A coin purchased by the Charlemagne Center in Aachen, Germany, bears the name of Queen Fastrada. This is the first known example of a queen being named on a Carolingian coin.
The coin represents the first known example of a queen, indeed of any woman (other than the virgin Mary) being named on a Carolingian coin, and because the coin type was only introduced in 793 and Fastrada died in August 794, it can be very precisely dated.
The dating of numismatic remains from the Carolingian period is difficult when it is not frankly conjectural. The coinage reflects both Charlemagne’s affection for Fastrada and the power he was willing to share with her.
The third wife of the great Carolingian king Charlemagne, Fastrada played a critical role in her husband’s reign. She was born around 765, the daughter of powerful East Frankish Count Rudolph. In 783, only five months after the death of his second wife, Himiltrude, Charlemagne married her to cement an alliance with her father in his war against the Saxons. They would have two daughters over 11 years of marriage before Fastrada’s death in 794.
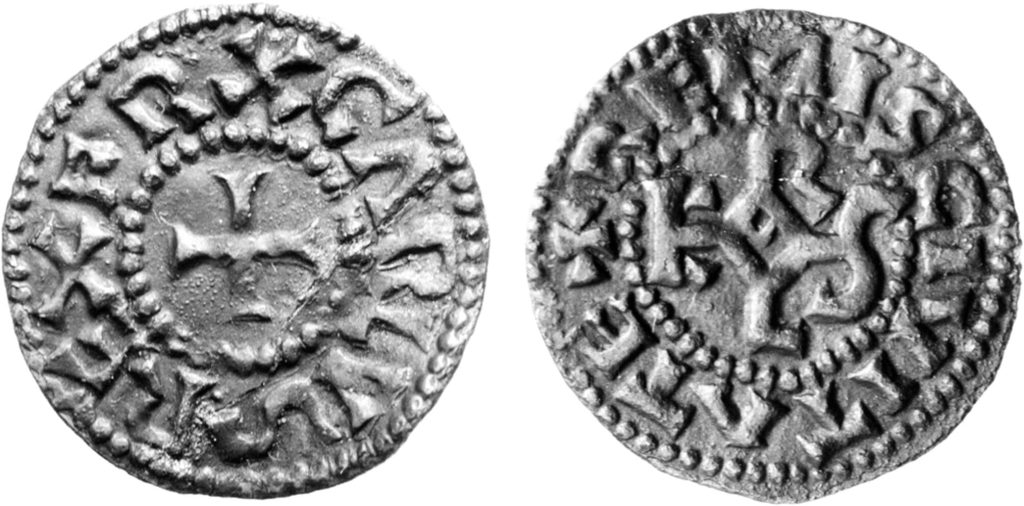

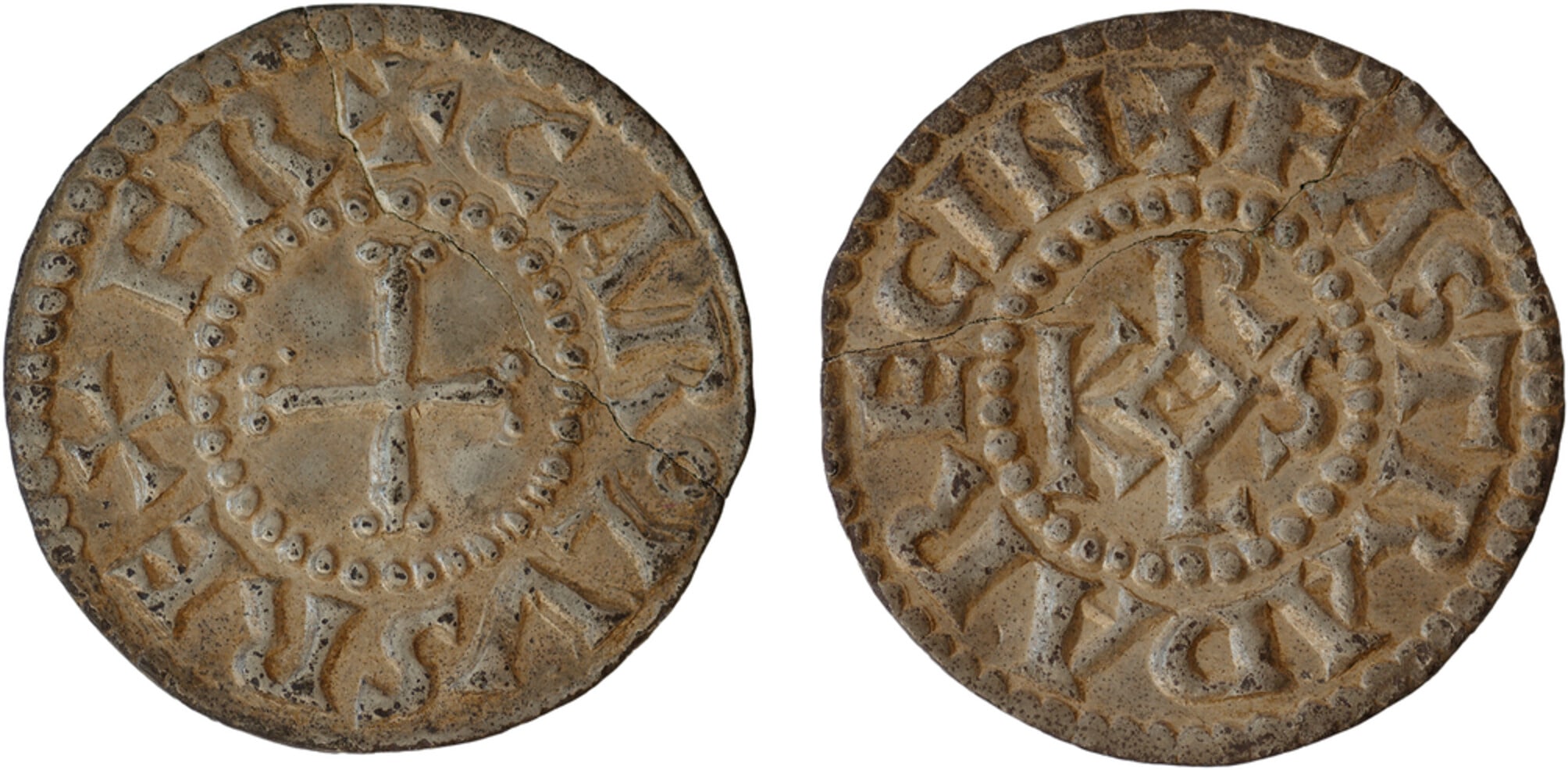
Minted between 793 and 794, likely in Aachen, the coin is inscribed on the obverse side with +CARoLVSREXFR[ancorum], (‘Charles, king of the Franks’), and on the reverse +FASTRADA REGIN[a], (‘Queen Fastrada’), around the royal monogram of Charlemagne (KAROLVS). It is a silver denier of a type known as the monogram denier after the KAROLVS monogram.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
As a result of their infrequent appearance in contemporary writings, historians of today can generally say little about the Carolingian queens. Fastrada is an exception, with a “uniquely well-documented queenly career” in terms of early medieval annalistic records, according to Janet Nelson. According to contemporary sources, Charlemagne had a genuine affection for Fastrada, which this coin also bears witness to.

King Offa of Mercia, who had a penny minted in 792 bearing the name of his wife Queen Cynethryth, must have inspired Charlemagne. They had extensive trade contacts and were actively planning a marriage between Charles’ son and Offa’s daughter at one point. It can’t be a coincidence that the silver denier uses the same syntax as the Cynethryth penny, with the Latinate title ‘REGIN(a)’ for Fastrada.
Despite the parallels between these Mercian and Carolingian coinages, three significant differences are also evident from the discussion above. The first is the scale: as was noted earlier, there are more than fifty recorded examples of Cynethryth’s coinage, from numerous different dies, but this is the first and to date only specimen of a coin of Fastrada.
https://doi.org/10.1111/emed.12640
Cover Photo: Monogram denier of Charlemagne and Fastrada, 1.63 g, 21 mm. Holger Hermannsen, Centre Charlemagne, Aachen