A sculpture of a snake-bodied Roman-German deity was discovered at the Roman fort in Stuttgart, Germany.
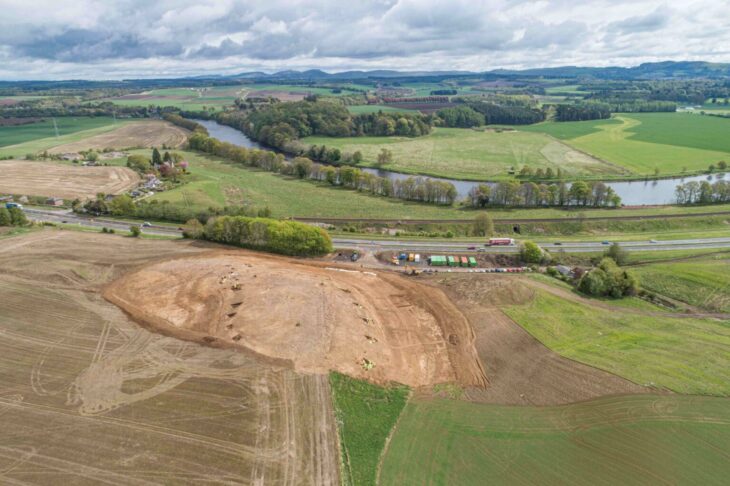
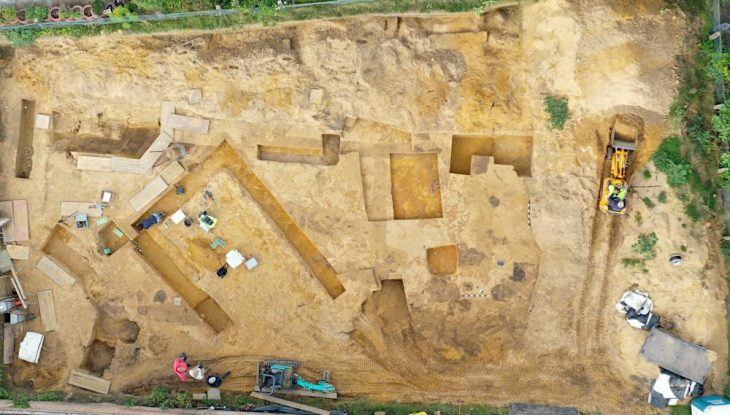
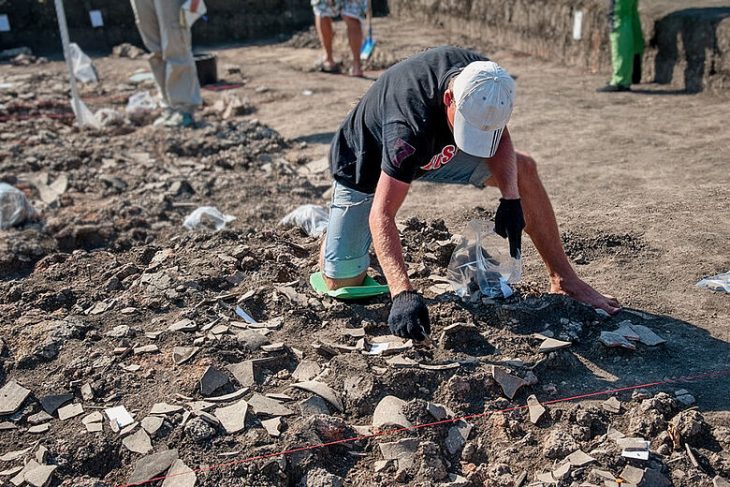
Since the beginning of the year, excavations have been taking place at the Roman fort on Altenburger Steige in Stuttgart-Bad Cannstatt under the expert supervision of the State Office for Monument Preservation (LAD) at the Stuttgart Regional Council. Archaeologists examine the construction site for the extension of the municipal Altenburg School.
In Roman times, from around 100 to 150 AD, there was initially a fort for an equestrian unit, which was followed by an extensive civilian settlement until around 260 AD.
