Archaeologists in northern China have uncovered an exceptionally preserved 8th-century Tang dynasty tomb whose breathtaking murals offer a window into everyday life — and feature a mysterious blond-haired foreigner.
A Rare Glimpse into Daily Life in Ancient China
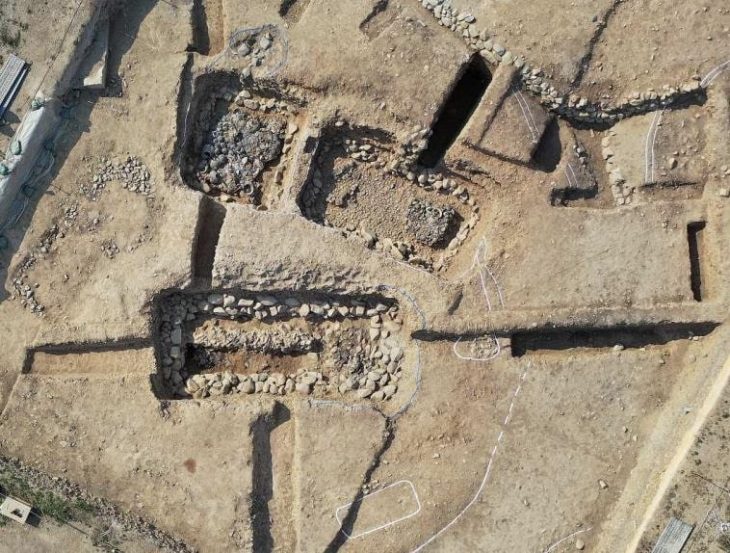
Discovered near Taiyuan, the capital of Shanxi Province, the tomb dates back to A.D. 736 and belonged to a 63-year-old man and his wife. The find was first made in 2018 during road construction, but only now have researchers revealed the full scope of its astonishing artistry.
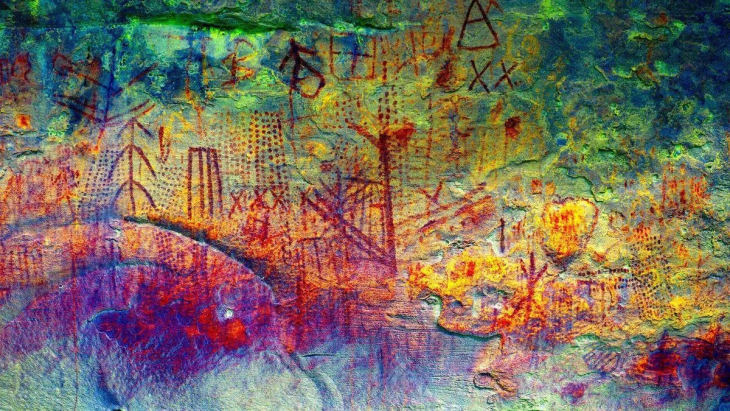
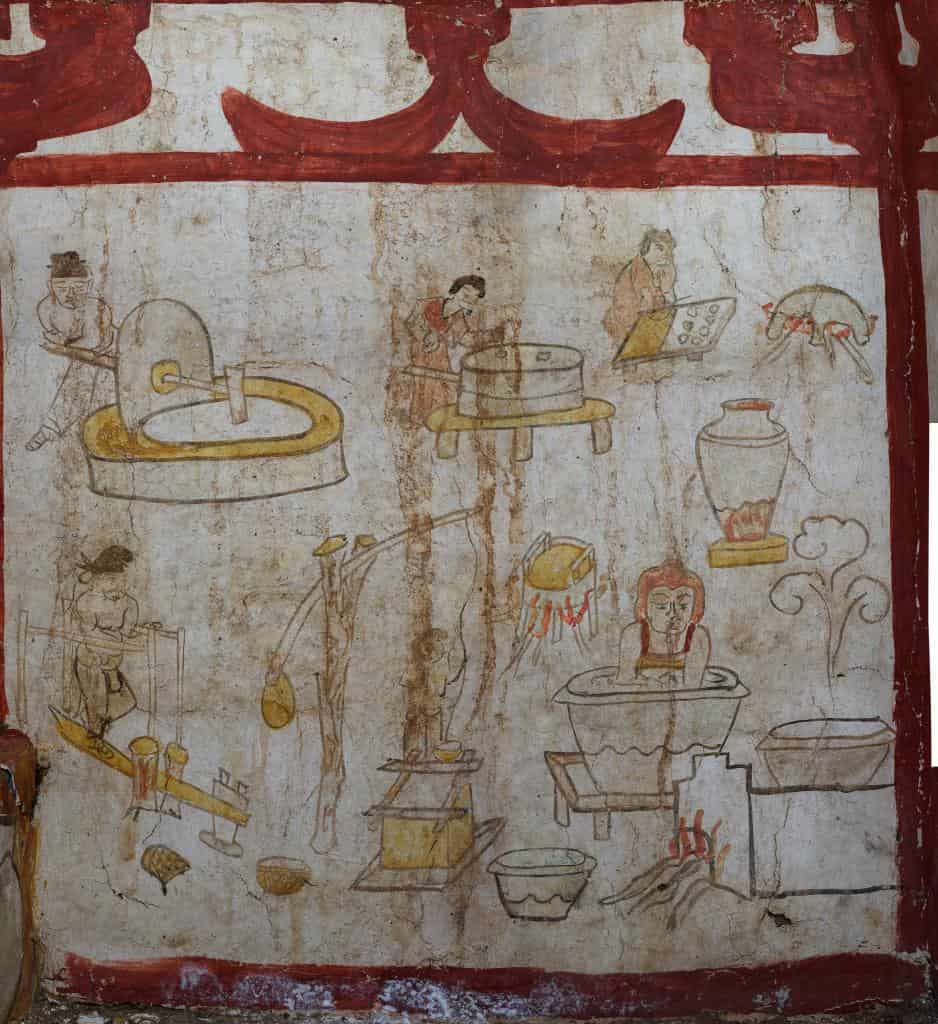
Every inch of the tomb’s walls — except the floor — is covered in vivid murals depicting scenes of Tang-era life. Farmers thresh grain, women fetch water from wells, cooks prepare noodles, and attendants lead horses and camels. These beautifully preserved scenes capture the daily rhythm of ordinary people during China’s golden age of culture, trade, and art.
The Blond Foreigner in the Tomb
Among these depictions, one figure stands out: a man with blond hair and a beard, painted with striking realism. Archaeologists believe this man was likely a Sogdian merchant from Central Asia, a region stretching across modern Uzbekistan and Tajikistan.
During the Tang dynasty (618–907), the Silk Road brought an unprecedented level of cultural exchange. Foreign traders, musicians, and diplomats flocked to the Chinese capital of Chang’an (modern Xi’an) — then one of the most cosmopolitan cities on Earth. The presence of a fair-haired figure in the Taiyuan tomb reflects that vibrant internationalism.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Who Were the Sogdians?
The Sogdians were an ancient Iranian people renowned as the great middlemen of the Silk Road. From their urban centers in Samarkand and Bukhara, they facilitated the flow of silk, spices, precious metals, and ideas between China, Persia, India, and Byzantium.
Historical and genetic evidence shows that some Sogdians possessed light hair and eyes, the result of centuries of intermingling between Indo-Iranian, Turkic, and steppe nomadic groups. Chinese texts from the Tang era even describe Sogdians as fair-haired and sharp-featured, often employed as traders, entertainers, or envoys in China’s frontier cities.
