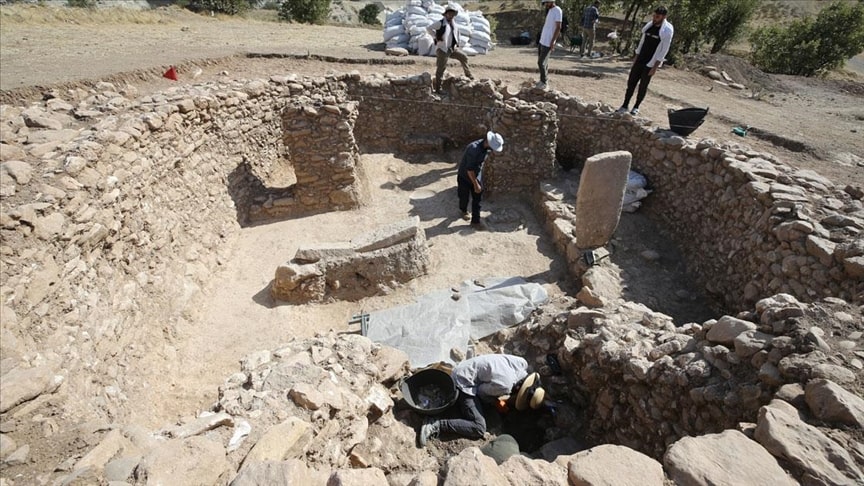
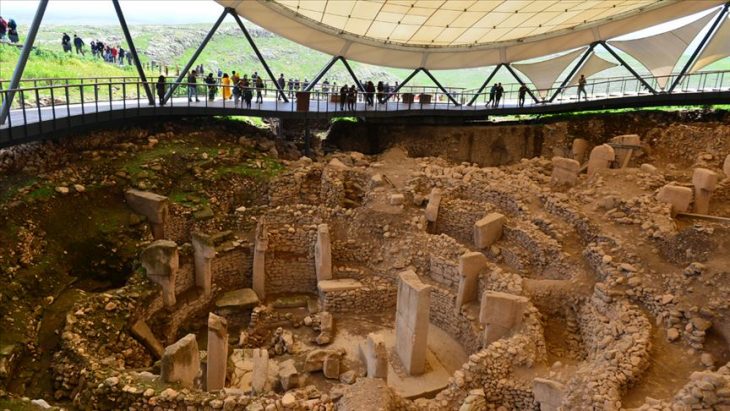
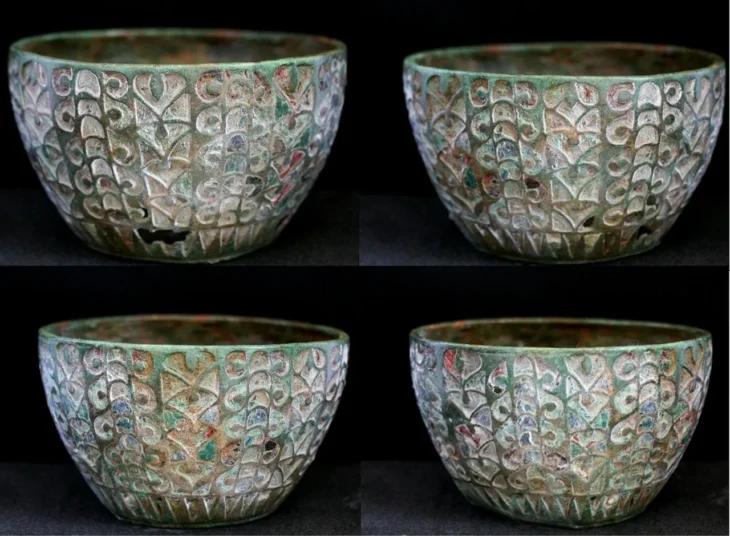
A temple thought to be 12 thousand years old was unearthed in Boncuklu Tarla in the Ilısu Neighborhood of Dargeçit district of Mardin province in southeast Turkey.
Archaeological excavations in the region, which were initiated in 2012 by the Mardin Museum Directorate, continue within the scope of “Works on Documenting and Rescuing the Cultural Assets Remaining in the Interaction Area of the Ilısu Dam and HES Project”.
