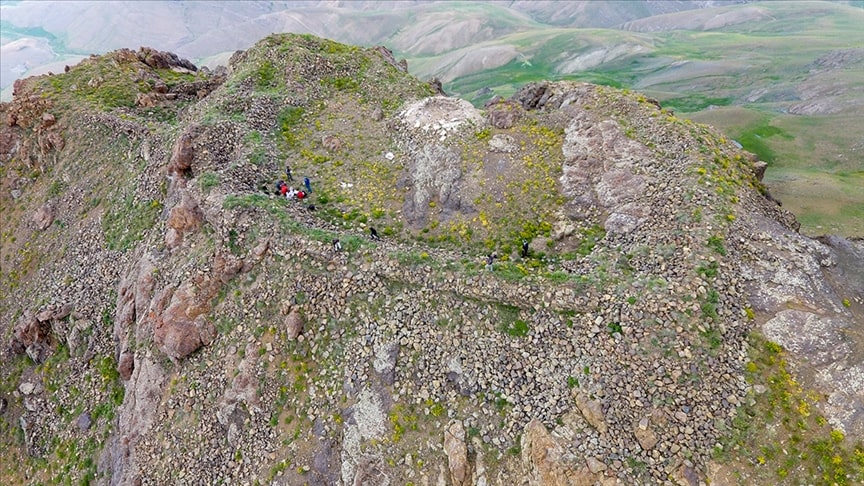
In the Gürpınar district of Van, located in eastern Turkey, a fortress ruin, which is considered to be used by the ruling class of the Urartians, was detected on a mountain at an altitude of 3,300.
The excavation team headed by Professor Rafet Çavuşoğlu, Head of the Archeology Department of the Faculty of Letters of Van Yüzüncü Yıl University (YYÜ), initiated an Archaeological Surface Research Project in order to uncover the historical structures in the district and bring them to tourism.
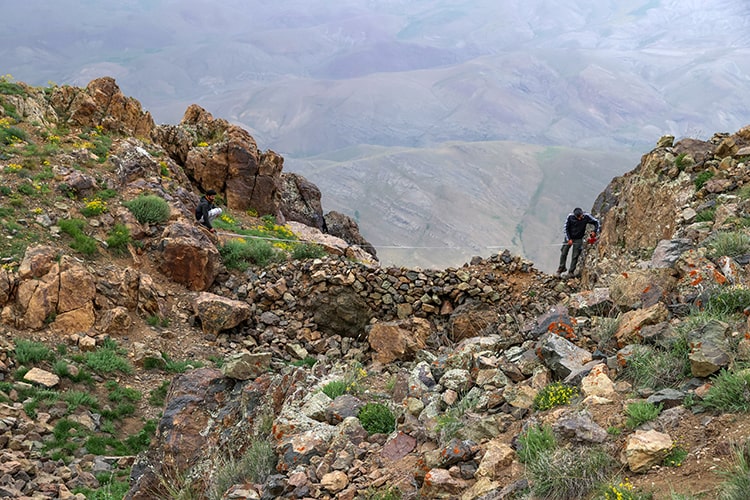
Within the scope of the project supported by the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the excavation team went to Örmeli neighborhood, 40 kilometers from the district, and climbed the Kara Dağ (Black Mountain) at an altitude of 3,300.
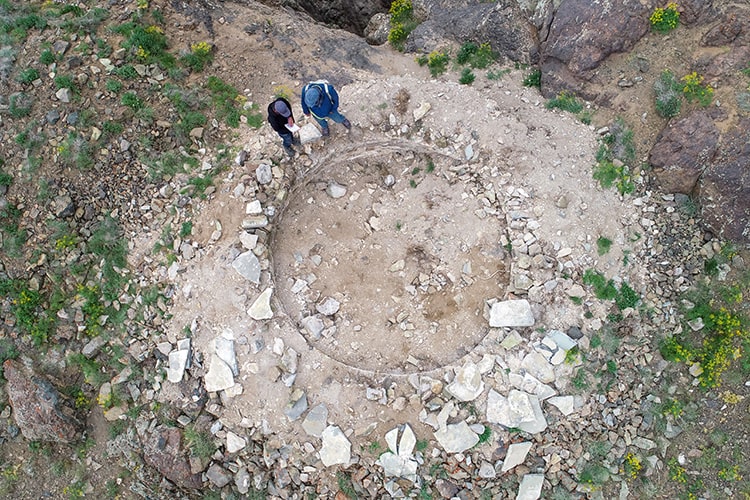

