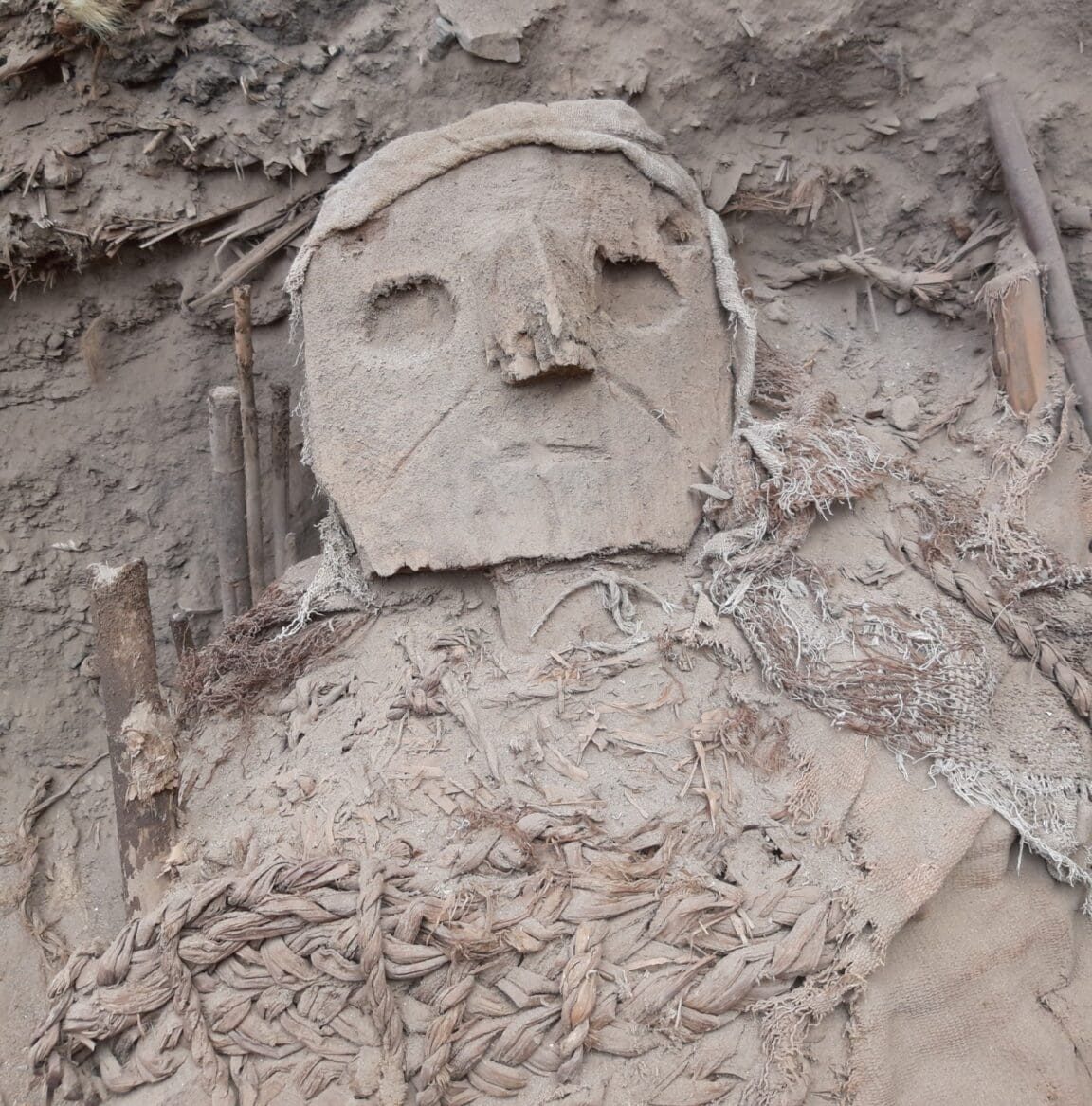
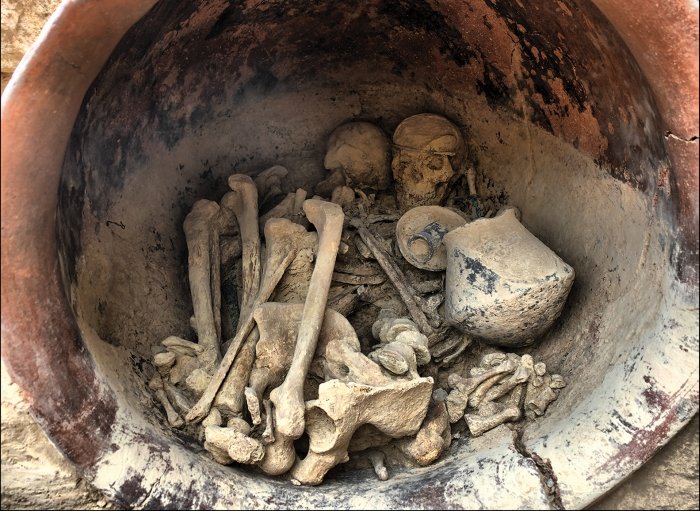
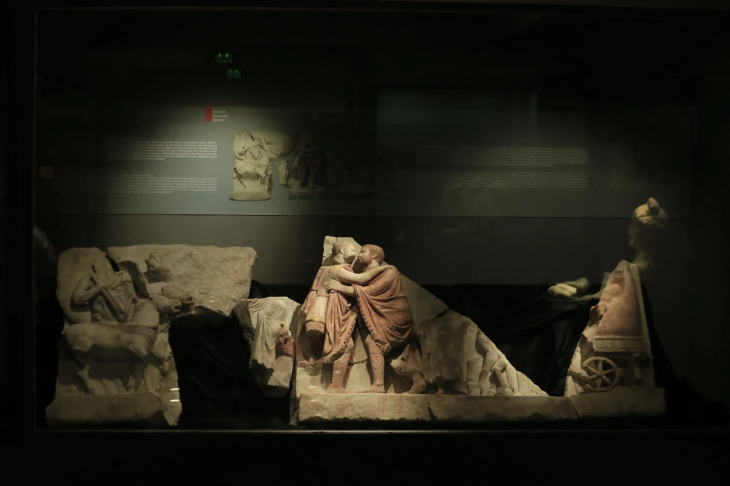
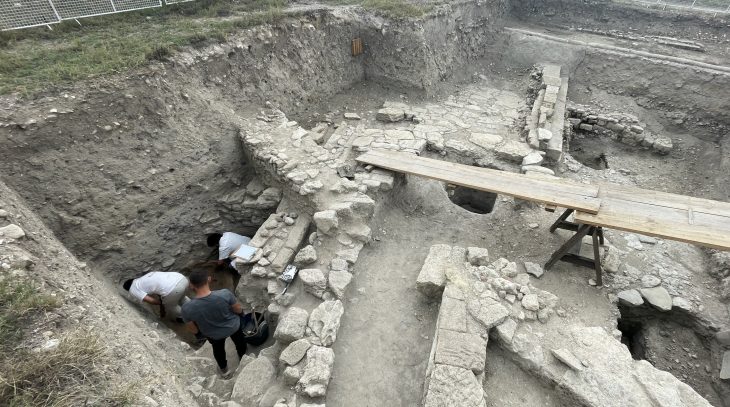
At Pachacámac, an archaeological site southeast of Lima in Peru, archaeologists unearthed bundles of 73 intact mummy bundles, some containing “false-heads” masks made of wood or ceramics.
The site of the find is an extensive complex of cemeteries from different periods at the foot of the Painted Temple. Nearby, wooden staff with images of dignitaries of the Wari Empire were also discovered.
The Wari culture belongs to the most important prehistorical cultures of Peru. It developed in the mountainous valley of Ayacucho in Central Peru based on local traditions and the influences carried by the Tiwanaku culture that flourished in the altiplano of Bolivia.
The finds date to the latter part of the Middle Horizon, between 800-1100 AD, corresponding to the expansion period of the Wari Empire’s reign.
