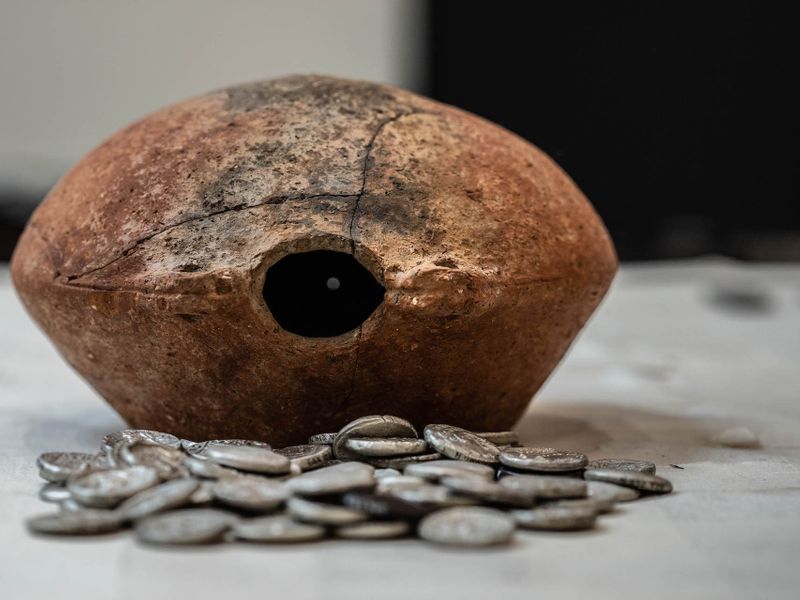
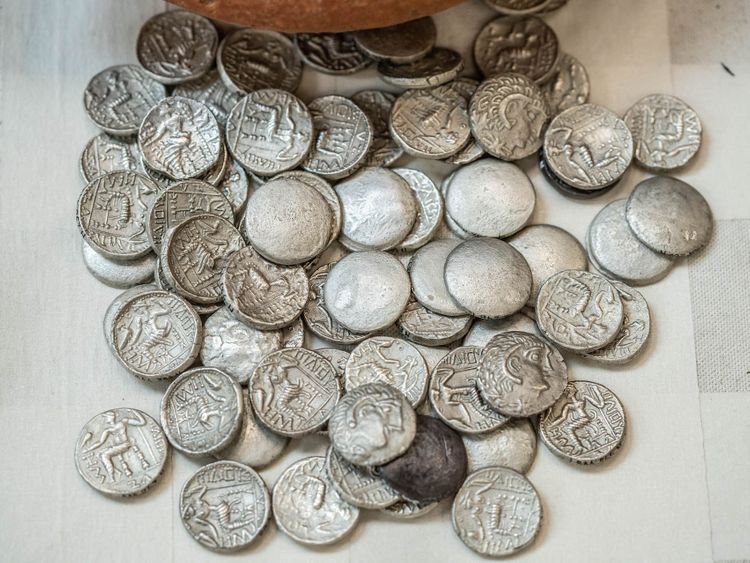
409 silver coins dating to the 3rd century have been found in the Mleiha area of Sharjah in the United Arab Emirates.
The Sharjah Archaeology Authority announced on Wednesday that an ancient jar containing several silver coins going back to the third century BCE (Before Common Era) was recently discovered in Mleiha.
The coins of Mleiha were influenced by the coins of Alexander the Great and his Seleucid dynasty successors (Hellenistic state in Western Asia that existed from 312 to 63 BCE).
According to the Sharjah Archaeology Authority, the first issues of the minted coins depicted icons of the time, such as the head of Hercules (represented by Alexander the Great) and Zeus (the Greek god sitting on his throne), as well as the word ‘Alexander’ engraved in Greek script. With the passage of time, the engraving was replaced with the word ‘Abel’ written in Aramaic script.

