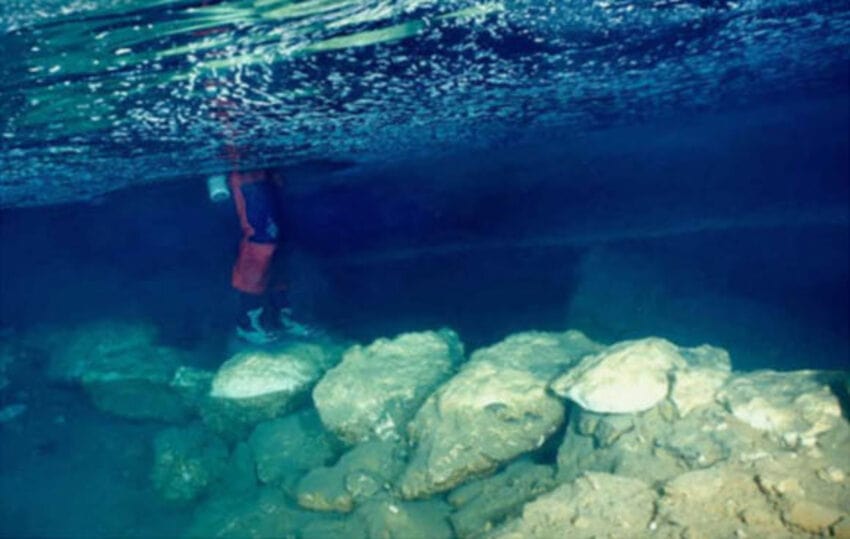
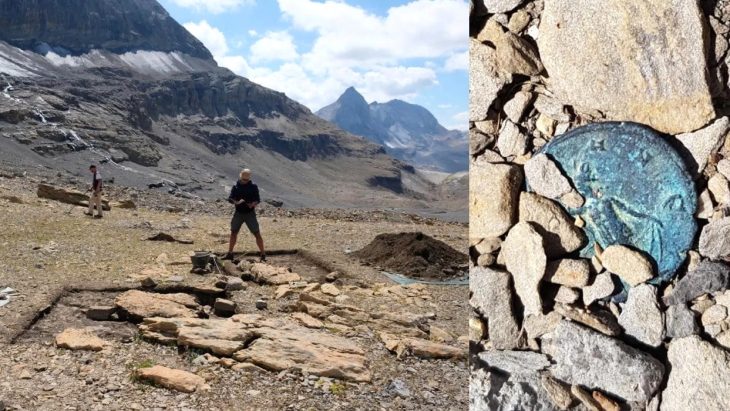
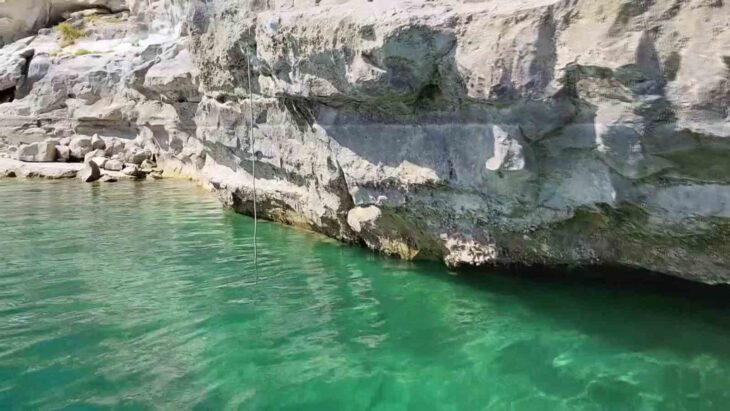
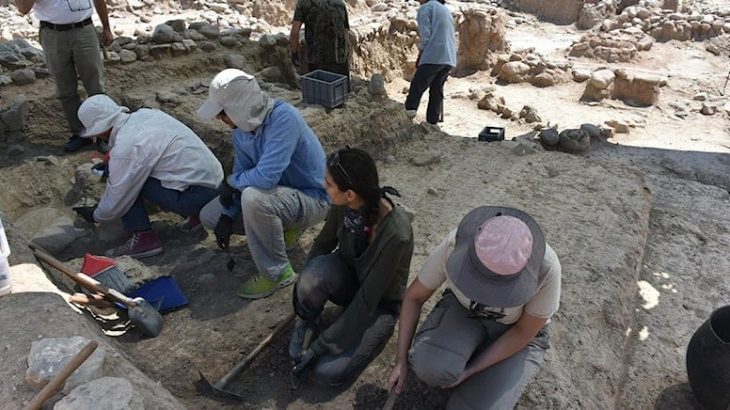
An interdisciplinary research team, led by University of South Florida (USF) geology Professor Bogdan Onac, has examined an ancient submerged stone bridge in Genovesa Cave on Mallorca, the main island of the Balearic Archipelago and the sixth largest in the Mediterranean Sea.
This new study has shed light on the human colonization of the western Mediterranean, revealing that humans settled there much earlier than previously believed.
Due to a lack of archaeological evidence, reconstructing early human colonization of the Balearic Islands in the western Mediterranean is difficult. Professor Bogdan Onac and his associates were able to present strong proof of past human activity inside Genovesa Cave by examining a 7.7-meter (25-foot) submerged bridge.
“The presence of this submerged bridge and other artifacts indicates a sophisticated level of activity, implying that early settlers recognized the cave’s water resources and strategically built infrastructure to navigate it,” Professor Onac said.
