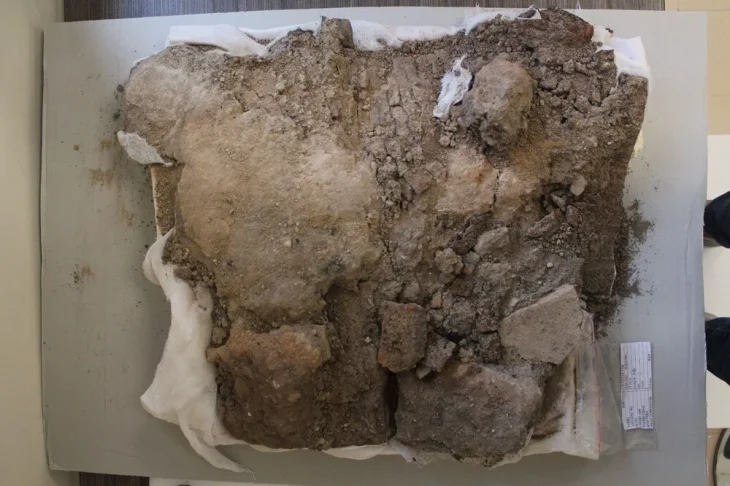
Traces of trepanation (skull drilling operation) were found on a skull found in the 9,000-year-old Çatalhöyük, near the modern city of Konya in central Turkey.
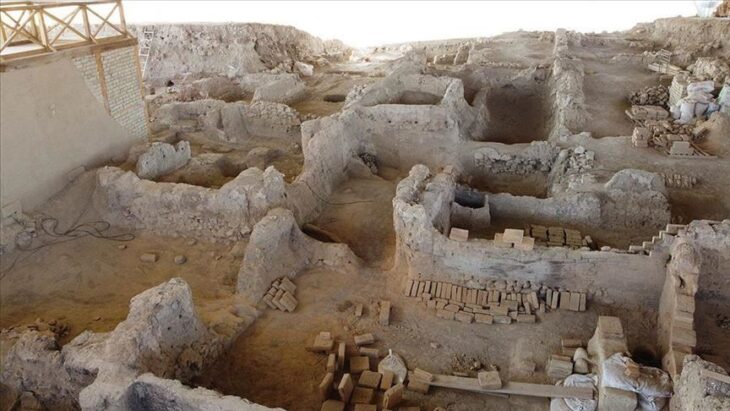
Millennia before the rise of Mesopotamian cities to the south, the proto-city Çatalhöyük thrived in central Anatolia. Sprawled over 34 acres and home to as many as 8,000 people, it was the metropolis of its day. People lived in this community continuously for almost 2,000 years.
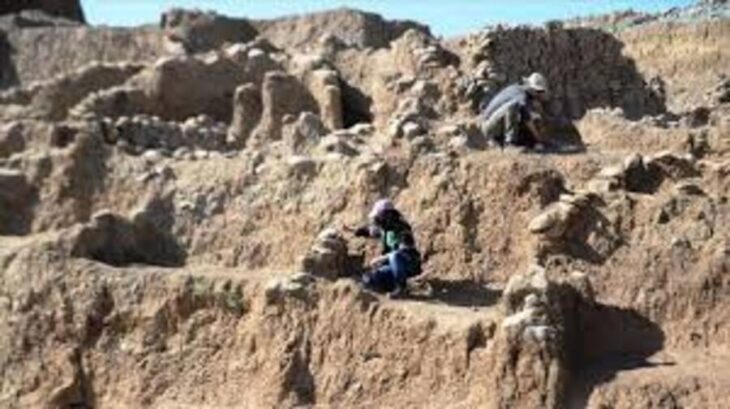
In their statement to the Anadolu Agency (AA), archaeologists said that they came across an interesting grave containing 7 individuals during the excavations last year.
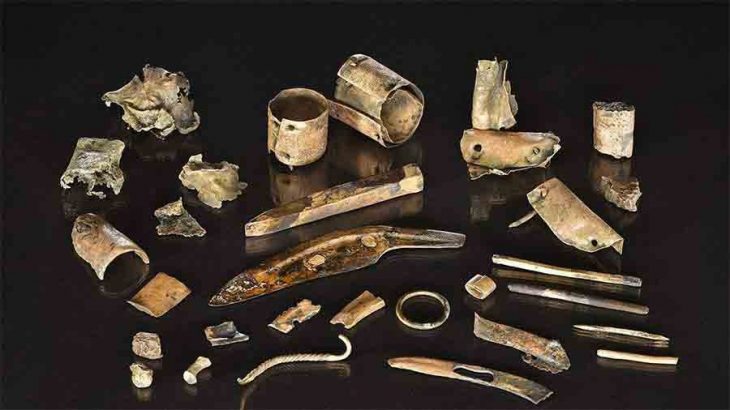
During the studies carried out on human skeletons excavated on the floor of a house, a hole with a diameter of 2.5 centimeters was found on the skull bones of a young male individual.