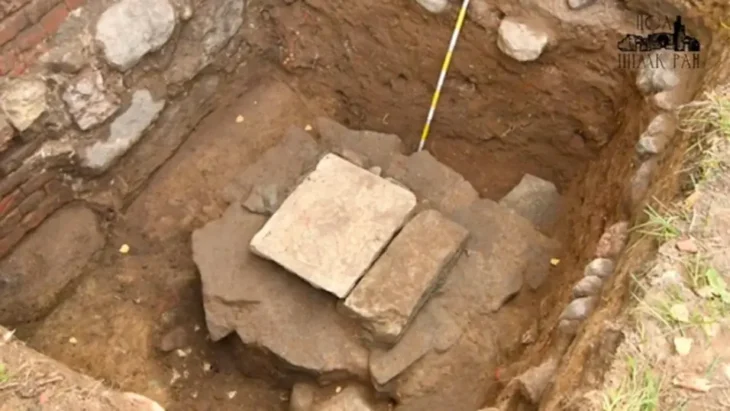
The artifacts were first discovered by the local archaeological team in February 2021.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Sabah Aboud Jasim, Director-General of Sharjah Archaeology Authority, told Gulf News: “When this heavy pottery jar (weighing 9kg) was discovered, it was suspected that it would contain rare artifacts. Upon carefully opening the pot at the Sharjah Archaeology Authority laboratory, we found it completely filled with numerous silver coins of the drachma (ancient Greek currency unit) quad category or ‘tetradrachma’.
Dr. Jasim added: “There were a total of 409 coins in the jar, with each coin ranging in weight from 16 to 17 grams, and the currency material was silver.” There were 387 coins in single-sided moulds and 22 in two-sided moulds.
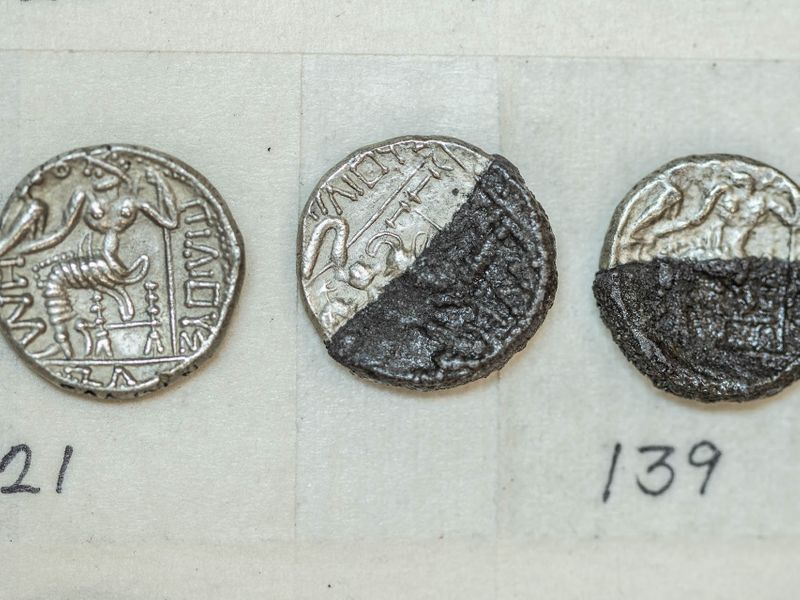

“Among the collection were coin designs that had been previously discovered throughout the Arabian Gulf region and also coin designs that were unique to this discovery at Mleiha. The current collection is considered to be more extensive than any other in the region” he added.
Mleiha is a Unesco-designated World Heritage Site in Sharjah that has a variety of notable monuments, such as Bronze Age tombs and pre-Islamic forts.
Mleiha was regarded as one of the most significant locations in the Arabian Peninsula during the pre-Islamic period. It became a significant trade center for convoys traveling between the north and south of the Arabian Peninsula in the early third century BCE.
A gravestone unearthed at Mleiha in the late third century BCE established the presence of the Oman Kingdom, and a study has revealed that Mleiha was most likely its capital at the time.