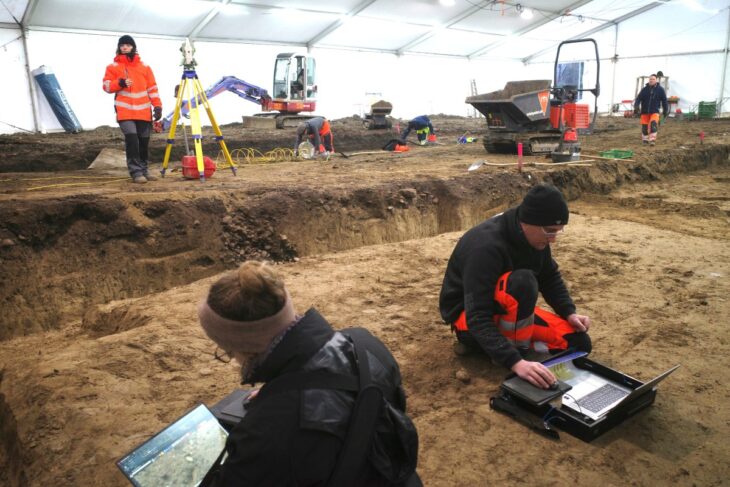
The discovery was made by a team of archaeologists from the Pontifical Catholic University of Peru, led by Professor Krzysztof Makowski at Pachacámac, south of Lima (Peru).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
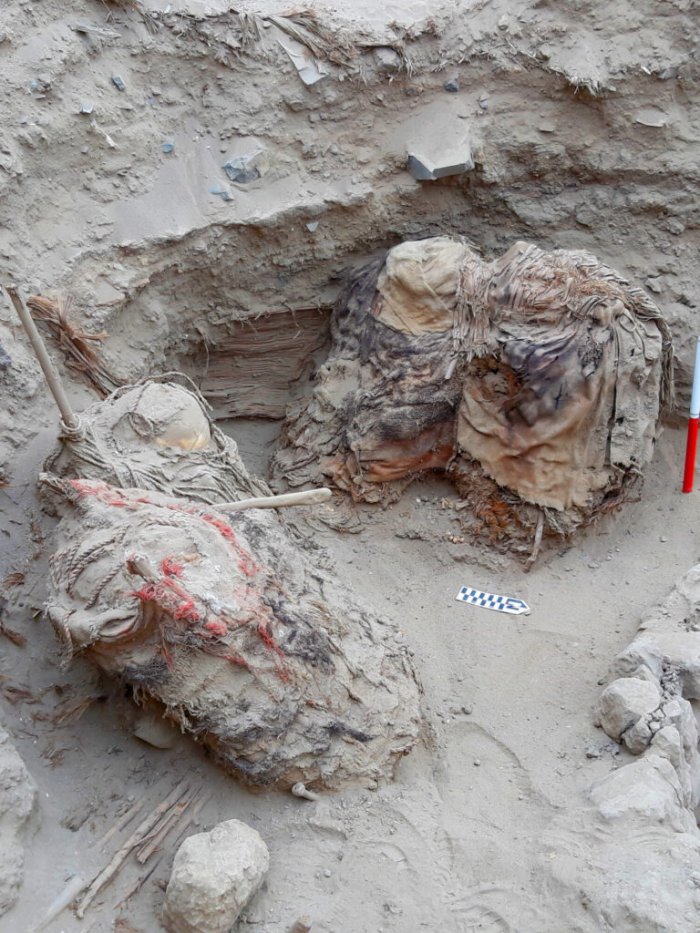

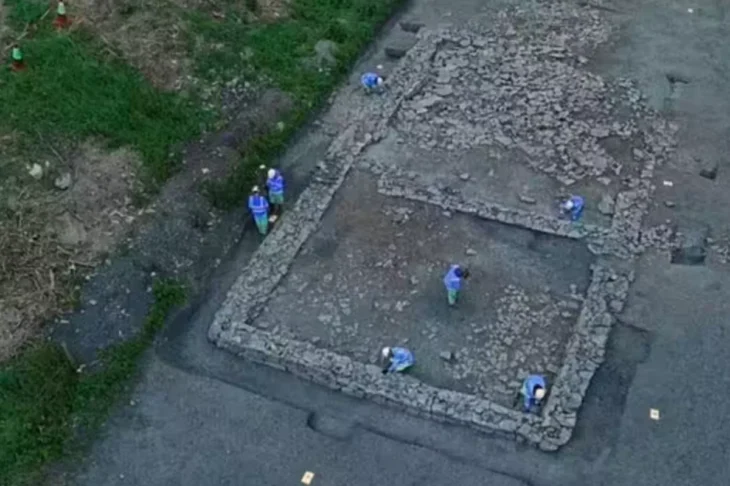
The cemetery complex was first discovered in the late 19th century by German archaeologist Max Uhle. They had been widely damaged in the “extirpation of the idolatries” during the colonial period and would be repeatedly looted after Uhle’s excavation. The discovery of 73 undamaged burials is therefore of great archaeological significance.
Professor Makowski’s team, consisting of Cynthia Vargas, Doménico Villavicencio, and Ana Fernández, purposefully focused their research on a site where a tall wall that was constructed during the Inca and colonial periods had collapsed. It had been assumed that the piles of adobe bricks would have made it difficult for robbers to access the graves. This turned out to be accurate.