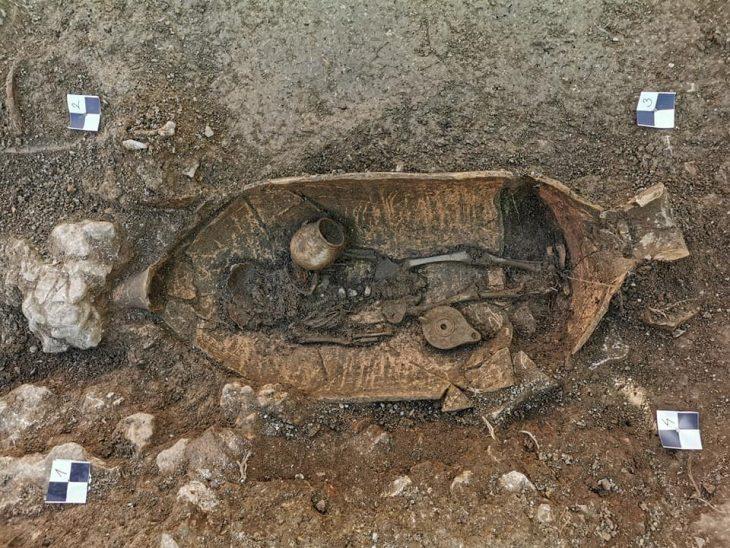
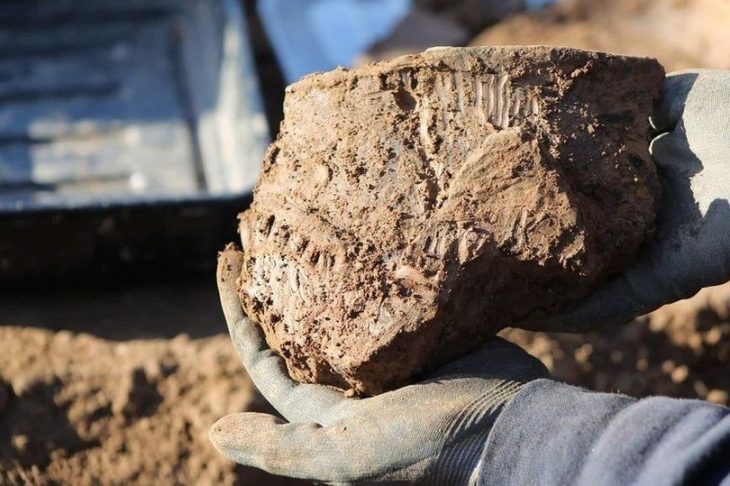
During the excavations, a stone figurine from the Roman world of gods was found, which can be linked to finds from over 100 years ago.
An employee of the executing company ArchaeoBW noticed an inconspicuous, mud-smeared sandstone. Upon closer inspection and after initial cleaning, the find turned out to be a 30-centimeter tall kneeling figure with a human head. Despite the weathering of the stone, you can see how her arms rest on the sides of her upper body and her hands rest on her hips and legs. However, the latter does not have a human shape, instead merging into a kind of snake body.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
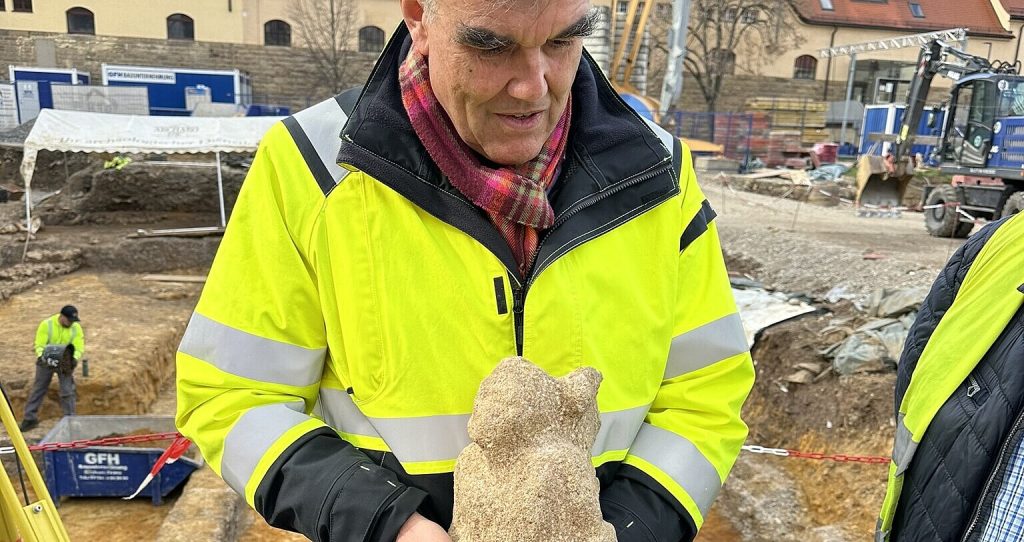

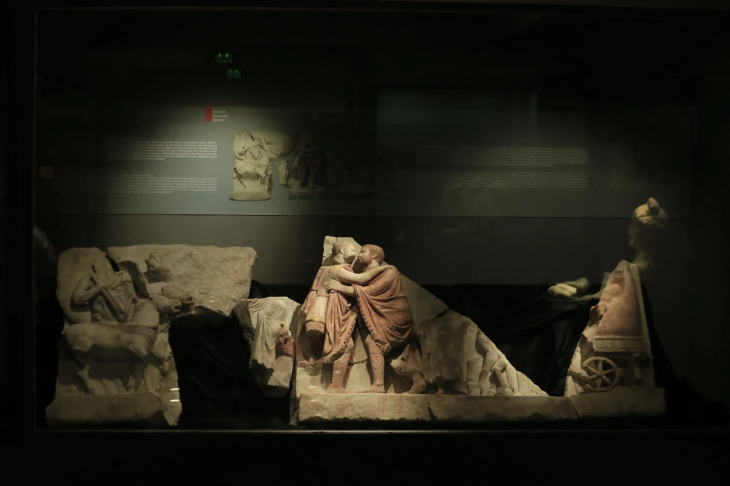
The chief archaeologist of the LAD, Dr. Andreas Thiel, explained: The figure is a hybrid creature from the Roman-Germanic world of gods, a ‘giant.’ As comparable finds show, the figure was part of a Jupiter-Giant column. These monuments combine classical antiquity with presumably Germanic beliefs: The thunderbolt-wielding Jupiter rides his horse over a crouching figure on the ground, usually naked and bearded, as can be seen, for example, in a group from Hausen an der Zaber, in the Heilbronn district. However, the figure beneath the horse is often depicted in a pose that seems to hold up the horse. These groups of figures topped tall stone pillars erected in public squares. It is presumed that Jupiter is represented here as the god of weather and lord of the forces of nature, Thiel says.