Çatalhöyük Excavation head and Anadolu University Faculty Member Associate Professor Ali Umut Türkcan said in his statement;
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“There has been a settlement throughout 16 stratifications. It is a unique region in the world. It is a settlement where the culture progressed very slowly and was abandoned. Our work continues especially in the neighborhood we found on the long street next to the exhibition area, which we call ‘northern Korugan’. We opened a new area towards the slope of the settlement. While opening that area, we found the second neighborhood. We identified a large building in the new area. We concentrated the work on the building of approximately 80 square meters, with 5 chambers. Last year, we came across a grave covered with a vulture’s claw in a house here. The anthropologists of the excavation made detailed examinations of the grave containing 7 individuals. A young man “The drilling process in the individual’s skull caught our attention. In Çatalhöyük, we saw a clear example of trepanation for the first time.”
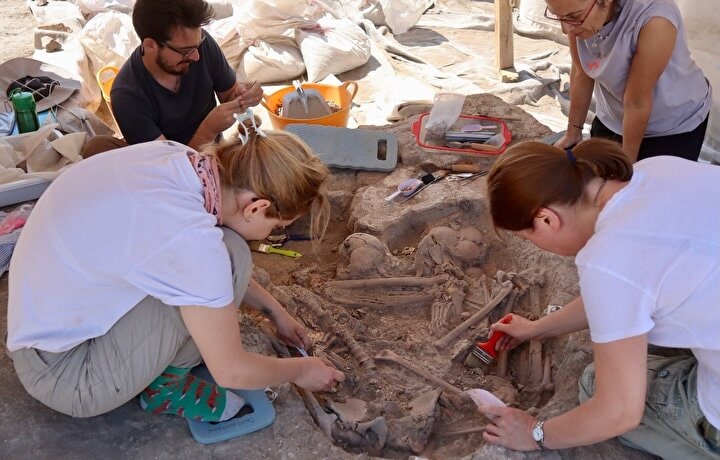

Türkcan stated that the academic study on the findings will be shared with the public soon.
The study was carried out by Professor Handan Üstündağ from Anadolu University, Professor Başak Boz from Trakya University, Professor Arzu Demirel from Mehmet Akif Ersoy University, and graduate student archaeologist Donald Kale.
Anadolu University Archeology Department faculty member Professor Handan Üstündağ, a member of the anthropology team of the excavation, said:
“A round piece of bone was removed from the side of the skull through a circular incision about 2.5 centimeters in diameter. We found many incision marks indicating that they had grazed the scalp during this process. We think this was a trepanation for therapeutic purposes. We identified this skeleton as belonging to a young male aged 18-19. There is no indication that the individual lived after this operation. Because there was no sign of healing in the bone tissue. When this operation was performed, this person was either dying or already dead.”
Üstündağ stated that the practice of trepanation is known to have been used in the past for medical treatment and that trepanation is a method used in the treatment of headaches, brain hemorrhage, cleaning of broken bone fragments and blood after head trauma, fluid accumulation in the brain, and mental disorders.
Emphasizing that there are many examples of trepanation application in excavations in Anatolia, Üstündağ concluded his words as follows:
“The example we found in Çatalhöyük is one of the oldest. Examples of practices that are at least 1000 years older than Çatalhöyük were found in the excavations of Aşıklı Höyük, located near Kızılkaya village in Aksaray, and Çayönü Mound, in Ergani district of Diyarbakır. At Çatalhöyük, we discovered the first conclusive example of trepanation.
“Our find is one of the oldest examples in Anatolia and differs from other examples from the same period in terms of the size of the hole opened. Our finding shows that people who lived 8,500 years ago tried to treat diseases, relieve the pain or suffering of their relatives, and prevent deaths. This finding is also remarkable in terms of medical history.”
Cover Photo: AA
















