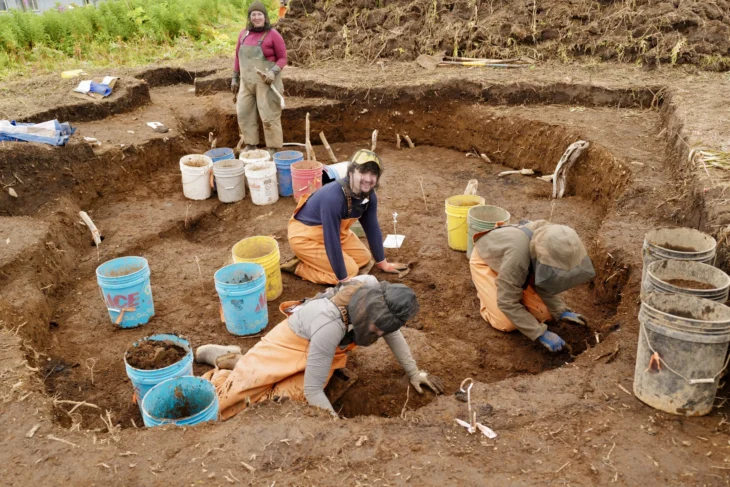
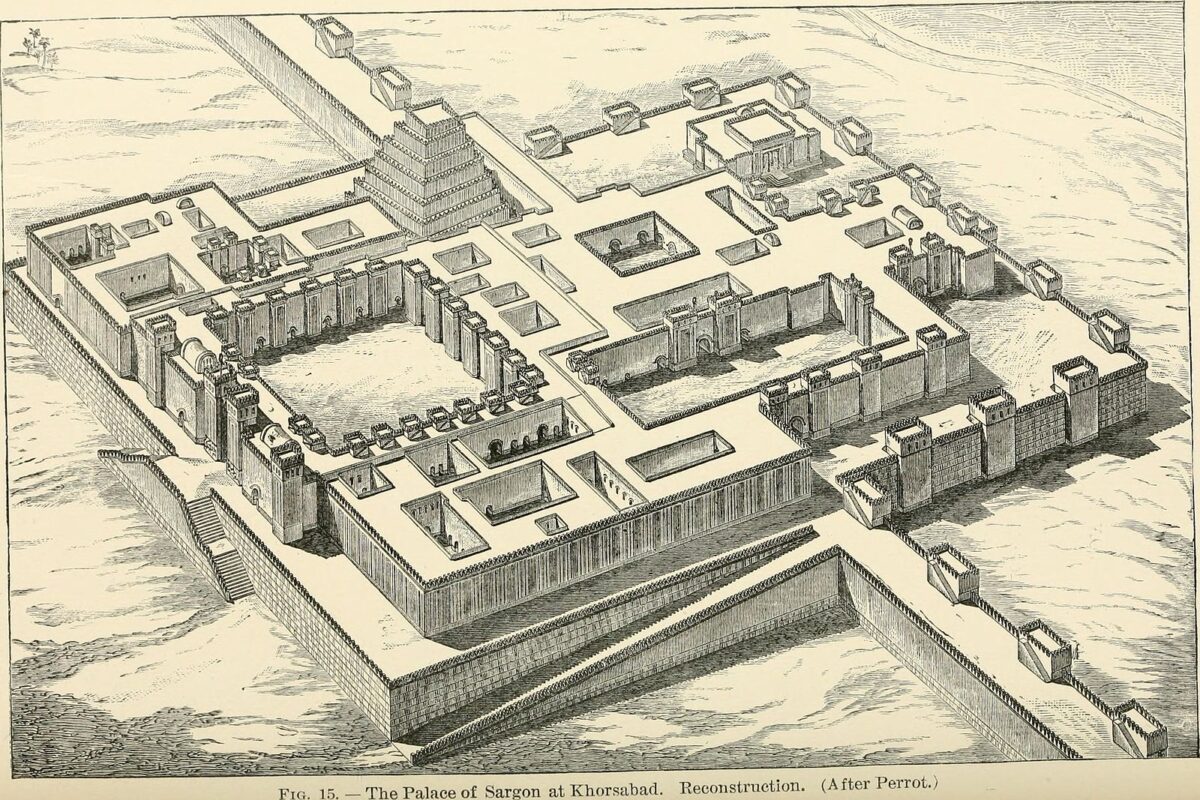
Archaeologists in northern Iraq have conducted an extensive magnetic survey using an exhaustive magnetic survey at Khorsabad, once the ancient Assyrian capital, and with the help of this technology have found the remains of a huge villa (with 127 rooms), royal gardens, the city’s water gate and five large buildings that may have been used for various purposes.
The site, dating back 2,700 years, was originally established as Dur-Sharrukin, or “Fortress of Sargon,” by Neo-Assyrian Emperor Sargon II in 713 B.C.
The Neo-Assyrian emperor Sargon II began building a new capital city, named after himself, in the desert of what is now Iraq. For a long time, archaeologists believed that this ambitious project had only just begun when it was abandoned, leaving behind nothing but the remains of a building site. However, a recent survey of the site challenges that notion. The city did indeed flourish outside the palace, as evidenced by visualizations of data from a precision magnetometer that reveal hitherto undiscovered structures and infrastructure inside the city walls.
Sargon II died a few years after work began on Dur-Sharrukin (“Fortress of Sargon”), now called Khorsabad. His son quickly set up his own capital in the city of Nineveh, and for the next 2,500 years, Sargon II’s building project was largely forgotten. In the 1800s, French archaeologists rediscovered the site.
