Approximately 3000 years old “lost golden city” has been unearthed in Luxor city in southern Egypt. The archaeological mission said in a statement on Thursday that it may be the most important discovery in Egypt since the tomb of the boy-king Tutankhamun.
The lost city, known as Aten, is believed to have been founded by King Amenhotep III, the ninth king of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, who ruled the country from 1391 to 1353 B.C., says the mission statement. It is believed to be the largest administrative and industrial settlement of the time, located on the west bank of Luxor.
Archaeologists began excavations in September in the area between the temples of King Ramses III and Amenhotep III. The original purpose of the mission was to find the mortuary temple of King Tutankhamen, the statement said.
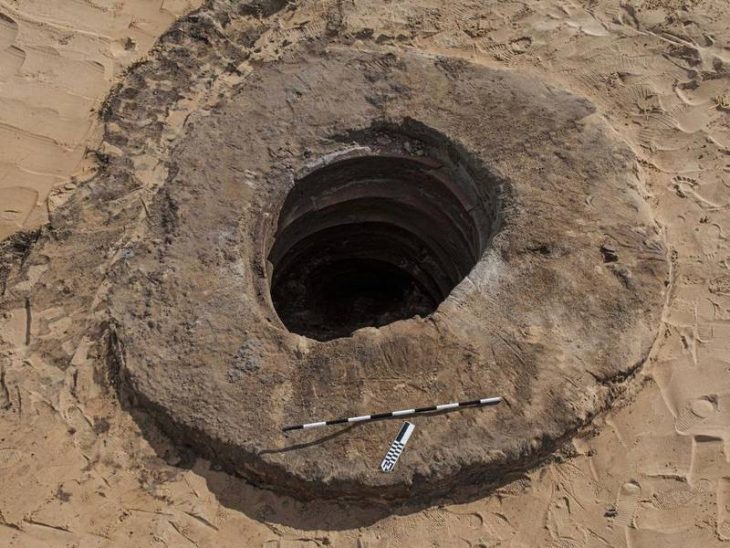
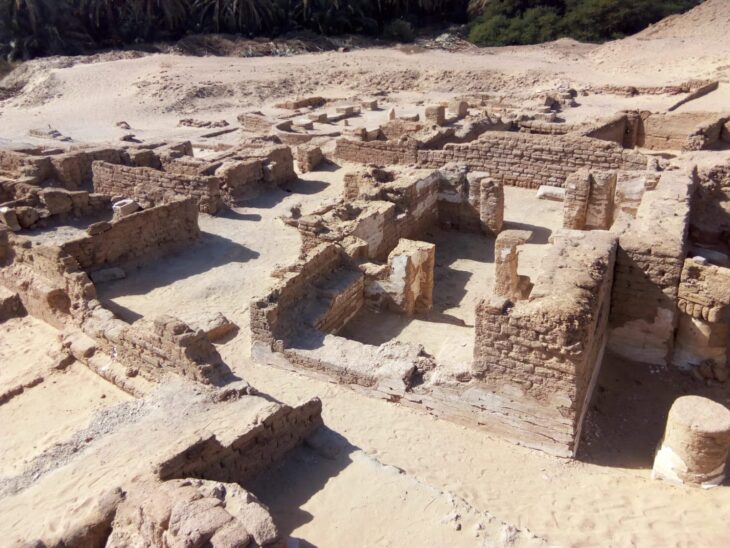
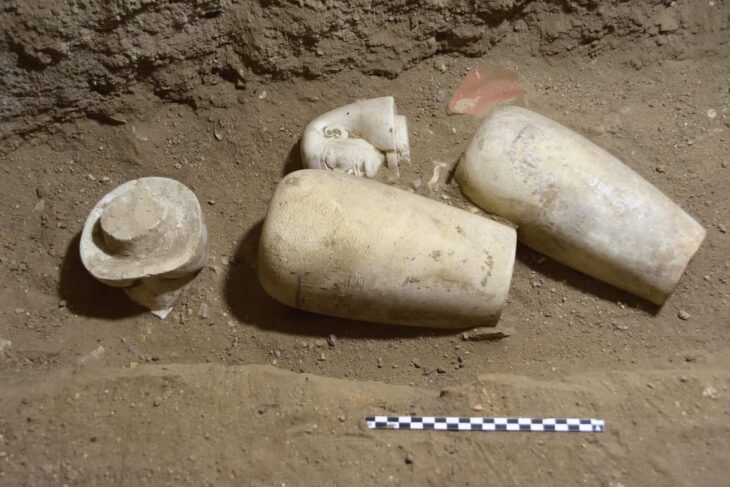
“Within weeks, to the team’s great surprise, formations of mud bricks began to appear in all directions,” the statement said. “What they unearthed was the site of a large city in a good condition of preservation, with almost complete walls, and with rooms filled with tools of daily life.
“The archaeological layers have [lain] untouched for thousands of years, left by the ancient residents as if it were yesterday,” it said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Many foreign missions searched for this city and never found it,” Zahi Hawass, an Egyptian archaeologist and former minister of state for antiquities affairs who led the mission, said in the statement.

The city was active during the reign of Amenhotep III as well as during his co-regency with his son, Amenhotep IV, also known as Akhenaton. The city was later used by Tutankhamen and his successor, King Ay.
Hawass said the city’s streets are flanked by houses, some of which have walls nearly 10 feet high.
The archaeological team dated the settlement through hieroglyphic inscriptions found on wine vessels, rings, scarabs, pottery, and mud bricks bearing the seals of King Amenhotep III’s cartouche, the statement said.
