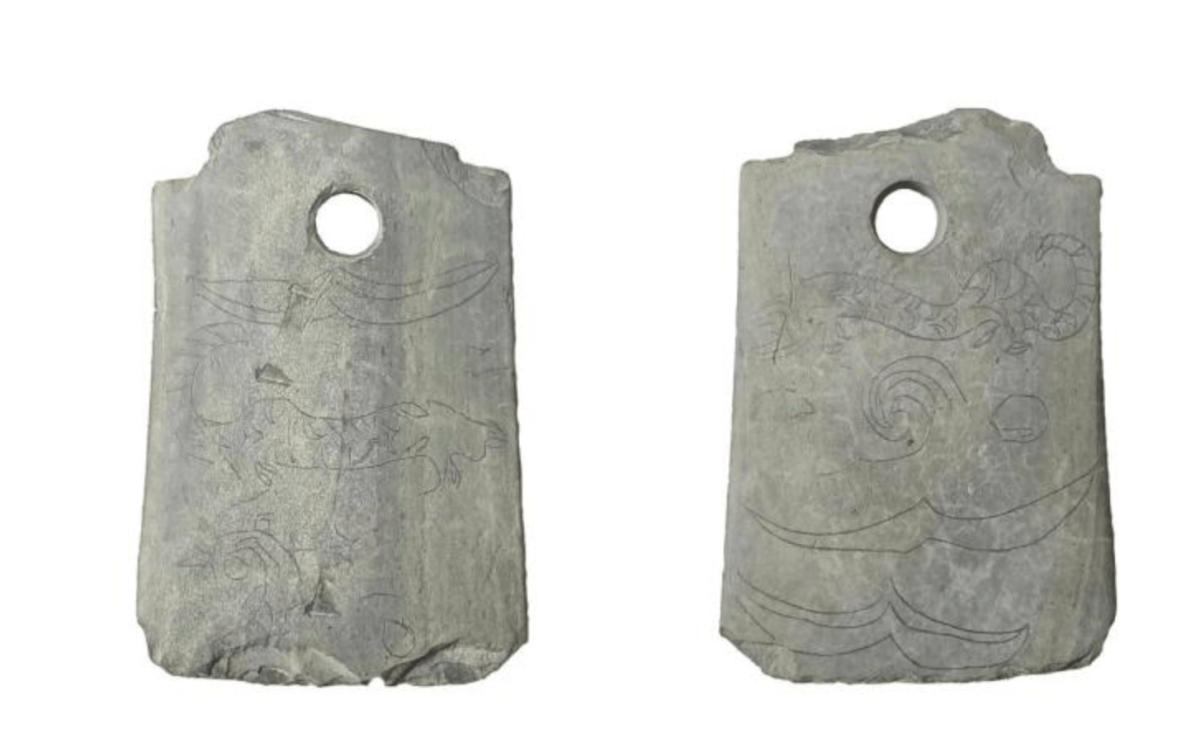
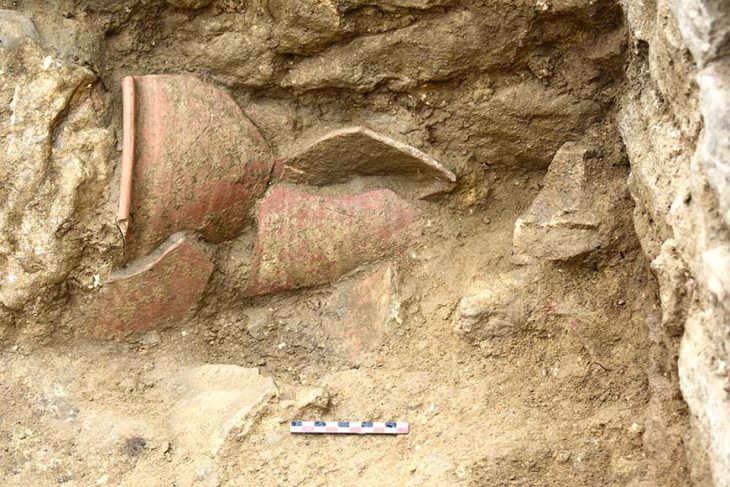
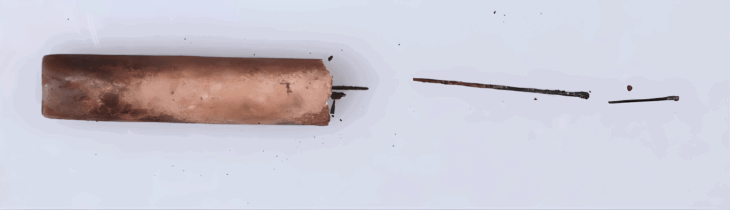
Archaeologists discovered an extremely rare stone relic, an axe-shaped weapon used for rituals in ancient China, engraved with a tiger pattern.
The extremely rare stone relic was found in Wuxi City in eastern China‘s Jiangsu Province. The relic dates back some 4,500 years, during the Liangzhu Culture period.