The team of archaeologists, anthropologists and art historians, who reached the summit after climbing for about 4 hours under the guidance of professional mountaineer Mustafa Bingöl, discovered the remains of an ancient road and a new castle from the Urartian period during the surveys in the region.
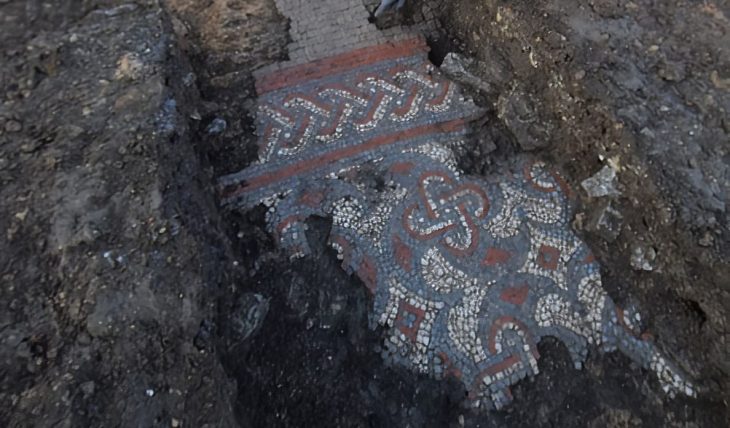
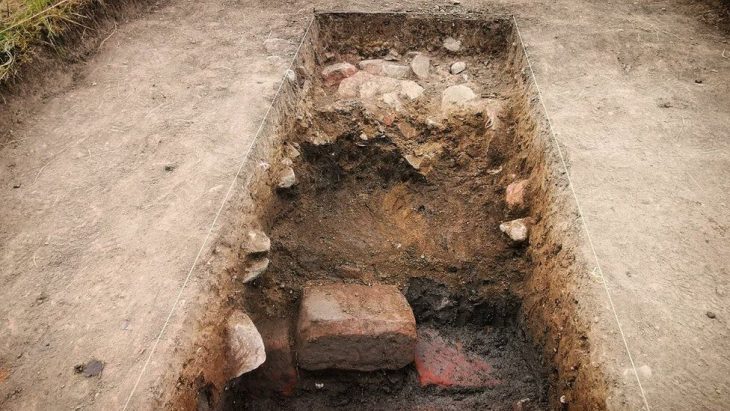
A large cistern with a diameter of 7 meters, walls and many ceramic remains were found in the ruins of an ancient road of about one kilometer made of rocks and sandstones and a 70-meter-long and 30-meter-wide castle.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
It was determined that the fortress, which is considered to be used by the Urartian executives, hosted different civilizations in the Iron Age.

Professor Çavuşoğlu told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they come across different finds every year in Van, which was designated as the capital city by the Urartians.
Stating that it was exciting to encounter a fortress at this height for the first time during the survey, Çavuşoğlu said, “During the climb, we first encountered an ancient road leading to the fortress. The ancient road is exciting. The summit is reaching by passing through this ancient road about 3 meters wide and one kilometer long. We see that the Urartians built a tremendous fortress at 3,300 meters. We found that this fortress was also used in the periods after the Urartians.” he said.
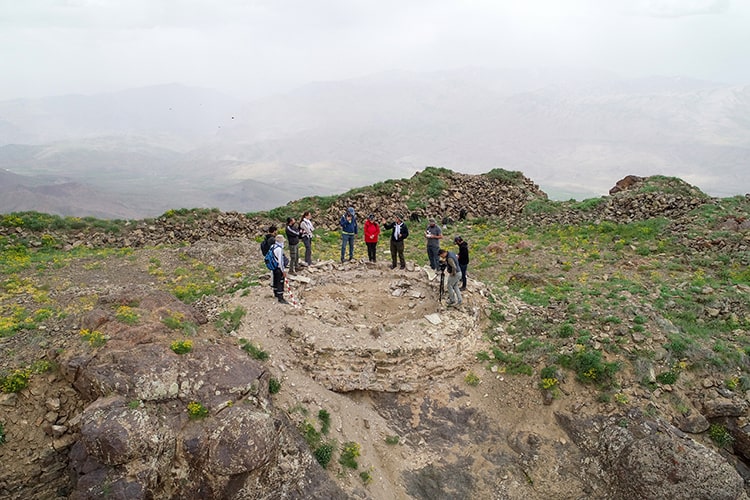

Stating that they encountered ceramic finds from different civilizations, especially Urartians, in the castle, Çavuşoğlu gave the following information:
“There is a cistern dug into the bedrock to meet the need for water during the summer months. It was re-knitted with Khorasan mortar in the Middle Ages. There are traces on it bearing the classical features of the Urartians. We observed that they cut the bedrock to form the walls. There is much pottery from the Urartian, Iron, and Middle Ages periods in the area. The fortress is on a summit with a cliff on all four sides. It is almost impossible to conquer this place. This is the administrative center. The ruling class lived here. Just below are the sections where those who served the administrative center lived.”
We have been researching the land for 30 years. Urartu has always surprised us, “This is the first time we’ve come across a fortress of this height. I can say it’s the most important fortress we’ve found so far.”
Cover Photo: AA