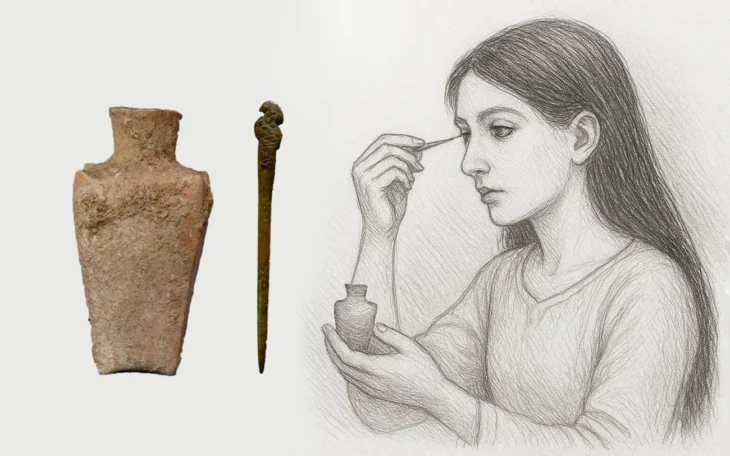A groundbreaking interdisciplinary study by Viking experts from the Universities of Nottingham and Leicester has shed new light on the experience of pregnancy during the Viking Age, revealing intriguing depictions of expectant mothers in art and literature alongside the stark realities faced by newborns.
The research, titled “Womb Politics: The Pregnant Body and Archaeologies of Absent” and published in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal, represents the first focused examination of pregnancy in this historical period. Led by Dr. Marianne Hem Eriksen, Associate Professor of Archaeology at the University of Leicester, and Dr. Katherine Marie Olley, Assistant Professor in Viking Studies at the University of Nottingham, the study synthesizes multidisciplinary evidence, including Old Norse texts, a unique Viking Age figurine, and burial records.
Dr. Olley’s analysis of Old Norse sources, while acknowledging the later dating of surviving manuscripts, uncovered evocative terms for pregnancy such as “bellyfull,” “unlight,” and “to walk not a woman alone.” These linguistic clues offer glimpses into how pregnancy might have been conceptualized in the Viking Age.
Intriguingly, some sagas depict pregnant women in assertive and even martial contexts. One saga recounts a fetus destined to avenge his father, already enmeshed in complex social and political dynamics within the womb. Another tells the tale of Freydís, a pregnant woman who, unable to flee during a violent encounter, bravely brandishes a sword and strikes it against her bare chest, successfully deterring her attackers.
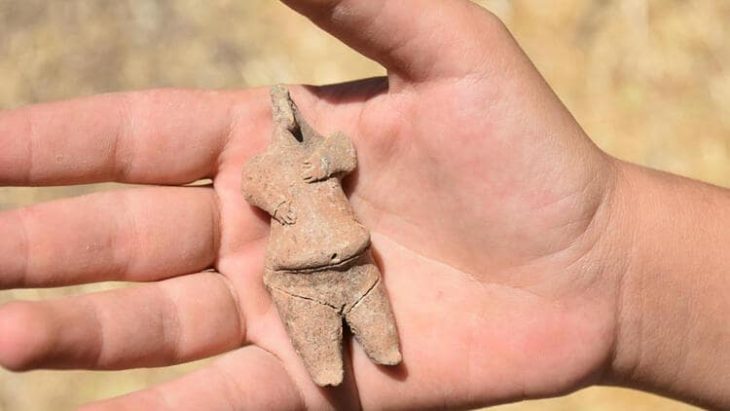
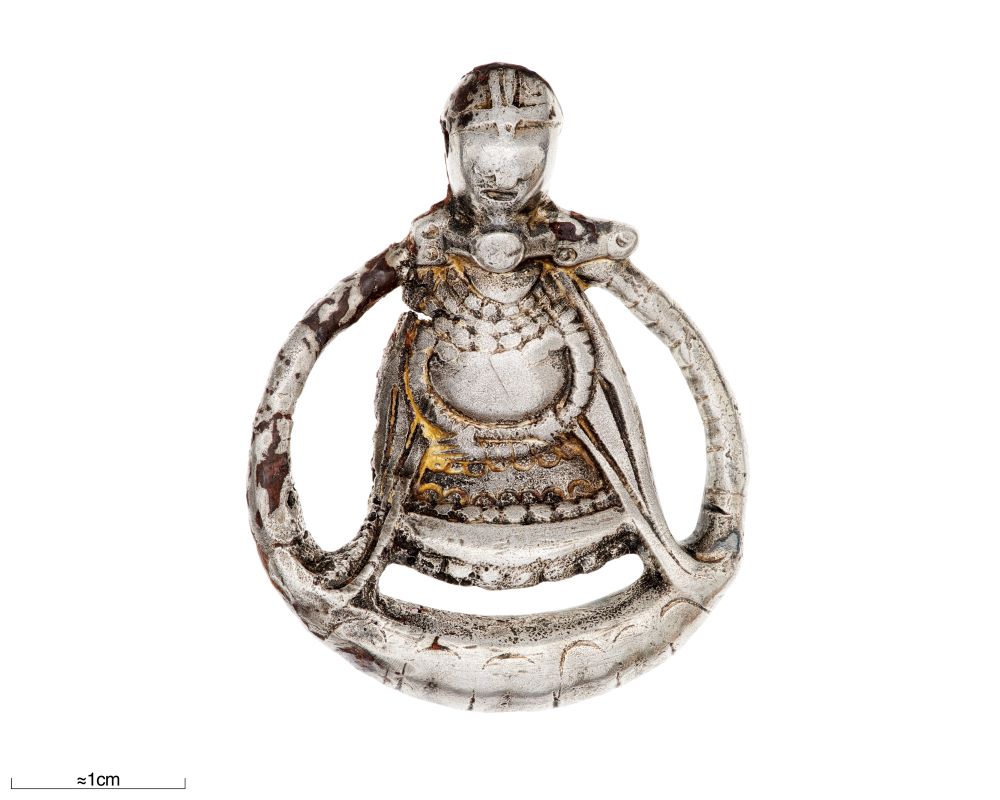
Dr. Olley notes the significance of a singular silver figurine depicting a pregnant woman wearing what appears to be a helmet with a noseguard. “While we are careful not to present simplified narratives about pregnant warrior women, we must acknowledge that at least in art and stories, ideas were circulating about pregnant women with martial equipment,” she states. “These are not passive, or pacified, pregnant bodies.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