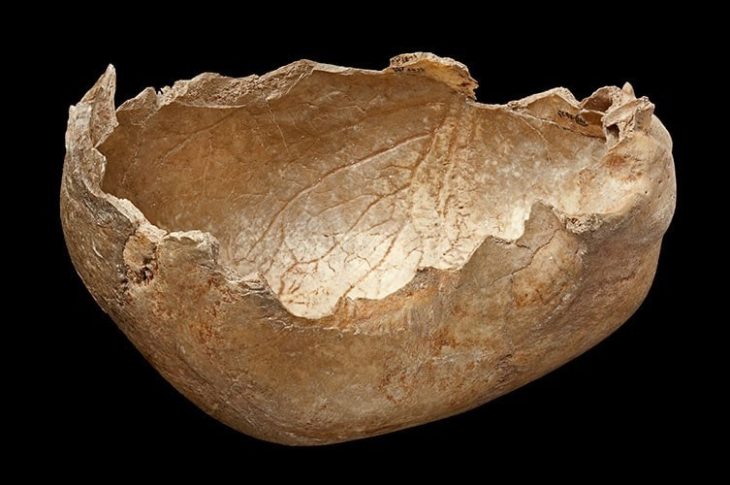
During the excavations, the fourth season of which has been completed this year, architectural remains, houses, private buildings, public buildings, 130 skeletons, and more than 100 thousand beads have been found in various cultural layers.
The most striking find of this excavation season was the temple, which is estimated to be 12,000 years old.
Ergül Kodaş, the head of the excavation and a faculty member of the Archeology Department of Mardin Artuklu University, told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the works continue as rescue excavations until 2020 have been carried out with the status of “Presidential Excavation” as of this year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

It bears similarities with Göbeklitepe
Stating that the Boncuklu Tarla mound is a settlement dating to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic period and covers all phases of this period, Kodaş said, “A large number of architectural remains, houses, private buildings, public buildings, many skeletal remains, archaeobotanical remains, and many ornaments belonging to the period in question were found. The skeletons of approximately 130 individuals have been unearthed during the excavations carried out so far. More than 100 thousand beads were found in these graves,” he said.
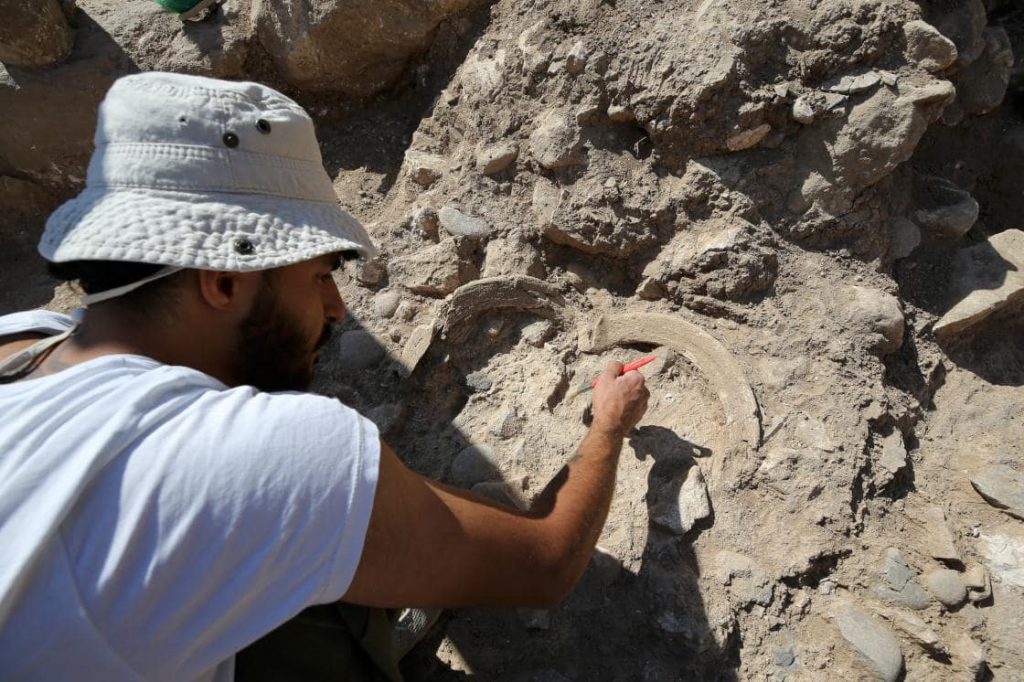
Kodaş stated that this year, more density was given to the area to the southeast of Boncuklu Tarla, adding that two buildings were unearthed in this section.
