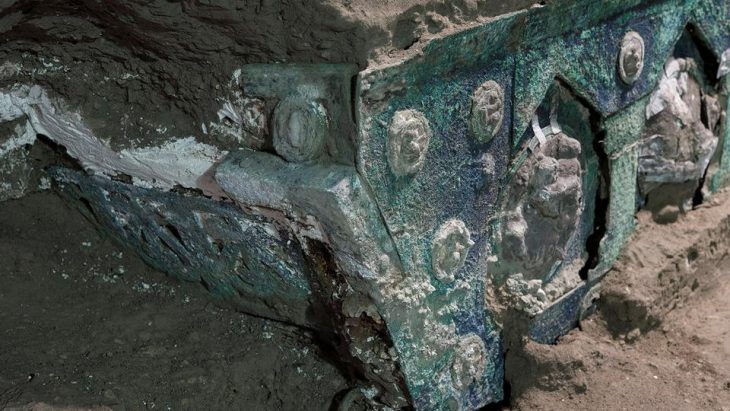
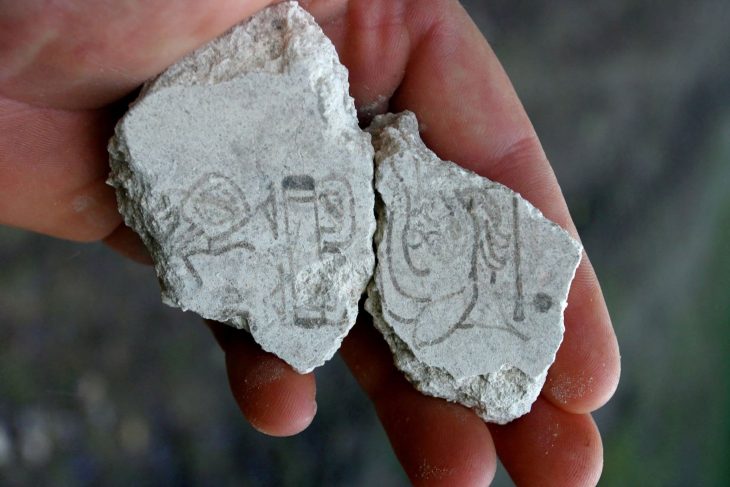
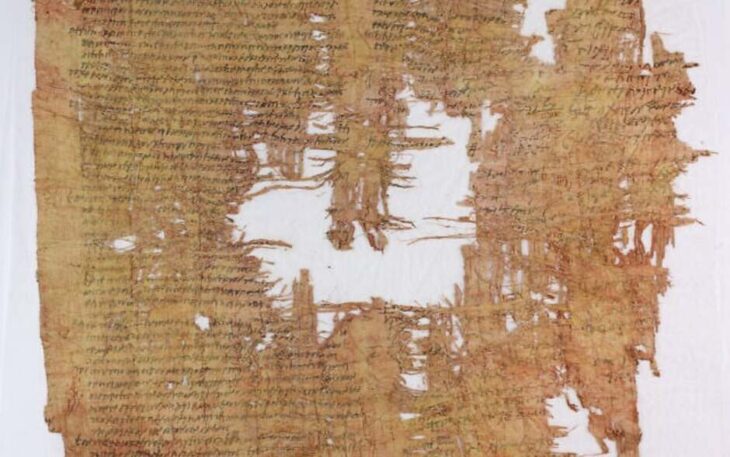
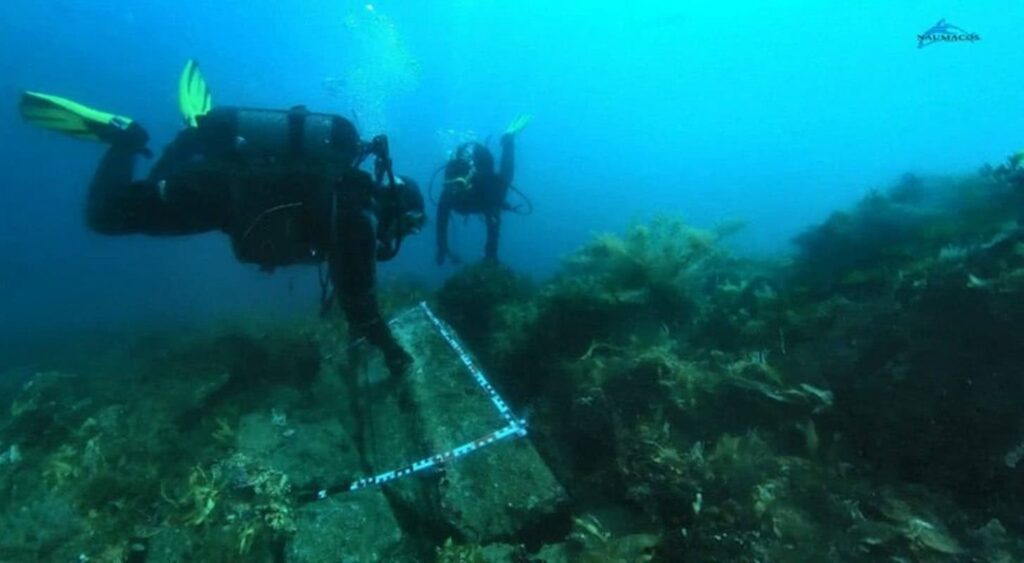
An underwater excavation off the coast of Bacoli, in southern Italy, has uncovered a remarkable Roman-era breakwater built from reused architectural and sculptural fragments.