The study also highlights a curious absence of direct references to pregnancy in the archaeological record. Despite the high estimated rates of obstetric death during the Viking Age, potential mother-infant burials are exceptionally rare among thousands of excavated sites. Furthermore, infants are generally underrepresented in Viking Age burials, with some appearing in domestic contexts, leaving the fate and burial practices for many newborns largely unknown.
Dr. Eriksen emphasizes the broader political implications of their findings. “It verges on the banal to say, but pregnancy is an absolute necessity for all forms of reproduction – demographic, social, economic, political,” she explains. “Questions such as whether a pregnant body is one or two, how kinship works, or when personhood begins, are not devoid of politics, and we don’t have to look very far into our contemporary world to recognize that.”
The research further points to legal regulations that viewed pregnancy as a “defect” in enslaved women and considered children born to subordinate populations as the property of their owners. Dr. Eriksen concludes, “Together with legal legislation such as pregnancy being seen as a ‘defect’ in an enslaved woman to be bought, or children born to subordinate peoples being the property of their owners, it is a stark reminder that pregnancy can also leave bodies open for volatility, risk, and exploitation.”
This study not only contributes to the growing body of research on gender, bodies, and sexuality in the Viking Age but also prompts a re-evaluation of how academic discourse traditionally frames issues related to women and the “private” sphere. The findings underscore the complex and multifaceted experiences of pregnancy in the Viking world, challenging conventional narratives and opening new avenues for understanding this crucial aspect of Viking society.
Eriksen, M. H., Olley, K. M., Marshall, B., & Tollefsen, E. (2025). Womb Politics: The Pregnant Body and Archaeologies of Absence. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 1–14. doi:10.1017/S0959774325000125