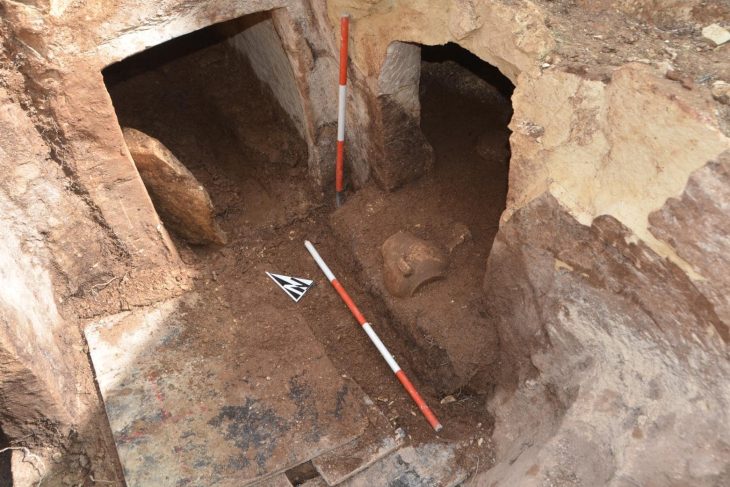
Pointing out that one of the structures in the form of a public building was a temple, Kodaş said:
“The building unearthed this year has features that we think are related to faith due to both its architectural features and the finds inside. There are steles inside. There is both columns stone mesh, and there are buttresses. Its base is limestone carved into the bedrock in places. It has hearths and altars inside. In addition, we can see that the heads of bulls were deliberately left inside some altars. That’s why, in this year’s studies, we started to think more intensely that these and similar buildings could be related to the scope of belief in the field with Boncuklu Tarla.”
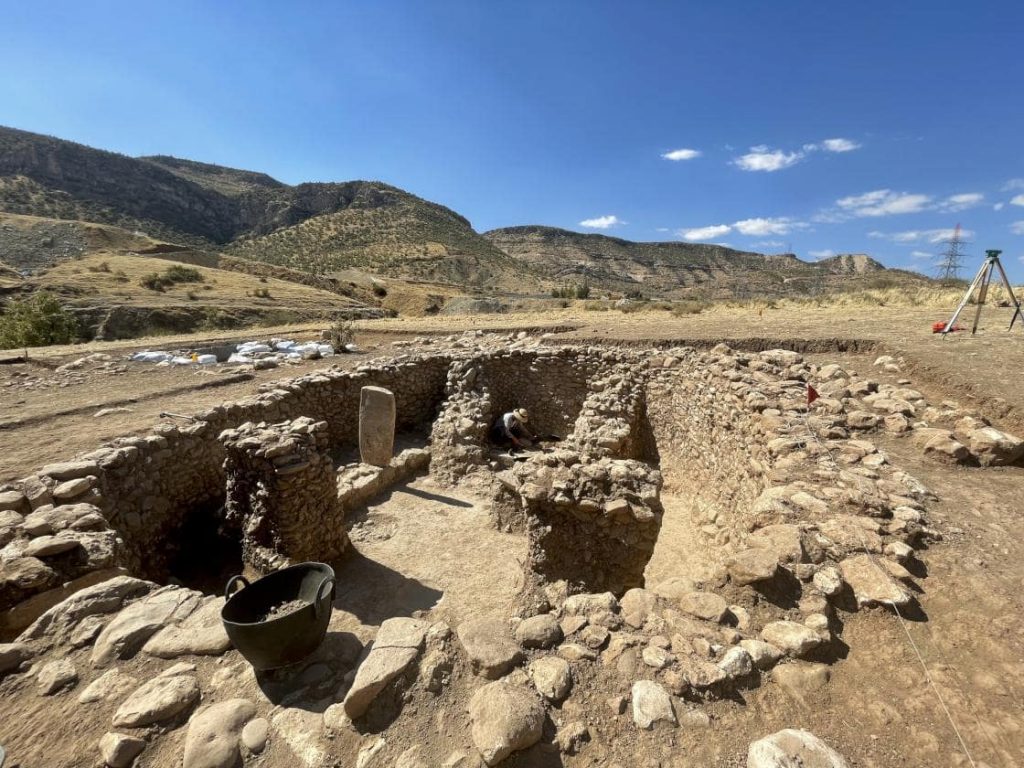

“The structure found has similar features with Göbeklitepe and the structures belonging to this period in the region. The building has a unique architectural style, shape, and interior arrangement. Unique with these features. We can say that it is a temple that dates back to 12 thousand years.” Kodaş said, adding that the work in the region will continue.