Artistry and Symbolism
The tomb’s single brick chamber features murals painted in a distinctive Tang style, characterized by bold outlines and delicate shading against a white background. Scholars refer to this artistic approach as the “figure under the tree” style — an aesthetic tradition dating back to the Han dynasty.
The domed ceiling is adorned with images of a dragon and a phoenix, symbols of imperial power and immortality. Near the entrance, guards in yellow robes stand watch, their swords drawn — traditional “tomb guardians” meant to protect the deceased in the afterlife.
According to Long Zhen, director of the Jinyang Ancient City Archaeological Institute, the artistic techniques resemble those found in the tomb of Wang Shenzi, a 9th-century ruler. However, the Taiyuan murals focus not on emperors or battles, but on everyday people — a rare and humanizing subject in Tang funerary art.

A Window into the Tang Dynasty’s Cosmopolitan World
The exceptional preservation of these murals offers a “never-before-seen” look at the daily lives of Tang-era commoners. Many of the figures appear to be repeated, suggesting that they depict the tomb’s occupants themselves — captured in an eternal portrait of their worldly lives.
This discovery joins a rich tradition of mural art in China, alongside masterpieces like the Mogao Grottoes of Dunhuang, whose sprawling frescoes line more than 25 kilometers of cave walls. Together, they illuminate a world where China stood at the crossroads of civilizations — a meeting point for East and West connected by trade, faith, and art.
As archaeologists continue to study the Taiyuan tomb, they hope to uncover even deeper insights into how global exchange shaped life, identity, and art in the Tang dynasty — one of history’s most cosmopolitan empires.
Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, N., Li, J., Qu, Y., Zhu, C., Zhang, F., Cai, D., & Ning, C. (2025). [Unraveling the origins of the Sogdians: Evidence of genetic admixture between ancient central and East Asians]. Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports, 61, 104957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104957
Cover Image Credit: Xinhua