In addition to its scientific significance, the new find also has another highly interesting aspect, according to Thiel: ‘Every archaeologist is delighted when a beautiful find is made. Every excavation on the Hallschlag brings pieces of the puzzle of the Roman past of the state capital to light. In this case, we are in the fortunate position that our giant fits in with other finds that came to light in Bad Cannstatt over a hundred years ago,”.
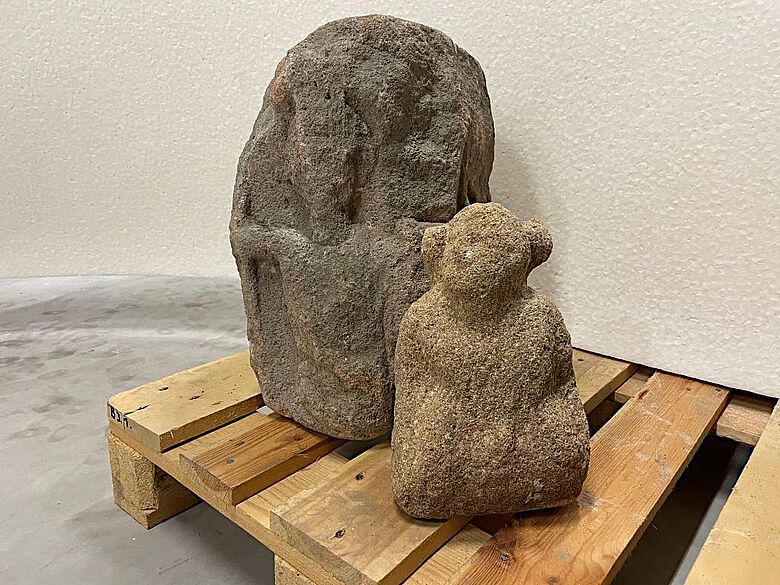

‘We have many artifacts from Roman Bad Cannstatt in our depot. When we heard about the new discovery, we immediately thought of another part of a Jupiter Giant column: its base usually included a so-called four-god stone. In the depot of the Württemberg State Museum there is a badly damaged four-gods stone with depictions of the Roman gods Mercury, Juno, Hercules, and Minerva,’ explained Dr Astrid Fendt, Head of the Department of Archaeology and Head of Classical and Provincial Roman Archaeology at the Württemberg State Museum in Stuttgart.
And Andreas Thiel added: ‘This very four-god stone comes from a well (which was located on the edge of the currently excavated area) and was found during the excavations in 1908. The inconspicuous giant could also have been lying there, but probably escaped the attention of our colleagues at the time, which is not surprising if you imagine the stone still dirty.’

Overall, it is a great stroke of luck that the recently discovered giant can be linked to a fragment that has long been stored in the Württemberg State Museum’s depot.
This allows for the reconstruction of a Jupiter giant column, which was once erected near an important road junction in the Roman settlement of Bad Cannstatt. Archaeologists see this as another piece in the puzzle of Stuttgart’s rich Roman past.
Cover Photo: Landesmuseum Württemberg Stuttgart/A. Fendt