“The whole village is shaped around this place”
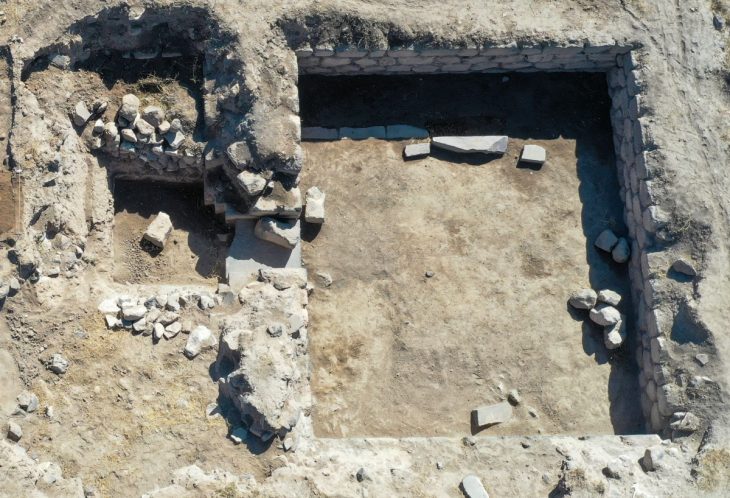
Archaeologist Dr. Yunus Ciftci, vice-president of the excavation, stated that they started work in a new area this year and that a new temple with different architectural features was unearthed.
Stating that the structure was dug into the soil with a diameter of about 10 meters and a depth of 2.5 meters and was raised as a wall with stones around the soil, Çiftçi said that the wall was supported by buttresses, especially from the west side.
Noting that the buttresses are the only example among the structures belonging to the Pre-Pottery A phase, Çiftçi said that this is seen as a feature belonging to the Boncuklu Tarla.
Stating that the columns were raised symmetrically opposite the buttresses, Çiftçi said, “At the same time, the steles similar to those we know from Göbeklitepe or other centers were unearthed in the building. However, unlike them, we found that these steles were used for a religious duty inside the building rather than carrying the roof structure.” he said.
Stating that they thought the building belonged to very special use in its own period, Çiftçi said, “Therefore, it is actually the common point of the settlement together with a religious center. In a way, the whole village is shaped around this place.” used the phrases.
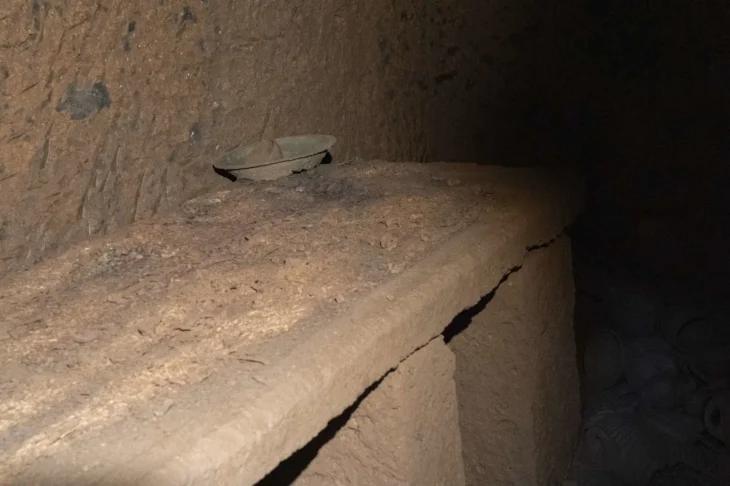
Pointing out that the round stone window unearthed in the building is the oldest known window, Çiftçi shared the following information:
“Especially the three niches on the eastern wall caught our attention as very interesting finds. This is the top entry, often found in Göbeklitepe, Hasankeyf, and other settlements, but usually related to the roof structure. However, with this building, we have revealed that it is embedded in the opposite wall and used as a window. The round stone window we uncovered is currently the only known artifact from this period.”