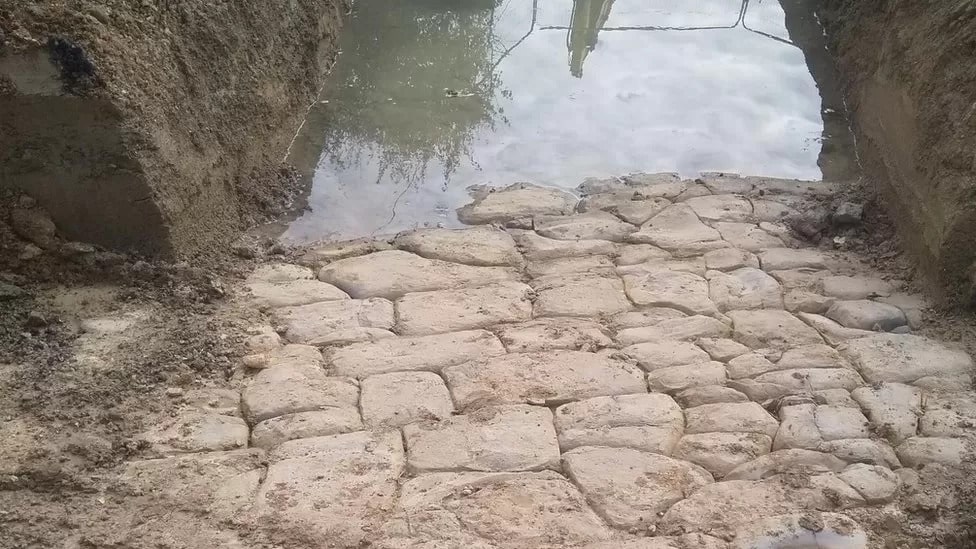
A cobbled ford believed to be of Roman construction has been discovered near Evesham in Worcestershire, England.
If the path is confirmed to be Roman, it will be the only of its kind in Britain. To protect the site, the exact location of the discovery is being kept under wraps. But a Roman-era villa complex across the river from the ford was discovered four years ago. The precision stonework is also reminiscent of Roman road-building abilities.
The 10m-stretch (32.8 feet), believed to extend to a depth of 3m (9.8 feet), was discovered during routine waterworks. Ruts in the stones indicate it was used by carts for a long time.
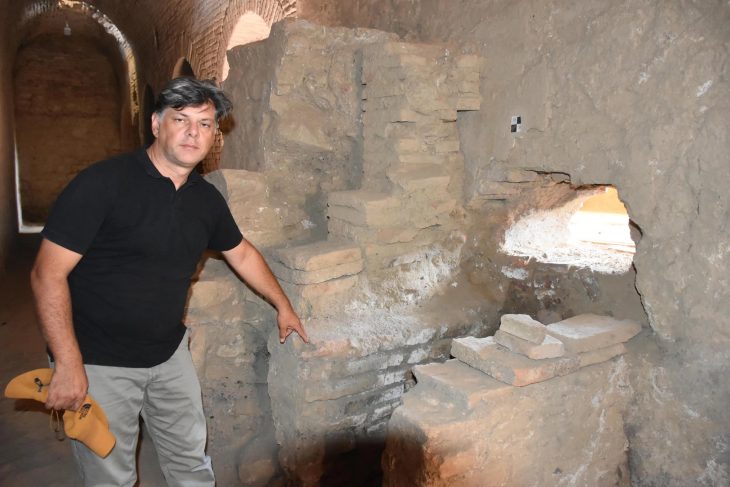
Wychavon District Council archaeology officer Aidan Smyth said the discovery “took his breath away.” If proven to be from the first century AD, it would be “beyond rare,” he added.
“The stonework is absolutely perfect,” he said. “It just ticks every box for being Roman,” Aidan Smyth said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“When I came down to look at it, honestly, I thought it’s too good to be true.
“But then you look at the alluvium [a deposit of silt] that it’s filled up, so that hasn’t happened in one or two centuries. That’s taken millennia to be able to get that deep.
“The only place I can see similar when I was doing some research is in Pompeii. I can’t find anything else anywhere like that.”
The council will bring in an archaeologist team from Historic England to conduct a test excavation at the ford to date it and confirm that it was built by the Romans.
Worcester was possibly the site of the Roman town of Vertis, with evidence of early military occupation.
The first Roman military expeditions to Britain were led by Julius Caesar in 55 and 54BC, but a full-scale invasion did not occur until AD43, under Emperor Claudius. Obviously, the county of Worcestershire did not exist then, but it is thought that the area fell largely within the territory of the Iron-Age Dobunni tribe and it was through this territory that the Roman army passed in the 40s and 50s AD as it pushed west to reach the River Severn on its way to Wales. The native population had to adjust to a new way of life. Roman conquest relied on building roads and forts.