessaloniki is another intriguing discovery. An extensive portion of the city’s eastern cemetery was discovered. Additionally, a three-kilometer cemetery basilica with mosaic floors was discovered on the site of an earlier structure. In particular, it made thousands of funerary monuments (3000) visible, which has improved our understanding of how the area was organized and continuously used from the Hellenistic era to Late Antiquity. The tombs belong to various types, pit-shaped, box-shaped, pot burials, altars, altar-shaped constructions, single or double vaulted, decorated with clay and glass vessels, clay figurines, gold and silver jewelry, and coins.
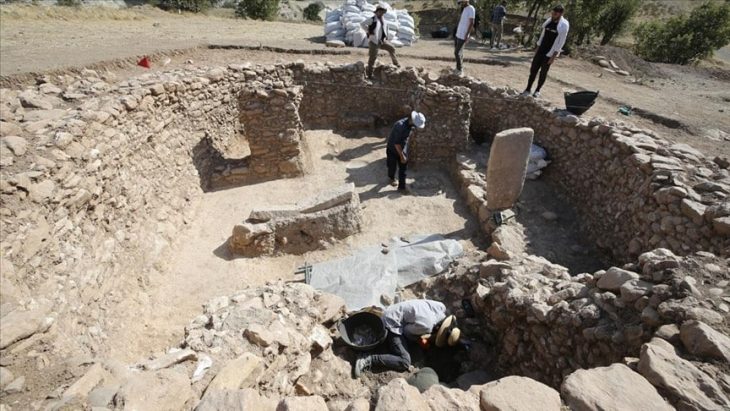
More than twenty archaeological excavations were conducted in stations and ventilation shafts in total. The archaeological layers ranged in depth from 0.5 to 7.0 meters, but some hydraulic structures, wells, conduits, reservoirs, and aqueducts were discovered at much deeper levels. Under the scientific oversight of the capable services of the Ministry of Home Affairs, the antiquities were meticulously documented and recorded using contemporary technical techniques.
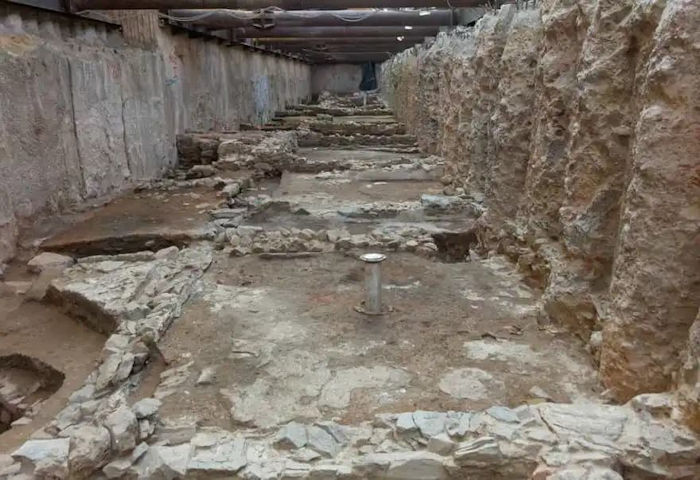

The 2,500 square meter excavation research at the Acropolis station demonstrated that the area was occupied from the end of the third millennium BC until the Byzantine era.
More than 300,000 artifacts, many dating back to the 4th century BC, have been excavated from 6 of the 12 station sites currently under construction. Ancient artifacts unearthed during the construction of the city’s new metro system will be exhibited at six stations and two new museums in this year.
Cover Photo: An ancient cemetery, uncovered near the site of the future subway station of Syntrivani. ©Hellenic Ministry of Culture and Sports