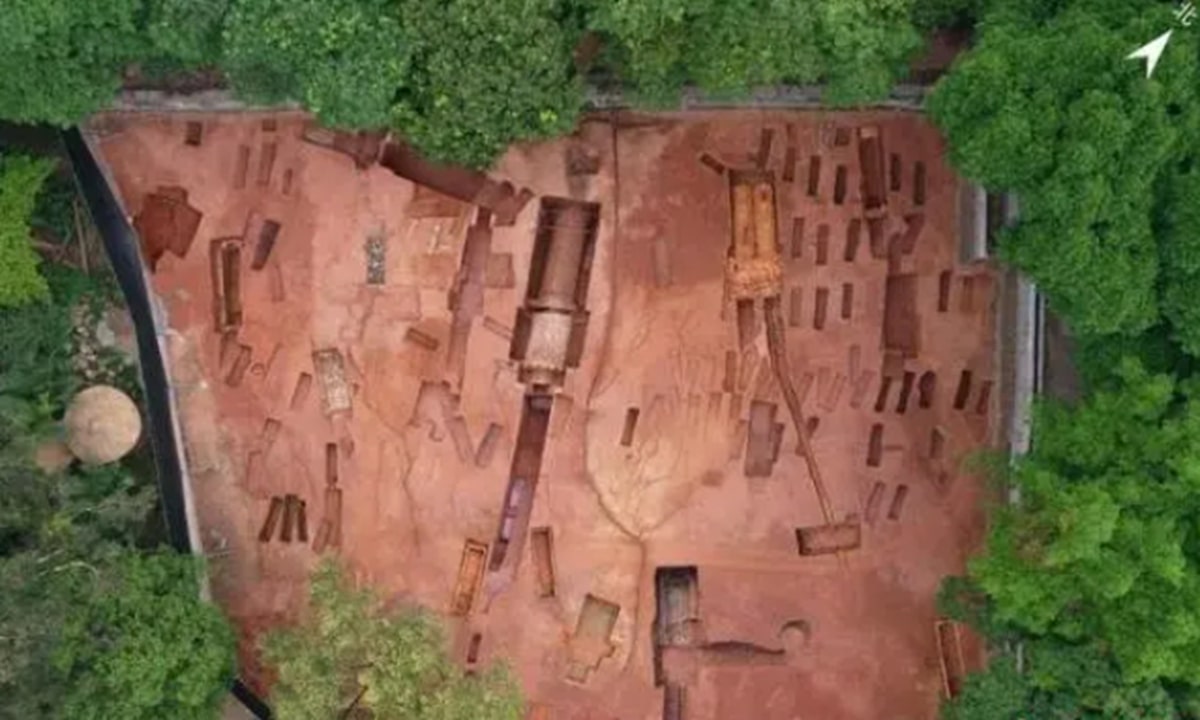
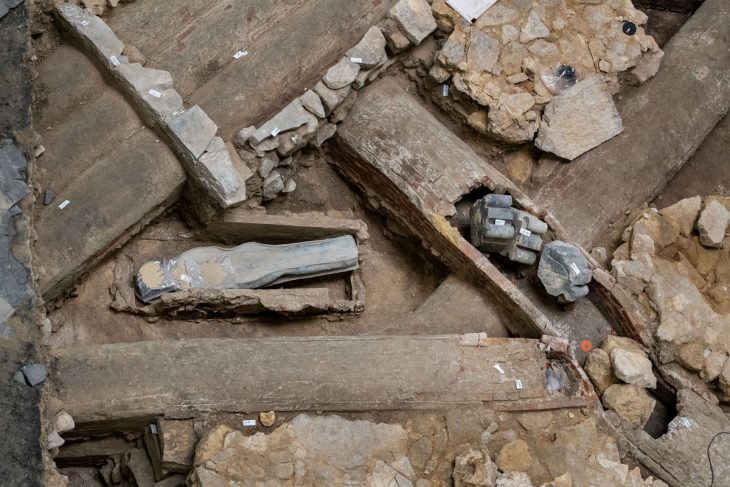
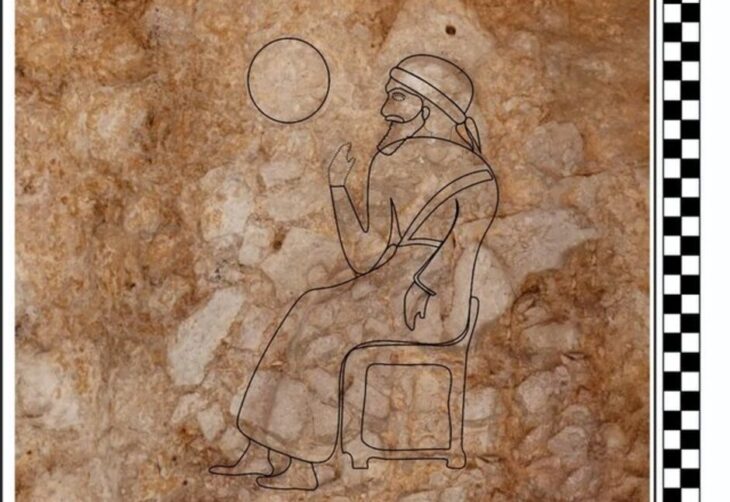
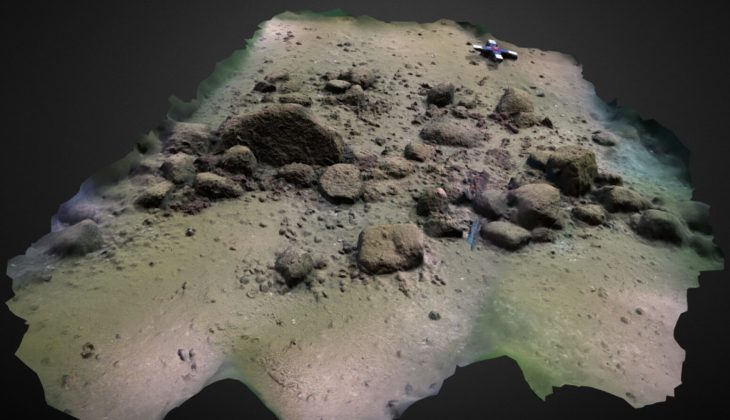
An ancient burial site with 148 tombs, spanning over 2,100 years, has been discovered on the construction site of the Guangzhou Zoo in South China’s Guangdong Province.
The tombs date from the Han Dynasty (206BC-AD220) to the early years following the founding of the People’s Republic of China, according to a report by the Xinhua News Agency.