Their excavation of Sargon’s palace uncovered treasures of Neo-Assyrian art and culture, but teams digging elsewhere in the city came up empty-handed. Archaeologists concluded that the palace was the only building begun within Khorsabad’s city walls, which enclose an area more than one mile square (1.7 by 1.7 square kilometers).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

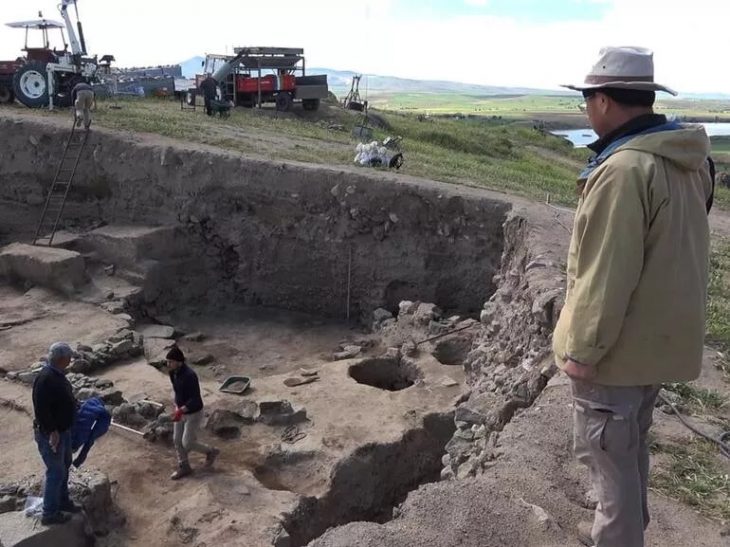
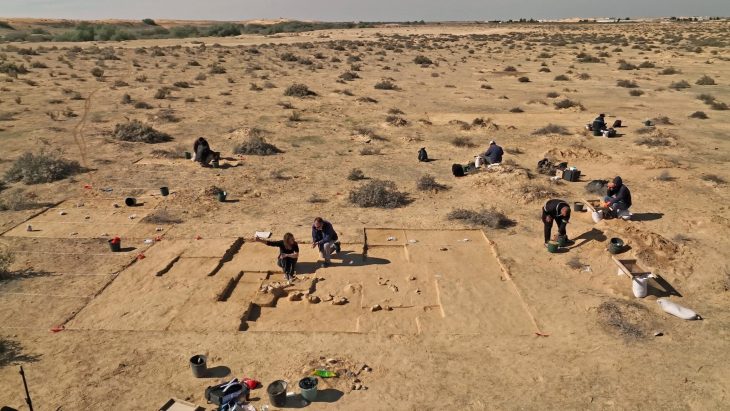
In 2017, the French Archaeological Mission in Khorsabad decided to launch a new project to evaluate above-ground damage and conduct the first geophysical survey of buried remains at the site after the Islamic State’s two-year occupation of Khorasabad officially ended. The survey was expected to uncover the city’s water infrastructure, provide fresh insights into the wall fortifications, and perhaps even uncover new signs of habitation outside the palace.
The archaeologists conducted this survey in extremely difficult conditions while buried deep underground. Buried deep underground, the archaeologists underwent extremely tough conditions to conduct this survey. The magnetometer is a device that detects buried structures by mapping subtle changes in the Earth’s magnetic field, reports a press release by the American Geophysical Union (AGU), and that makes it an incredibly useful tool for archaeologists seeking to find hidden structures that have been lost for centuries.
Jörg Fassbinder, a geophysicist from Ludwig-Maximilians-University in Munich and the study’s lead author, presented the results of this research at the 2024 American Geophysical Union (AGU) Annual Meeting.
Fassbinder noted, “Every day we discovered something new… all of this was found with no excavation. Excavation is very expensive, so the archaeologists wanted to know in detail what they could expect to achieve by digging. The survey saved time and money. It’s a necessary tool before starting any excavation.”
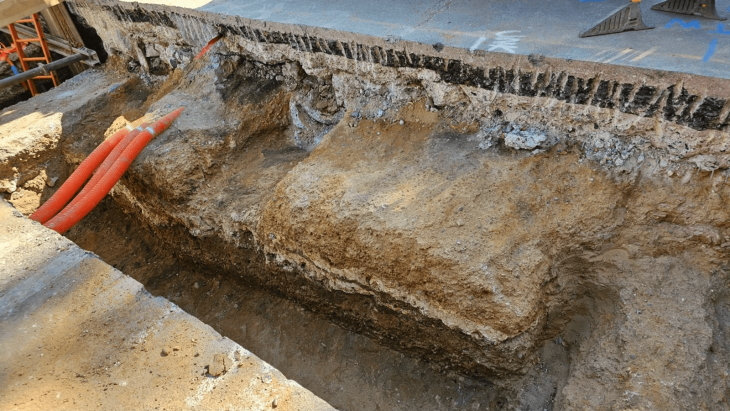
When the data were visualized as grayscale images, ghostly outlines emerged of structures as deep as six to ten feet (two to three meters) below ground. The data revealed the location of the city’s water gate, possible palace gardens, and five enormous buildings, including a 127-room villa twice the size of the U.S. White House. These and other discoveries are evidence that, at least for some time, Khorsabad was a living city.
Fassbinder’s discoveries reveal a bustling urban landscape extending beyond the palace walls, suggesting a vibrant capital teeming with activity.
American Geophysical Union (AGU)
Cover Image Credit: Reconstructed Model of Palace of Sargon at Khosrabad. Public domain