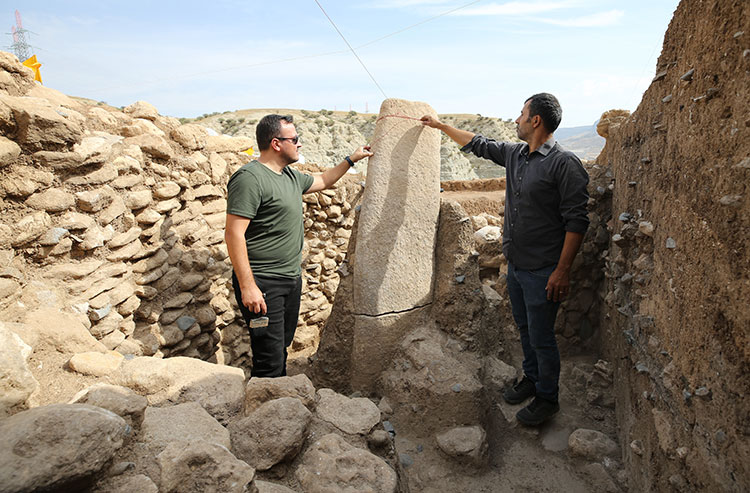
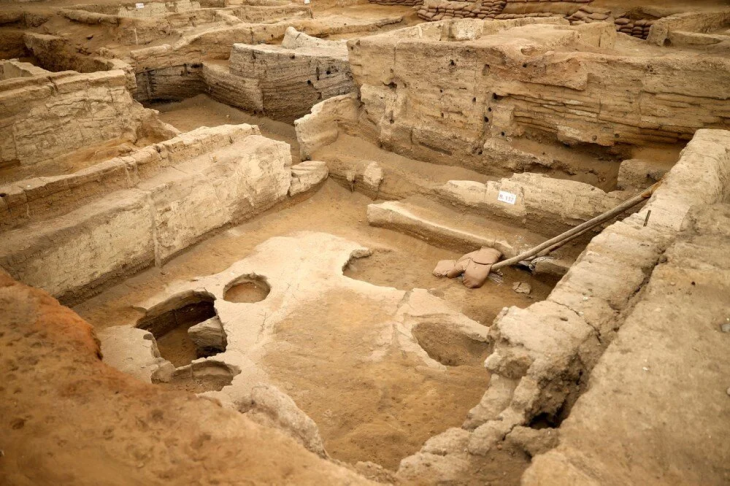
A remarkable 2-meter by 20-centimeter processed stone block was discovered during the archaeological excavations at Boncuklu Tarla (Beaded Field), which illuminates the history of humanity with its 12,000-year past in the Ilısu neighborhood of the Dargeçit district of Mardin.
The region, which has hosted 25 civilizations throughout history, including Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, Hittites, Assyrians, Urartians, Romans, Abbasids, Seljuks, and Ottomans, continues to reveal ancient human life.
Archaeological excavations in Boncuklu Tarla, initiated in 2012 by the Mardin Museum Directorate have been continuing and led by Associate Professor Ergül Kodaş, a faculty member in the Department of Archaeology at Mardin Artuklu University.
In Boncuklu Tarla, which has an area of approximately 2.5 hectares and was included in the ‘Heritage for the Future Project’ of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism this year, many finds belonging to the period from the Late Epipaleolithic period to the Neolithic Age have been unearthed so far.