The Yuefu, which collected musical descriptions; the Shiji, a history penned by Sima Qian, the fu, a poetic form; lacquerwork and woven silk; and scientific breakthroughs like the invention of paper, the use of water clocks and sundials to measure time, and the development of a seismograph are among the many notable accomplishments of the Han dynasty.
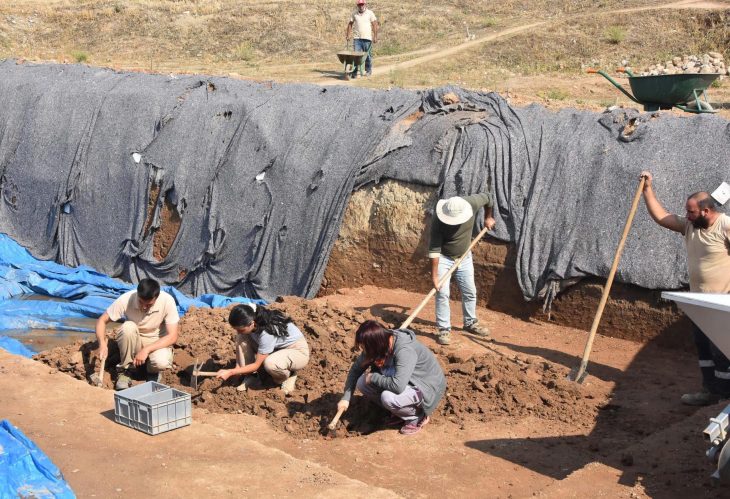
The tombs were discovered in the zoo’s construction area between April and July 2024. The Guangzhou Municipal Institute of Cultural Heritage and Archaeology led the excavation of approximately 1,300 square meters in this area.
