The Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) said Monday that 1,500-year-old magical “incantation bowls” and other rare and ornate bone and ivory items from the Biblical period were unearthed in the home of a Jerusalem resident suspected of participating in the illegal antiquities trade.
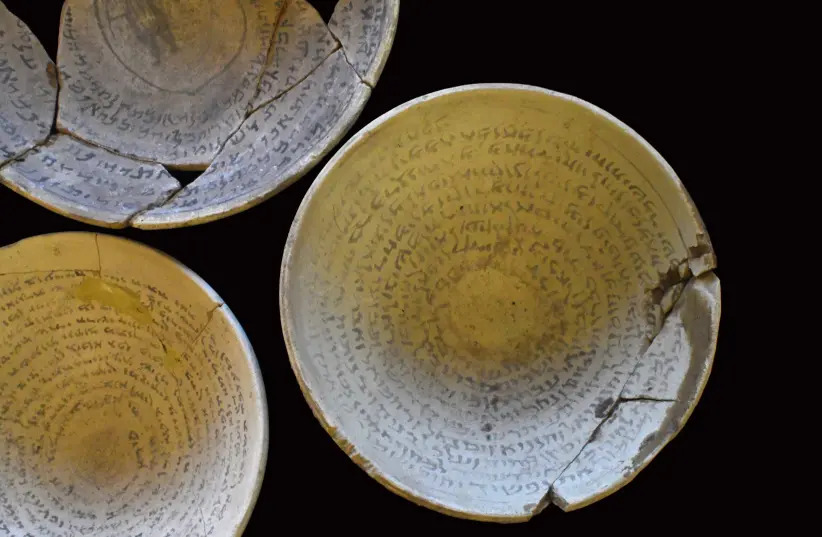
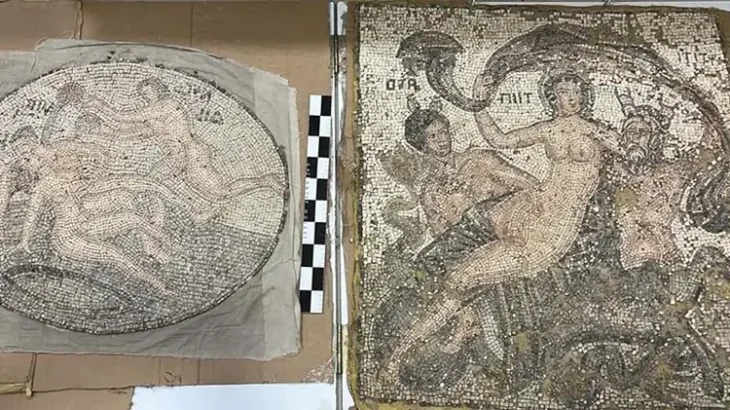
Among the items the IAA found in an individual’s home are numerous “Swearing Bowls” that date from the 4th-8th centuries CE in what is now Iraq.
The incantation bowls, known as the “swearing bowls”, came from Mesopotamia, and were used as a kind of amulet to fight curses, demons, diseases, and pests.
In an era when literacy was rare, some people made a living by writing personalized messages to repel curses, demons, or other perceived threats. One of the bowls collected carries a painted figure of the “night demon,” representing the individual that the bowl was meant to ward off.
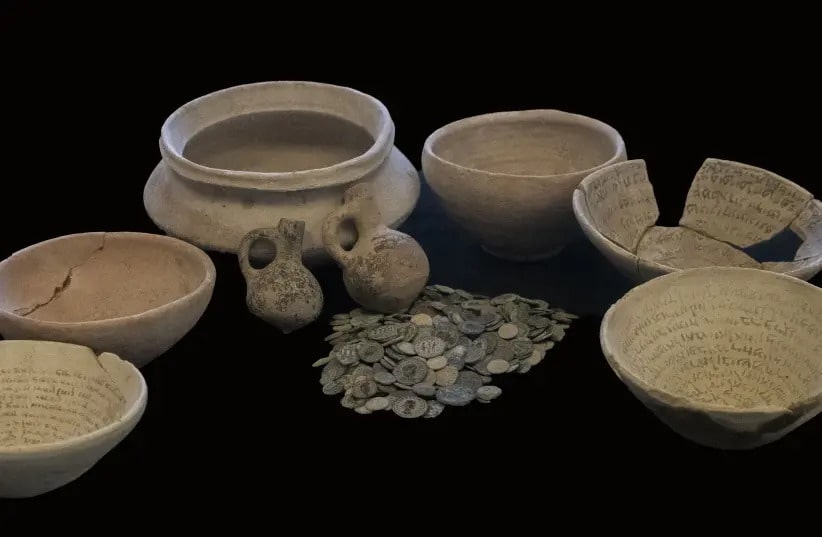

It was common practice to bury such bowls under the house floor for protection, according to the IAA.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Various chemicals that were confiscated from the house are believed to have been intended for use in the restoration of the pottery and for cleaning ancient metals and coins. The IAA believes the suspect repaired and restored the bowls to sell them.
Hundreds of antique bronze and silver coins, glassware and ancient weapons were also discovered in the Ramat Shlomo neighborhood home during a search by the IAA’s Robbery Prevention Unit and the Israel Police, the IAA said in a press release.