The discovery of a well-preserved assemblage of individual and group burials with dates precisely to the second half of the Middle Horizon.
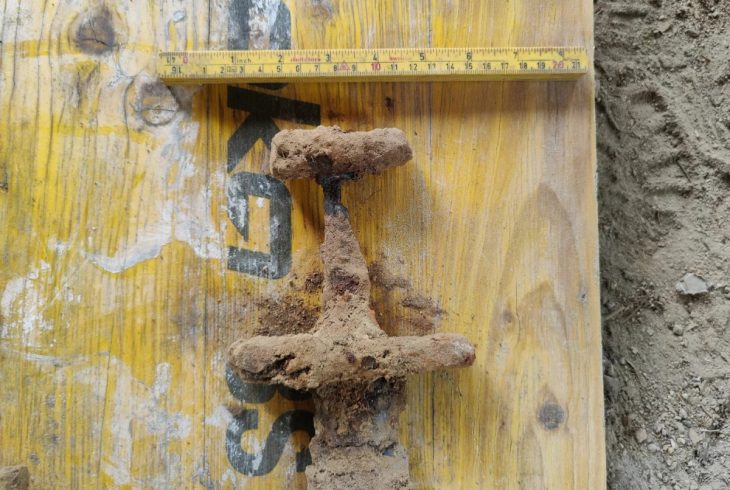
In addition to the burial discoveries, archaeologists stumbled upon two wooden staffs near the cemetery within the remnants of a nearby settlement. These staffs were found in a deposit of “thorny oyster” ( Spondylus princeps) shells, believed to have been imported from present-day Ecuador, situated to the north of the Wari Empire.
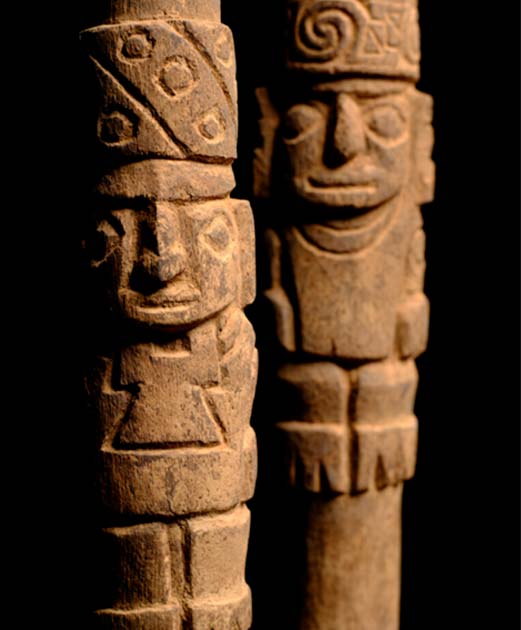

The carved iconography on these staffs potentially suggests that the inhabitants of Pachacámac had established some form of contact with individuals from the Tiwanaku kingdom. The Tiwanaku kingdom, positioned to the south of the Wari Empire, spanned the present-day regions of Peru, Bolivia, and Chile – an indicator of ancient trade routes and cultural exchanges.
The wooden staffs depict dignitaries donning headgear reminiscent of the styles worn in the Tiwanaku kingdom. The shared elements in the headgear design along with the stylistic similarities make these finds historically and culturally unique, according to Archeowiesci blog.
The team’s findings contradict the previous understanding of Pachacámac history. It was not, as historians have posited, a sacred city from the construction of the Old Temple during by the Lima culture ca. 200 A.D. through the arrival of the Spanish. During the Wari Empire, it was not the monumental sacred site that was one of the most important in the central Andes. That only happened after it was absorbed in the Inca Empire.

Due to the state of preservation and the precision of the documentation of the context of the finds at the time of excavation, as well as the laboratory analyses, the burial assemblages uncovered are a veritable goldmine of information on the social position of men, women and children according to kinship ties, the care of invalids, indicators of war and domestic violence.
Nineteen of the bundles, with their lower part preserved and an intact structure, could be transferred to the laboratory in their entirety in order to document them three-dimensionally using CT scanning without having to be opened. Their contents will be analysed on a computer screen by bioarchaeologists Professor Dr. Andrew Nelson and Dr. Lucía Watson.
Cover image: Carved wood mask on the so-called “false head” of a burial tomb, Pachacámac, Peru. Photo: PUCP Archaeology Program “Valley of Pachacámac”, published under CC BY-SA 4.0