Genovesa Cave, which is close to Mallorca’s coast, features passageways that are currently underwater as a result of sea level rise. During times of high water, unique calcite encrustations form within the cave. These formations act as proxies for accurately tracking historical sea-level changes and dating the bridge’s construction, along with a light-colored band on the submerged bridge.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Previous research suggested human presence as far back as 9,000 years, but inconsistencies and poor preservation of the radiocarbon-dated material, such as nearby bones and pottery, led to doubts about these findings. Newer studies have used charcoal, ash and bones found on the island to create a timeline of human settlement about 4,400 years ago.
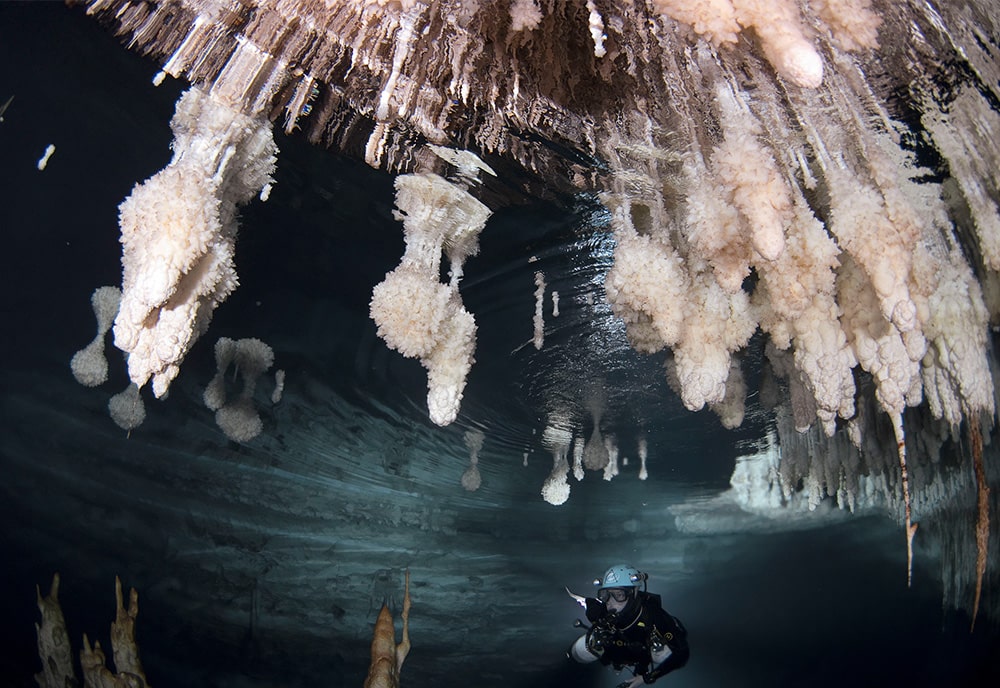

This aligns the timeline of human presence with significant environmental events, such as the extinction of the goat-antelope Myotragus balearicus.
By analyzing overgrowths of minerals on the bridge and the elevation of a coloration band on the bridge, the authors discovered the bridge was constructed nearly 6,000 years ago, more than 2,000 years older than the previous estimation — narrowing the timeline gap between eastern and western Mediterranean settlements.
“The history of the bridge construction appears to be closely associated with rapid Holocene sea-level rise just prior to 6,000 years ago and a brief sea-level stillstand that led to some upper sections of the cave being flooded,” they said.
“According to our chronology, the sea-level rise ceased and remained stable for several hundred years between 5,964 and 5,359 years ago. During this time, the so-called phreatic overgrowths on speleothems (POS) formed in the cave lake, and a distinctive ‘bathtub ring’ developed on the bridge.”
“The building of the bridge likely began early during this period, when crossing the 0.25 m-deep lake required its construction. However, the structure must have been completed before 5,600 years when the upper part of the bridge became submerged.”
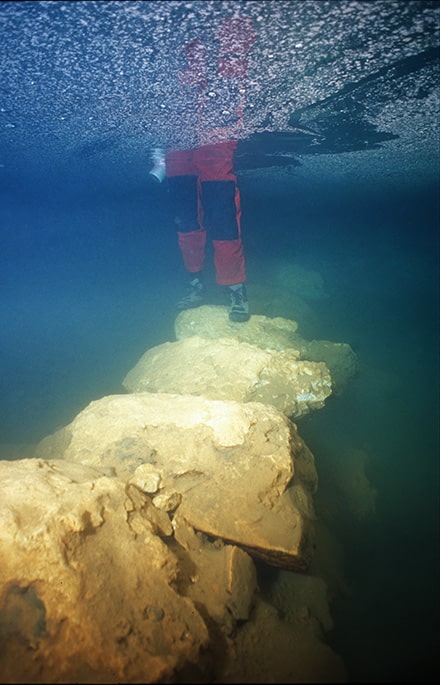

“Evidence indicates that humans constructed a stone-paved pathway leading to the cave’s water pool and a robust bridge, facilitating access to the only other dry section of the cave situated beyond the lake, in the Sala d’Entrada.”
“The exact reasons behind the construction of these structures in Genovesa Cave remain elusive.”
“Nevertheless, the chronological constraints posed by the depth of the bridge, coupled with the similar depth at which POS and the coloration mark occur, support the idea of an early human presence on the island by 5,600 years ago and potentially dating back as far as 6,000 years ago.”
This research was done in collaboration with Harvard University, the University of New Mexico, and the University of Balearic Islands.
A paper describing the findings was published today in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.
DOI: 10.1038/s43247-024-01584-4
Cover Image: The 5,600-year-old submerged stone bridge in Genovesa Cave, Mallorca, Spain. Image credit: R. Landreth.