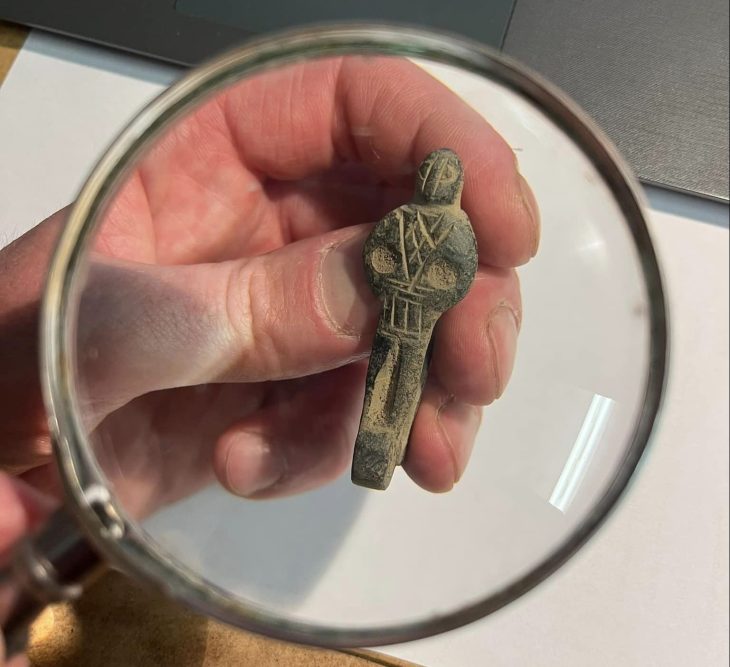
The finds also include 3,000-year-old rare bone and ivory artifacts, decorated in Phoenician style, with Egyptian motifs that included scenes from the animal world, alongside geometric ornaments.
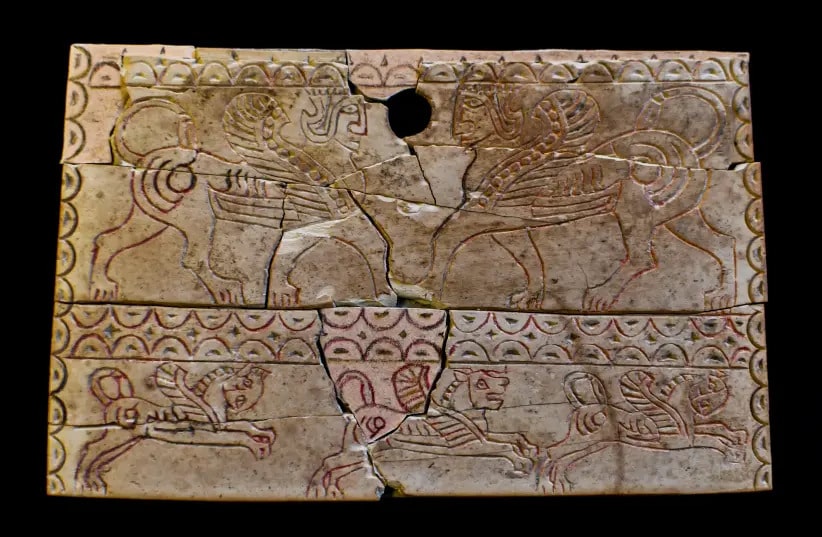

Two griffons (winged lions with human faces) facing each other appear in one of the objects, and another artifact included a description of a convoy of four-winged lions marching one after the other, the IAA said.
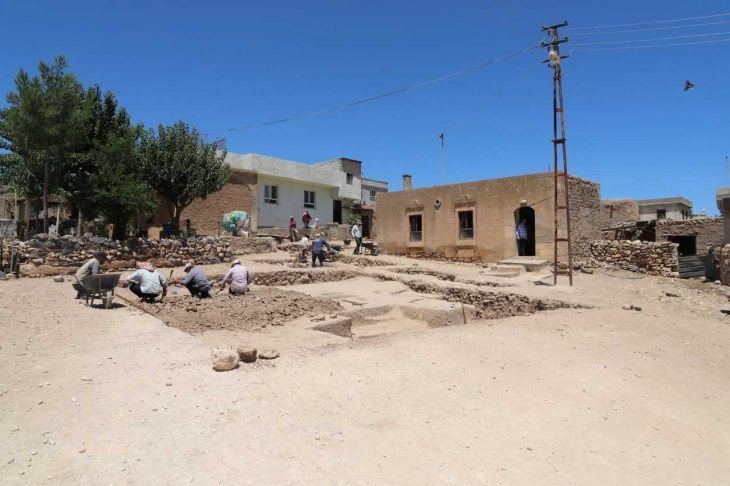
Similar ivory objects have been discovered in past excavations in an antiquity site in Samaria, where a large collection of ivory, known as “Samaria Ivories,” was discovered, as well as at other antiquity sites, such as Tel Megiddo, the IAA said.
The items were used as decorations, attached to wooden furniture by nails in the ninth and eighth centuries BCE.
The IAA said finding decorated artifacts made of ivory from this period is extremely rare. The Robbery Prevention Unit believes they were excavated illegally in one of the biblical mounds in Samaria or in the North.
“Antiquities belong to all of us. They are our heritage,” said the Authority’s director Eli Eskosido “Unauthorized antiquities dealers encourage looters to go out and destroy ancient sites in search of finds for sale on the antiquities market. In the name of greed, they plunder antiquity sites, removing the finds from their historical context, thus obscuring parts of human history.”
The Authority also hopes that documents seized at the home will allow them to identify who the items were bought from, potentially implicating a much wider network.
Cover Photo: Swearing bowls (Photo: YOLI SCHWARTZ/ISRAEL ANTIQUITIES AUTHORITY)