The submerged structure, located at the ancient port of Misenum (Portus Iulius), reveals how Roman engineers deliberately arranged columns, architraves, and statues on the seafloor to serve as a protective barrier against the fierce Sirocco winds. This discovery offers rare insight into how the Roman Empire reused monumental materials to safeguard its naval infrastructure, blending maritime engineering with cultural heritage.
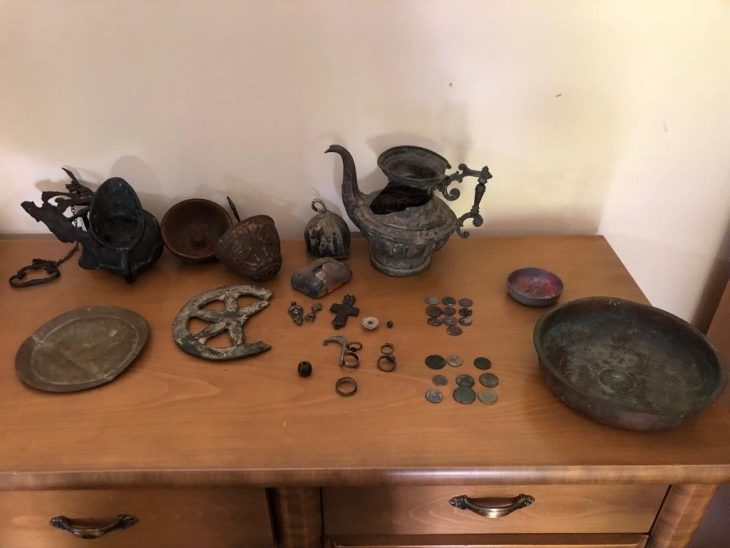
An extraordinary underwater archaeological mission in Bacoli, southern Italy, has led to the recovery of valuable Roman-era architectural fragments from the ancient Portus Iulius, once the main naval base of the Roman Empire in the Tyrrhenian Sea. The excavation, carried out by a multidisciplinary team of archaeologists and underwater heritage experts, brought to light sculptures, architraves, columns, and inscribed bases dating back to the Imperial period.
The operation took place in the submerged section of the ancient Roman harbor, located between Punta Terone and Punta Pennata. The area extends over 90 meters in length, with an average width of 22–23 meters and lies at a depth ranging from five to nine meters. Systematic excavations in this location began in 1996, following decades of sporadic accidental discoveries since the 1980s.
What makes this recent recovery particularly significant is the discovery that the artifacts were not the result of structural collapse or natural geological shifts such as bradyseism, which is common in the Phlegraean Fields. Instead, archaeological analysis indicates a deliberate placement of these materials on the seabed, most likely to form a barrier against the Sirocco winds—a function comparable to modern breakwaters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Among the recovered pieces are two marble architraves featuring refined relief moldings and a fragment of a column made of cipollino marble. These were extracted using inflatable lifting balloons and transported by the Carabinieri Underwater Unit’s patrol boat. The artifacts will undergo desalination and restoration at the Bourbon Park of Fusaro, after which they will be exhibited at the Palazzo dell’Ostrichina, a historic building near Lake Fusaro now repurposed as a cultural venue.
The underwater excavation employed cutting-edge technologies including 3D scanning, high-resolution photogrammetry, and hyperspectral imaging, enabling precise mapping of the submerged structures before recovery. Notably, this operation also marked the first time in Italy that such a complex underwater intervention was broadcast live to the public, aligning with the principles of transparency and education promoted by the 2001 UNESCO Convention on the Protection of Underwater Cultural Heritage.
Simona Formola, head of the Underwater Archaeology Office of the Superintendency, emphasized that the discovery is a powerful example of Roman ingenuity in environmental adaptation. Traces of marine erosion on the recovered elements, particularly from lithodome mollusks, confirm their prolonged exposure before being repurposed in antiquity for maritime defense.

Superintendent Mariano Nuzzo described the recovery as a crucial contribution to understanding the urban and military landscape of ancient Misenum, home to the Classis Misenensis fleet, which was led by Pliny the Elder during the eruption of Vesuvius in 79 AD. Mayor Josi Gerardo Della Ragione also praised the project as a collaboration between national institutions and the local community to reclaim and showcase Bacoli’s submerged cultural treasures.
This project not only enriches our understanding of the strategic importance of Misenum in Roman times but also sets a precedent for public-facing, technologically advanced approaches to underwater heritage preservation.
Cover Image Credit: Soprintendenza ABAP dell’Area Metropolitana di Napoli