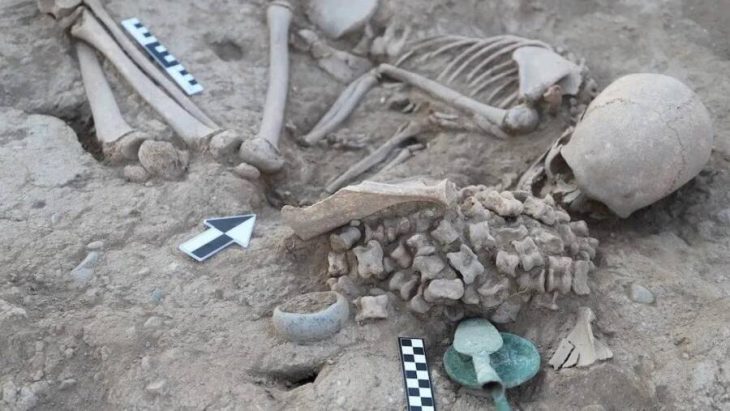
The site includes four Han Dynasty tombs, eight from the Jin and Southern dynasties (265-589), 15 from the Tang Dynasty (618-907), and 121 from the Ming and Qing dynasties (1368-1911). A total of 196 artifacts, including pottery, porcelain, bronze items, jade, and bead ornaments, along with 48 gravestones from the Republic of China (1912-49) period to the early years of the PRC, were unearthed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
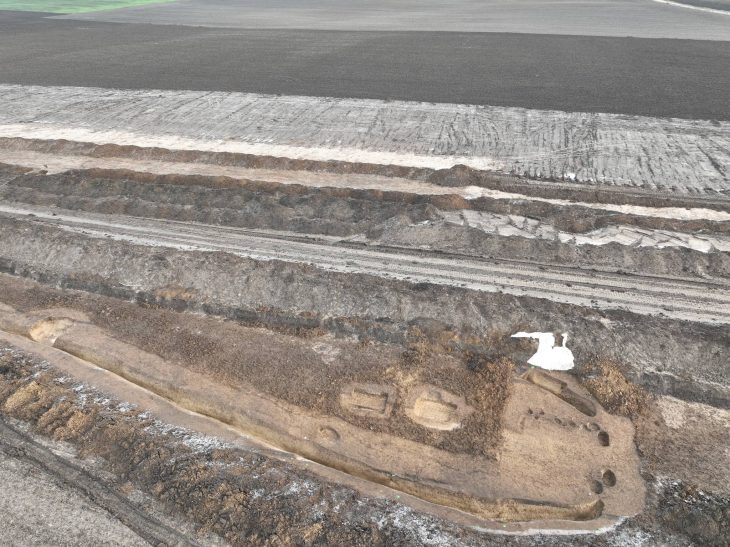
Among the most significant discoveries are a nearly intact Eastern Jin Dynasty (317-420) tomb and a well-preserved Southern Dynasties (420-589) tomb.
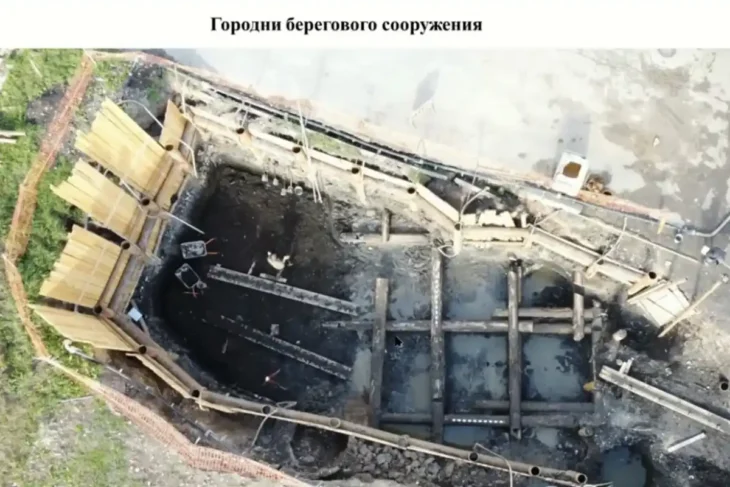
Notably, the discovery includes a well-preserved Eastern Jin tomb, which is large and structurally complex. The 10-meter-long tomb chamber shows no significant damage, aside from a robbery hole above the sealing door. It is the largest and best-preserved Eastern Jin tomb discovered in Guangzhou.