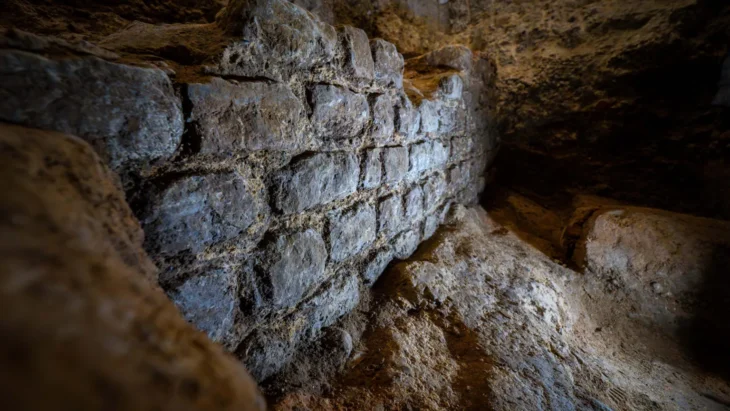
The excavations finally uncovered the remains of a ‘public building’, which is estimated to be about 12 thousand years old.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
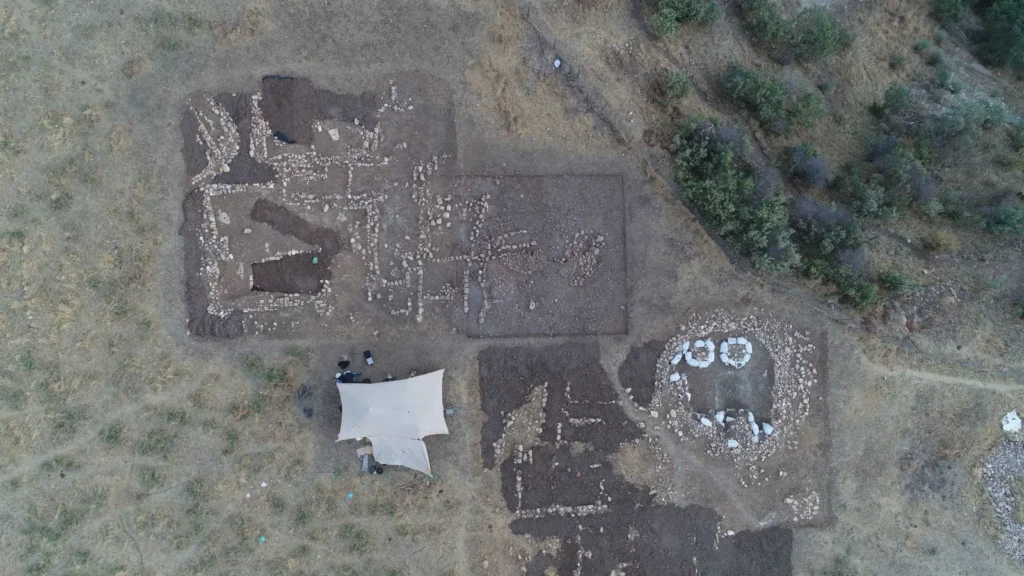

This roughly 10-meter-diameter structure looks to have been in continuous use for a number of phases. It is noteworthy that the building underwent at least four renovations, each of which involved filling in the floor. This finding casts doubt on previous theories that the buildings at Boncuklu Tarla were occupied only once before being abandoned.
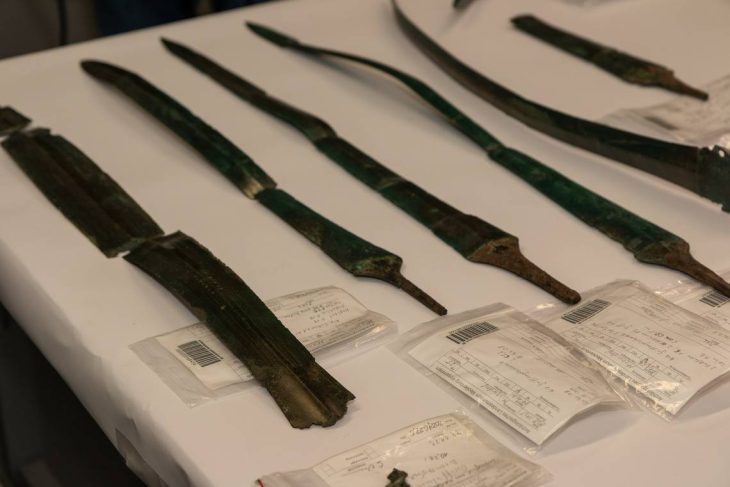
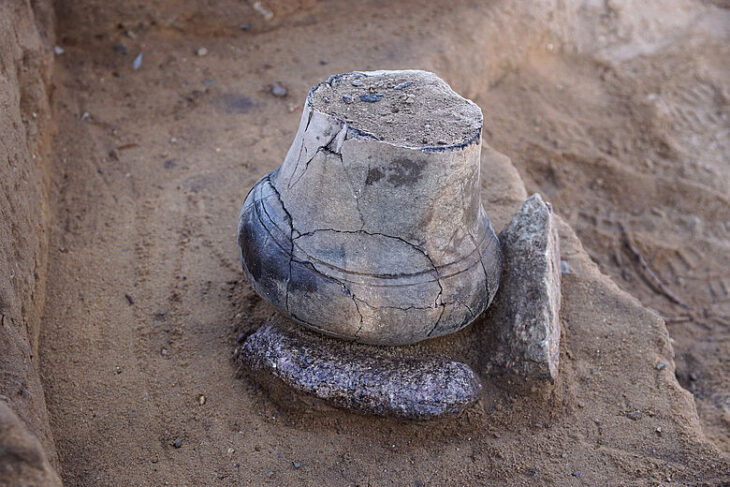
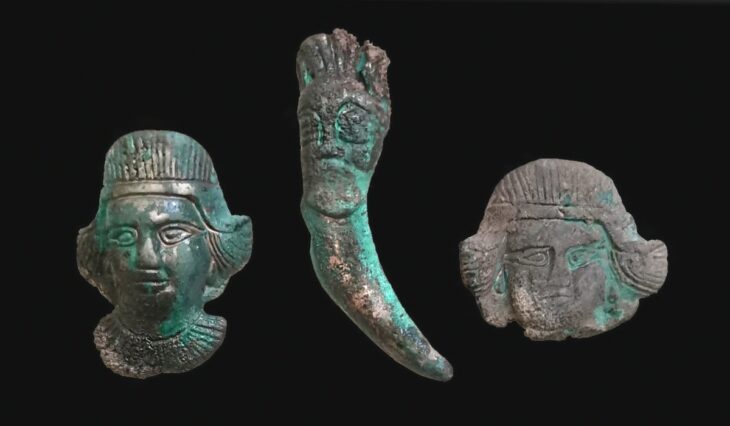
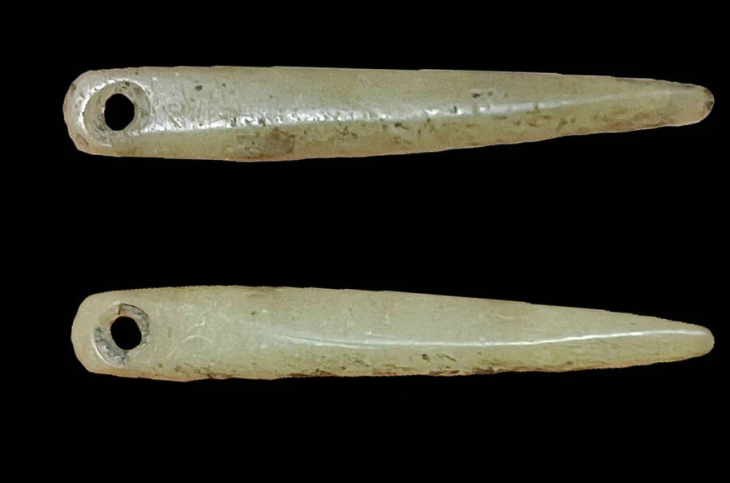
In the remains of the structure, a stele (worked stone block) measuring 2 metres 20 centimetres in length and many find such as miniature steles, beads, arrowheads, and bull horns were unearthed.