So far, several enclaves in the city have been discovered. The statement said that in the south, archaeologists found a bakery and a large kitchen equipped with ovens and crockery to store food. They also found an administrative and residential area surrounded by a jagged wall with only one entrance, implying that it was to provide security.
In a third area was a workshop. The team found casting molds to produce amulets and ornaments, apparently for temples and tombs, according to the statement.
“All over the excavated areas, the mission has found many tools used in some sort of industrial activity like spinning and weaving,” the statement said, adding that metal and glassmaking slag has also been found.
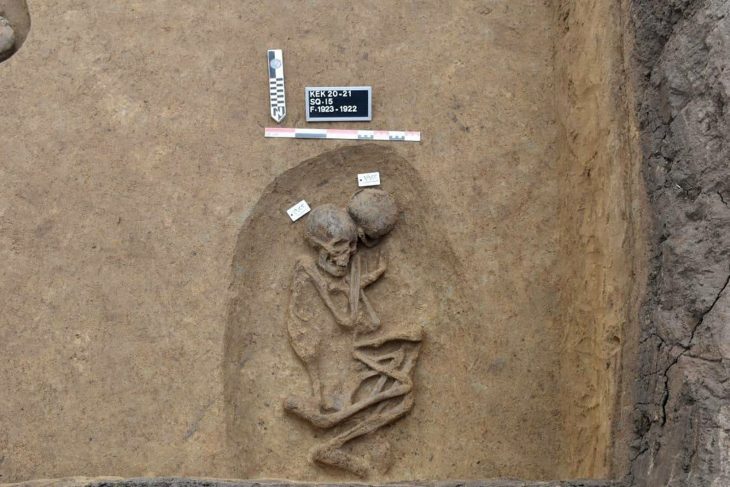
In other parts of the city, the graves of two cows or bulls were found in a room. And in another area where the remains of a person, found with arms outstretched to his side and a rope wrapped around his knees. The team is investigating both cases to glean more information about social practices during that era, the statement said.
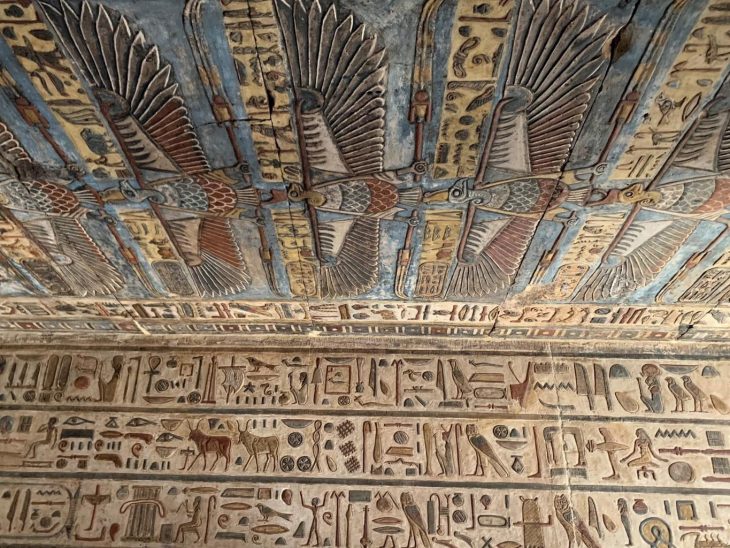
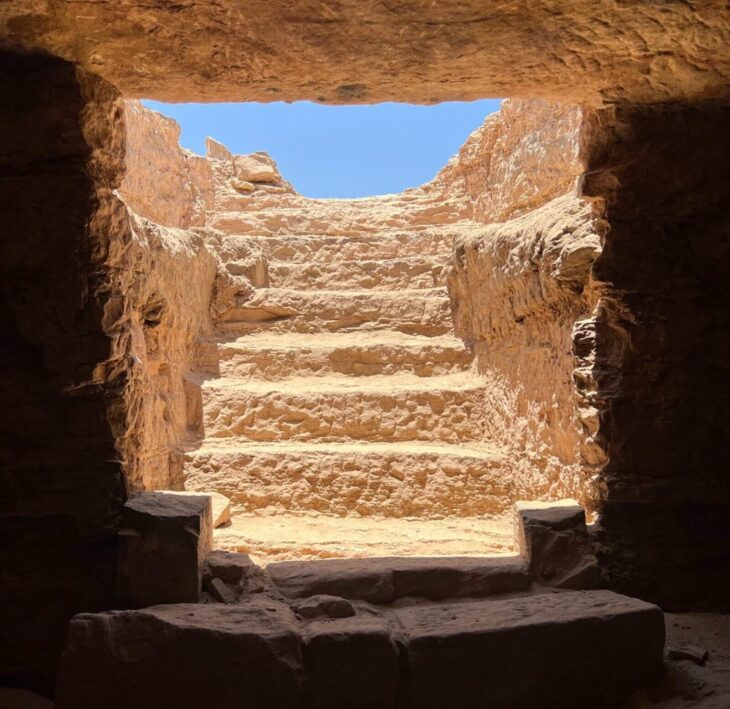
A large cemetery was found to the north of the city, as well as a group of tombs cut from the rock.
“Work is underway and the mission expects to uncover untouched tombs filled with treasures,” the statement read.
This lost city is the latest in a series of archaeological discoveries excavated in the country in recent months, which gave people a new understanding of the dynasty that ruled ancient Egypt. The Egyptian government hopes that these discoveries will boost the country’s most important tourism industry, which has been hit by the coronavirus pandemic, attacks by Islamic radicals, and political unrest in recent years.
Cover Photo: The photo is illustrative / iStock / Getty Images