Archaeologists date the influential Liangzhu culture from 3300 to 2250 BCE. Located south of the Yangzi River, the enormous settlement has been named Liangzhu after the modern site where evidence of the culture was first discovered in the early twentieth century.
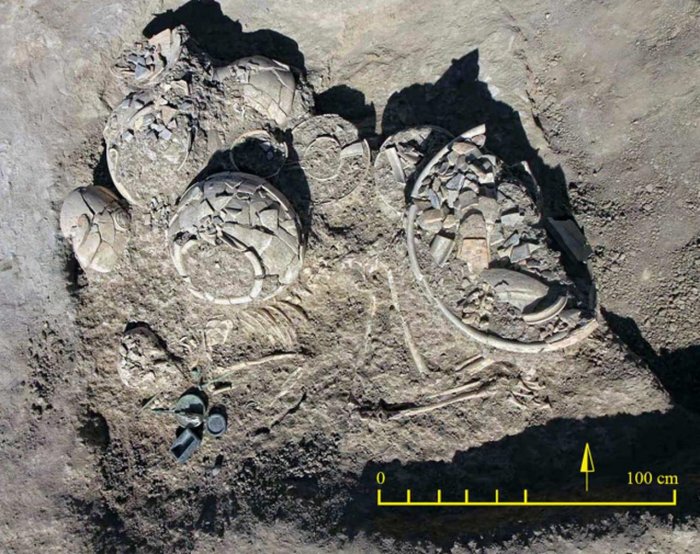
Archaeologists discovered 329 stone tools at the Dinggeng archaeological site in Wuxi City recently. In addition, the team discovered 73 stone and bone arrowheads, as well as numerous ceramic and jade artifacts.
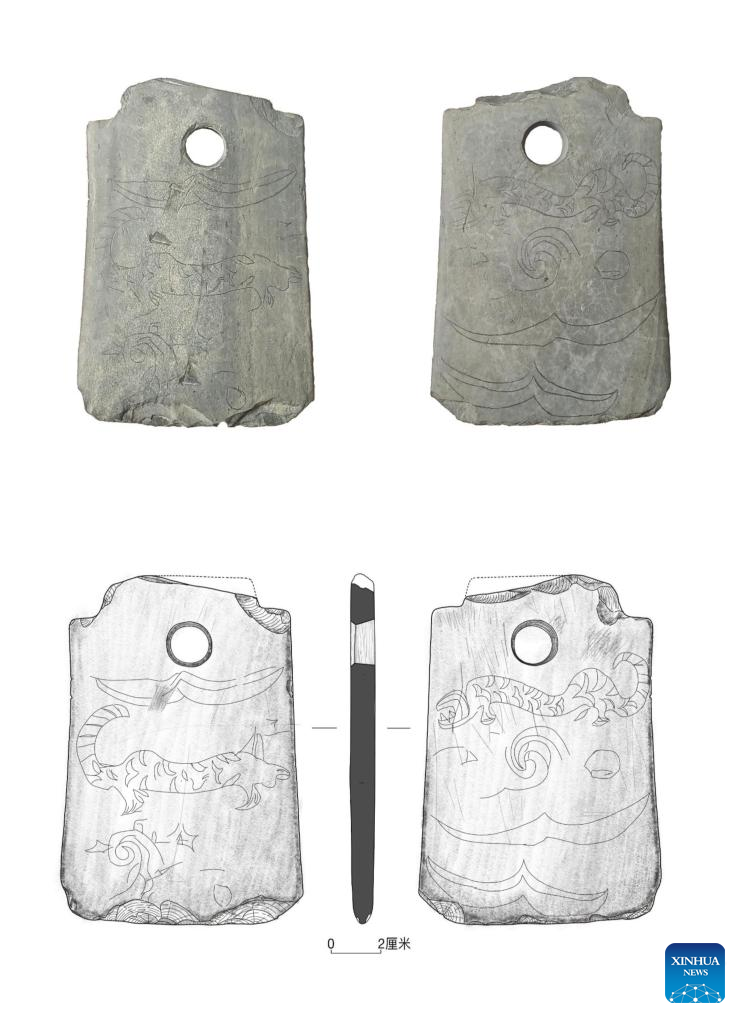

A 4,500-year-old stone relic carved on both sides with depictions of tigers and patterns of clouds and birds surprised archaeologists, according to a statement at the Dinggeng Relics Site archaeological site on Saturday. 16 archaeologists from home and abroad said it was the first time they had seen such a tiger-patterned stone relic, which they believed to be a symbol of power.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Liu Baoshan, head of the Wuxi institute of cultural relics and archaeology, said these patterns had single, relatively smooth lines.
The axe was found on a sacrificial platform and exhibits evidence of wear and damage.
The Archaeological Ruins of Liangzhu City reveal an early regional state with rice-cultivating agriculture as its economic base, social differentiation, and a unified belief system, which existed in the Late Neolithic period in China.
Cover photo: XİNHUA