According to Associate Professor Ergul Kodas, the excavation leader from Mardin Artuklu University, this large stele is a groundbreaking find for the site and the Upper Tigris Valley. “For the first time, such a large stele has been discovered both at Boncuklu Tarla and in the Upper Tigris Valley,” said Kodas.
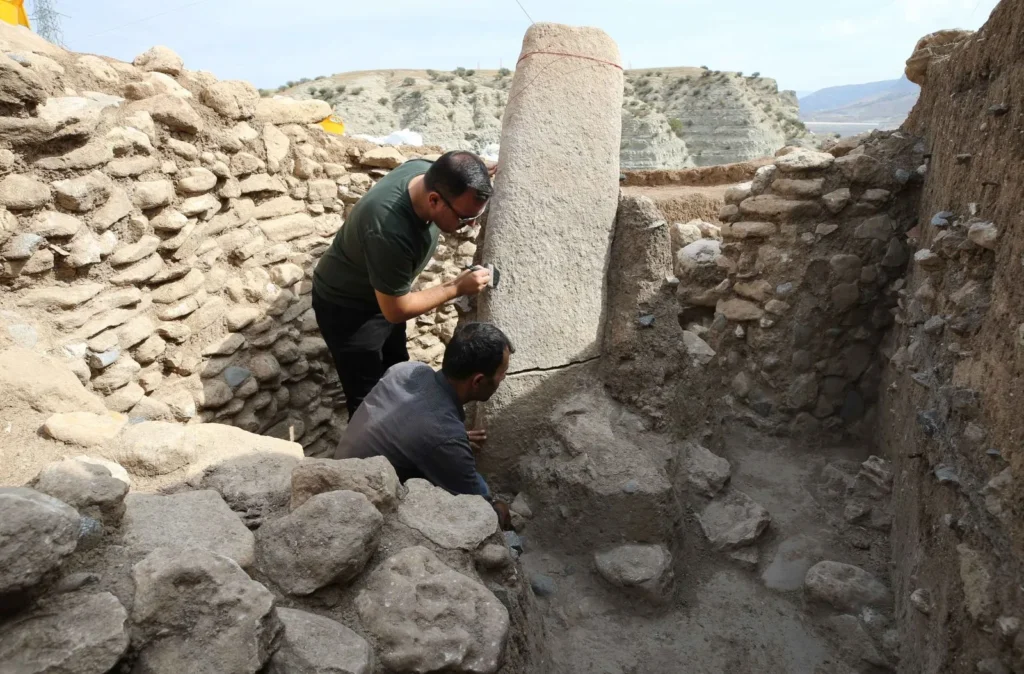

The stele is especially noteworthy because it bears similarities to those in the Sanliurfa region, indicating a historical relationship between these two regions. Moreover, a miniature replica of the stele was found inside the structure, offering more information about the connections between the areas at this time.
An invaluable window into the lives of ancient societies in the Upper Tigris Valley is offered by the discoveries made at Boncuklu Tarla. Continued excavations hold the potential to deepen our knowledge of early human civilization in Turkey by illuminating the lengthy history of the area’s architectural and cultural development.
Cover Image Credit: AA