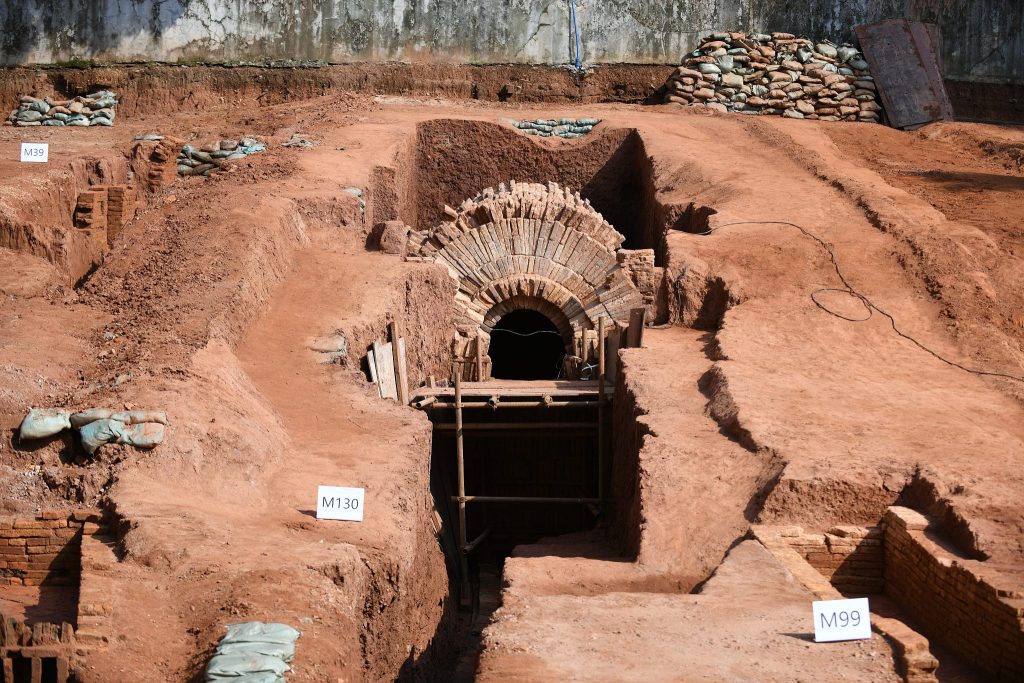

The slightly smaller tomb from the Southern Dynasties was identified to be a shared burial place for a married couple. Small holes at the top indicate that it was also looted, but otherwise, the structure is nearly intact.
Cheng Hao, an official with the institute, said that the tombs discovered this time are very densely distributed, and span a period of more than 2,100 years.
“The discovery of these two tombs is of great significance to the study of burial shapes, stages and funeral customs during the Six Dynasties period (222-589) in Guangzhou, as well as to the research on the construction technology during the Jin and Southern dynasties’ architecture,” Cheng said.
There is a pattern to the way the tombs are arranged, especially in the Ming and Qing burial chambers. They are not only oriented and scaled similarly, but they also have a uniform gap between them. This implies that the area was a planned and well-organized cemetery.
These discoveries are crucial for understanding burial practices, architectural techniques, and historical customs in Guangzhou during these periods.
The Guangzhou Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology has engaged the public through educational tours in collaboration with the Guangzhou Zoo, allowing visitors to learn more about the significance of these archaeological activities.
Cover Image: China News Service