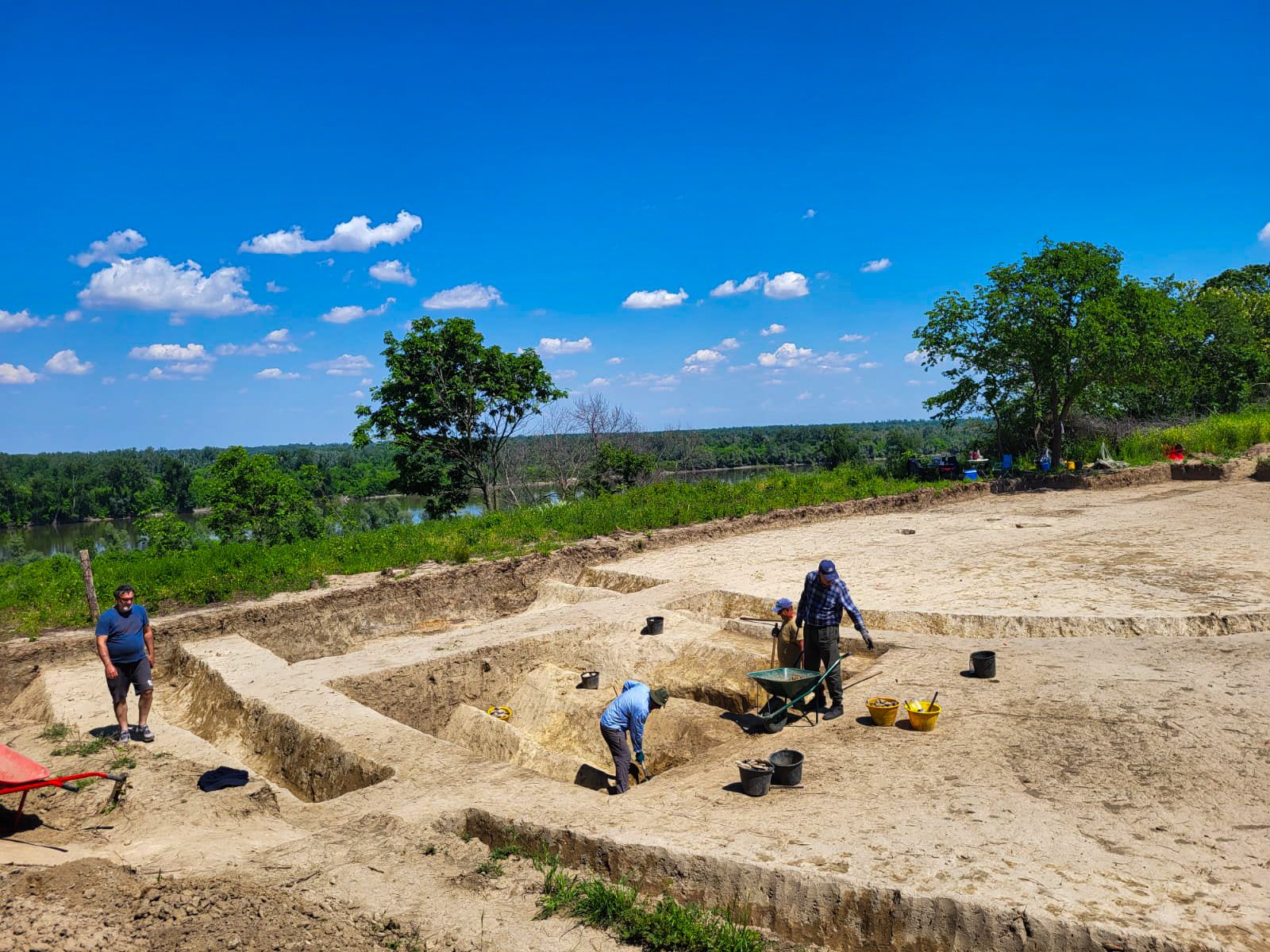
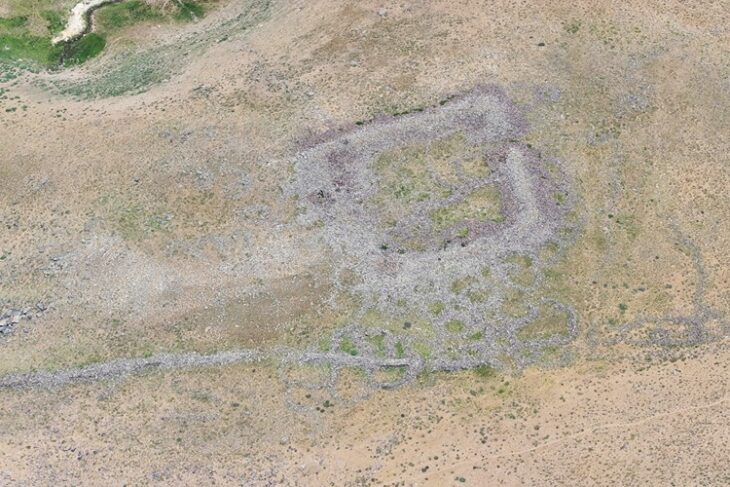
Archaeologists in Croatia have uncovered the remains of a 1,800-year-old Roman watchtower that once stood guard along the empire’s northern frontier.
Nestled in the village of Mohovo on the banks of the Danube River, this remarkable structure sheds new light on the Roman Empire’s vast border defense system — the Danubian Limes — and its military response to external threats during the reign of Emperor Marcus Aurelius.
A Strategic Guardian of the Danube
The watchtower, likely built in the late second century A.D., played a crucial role in protecting the Roman Empire during the Marcomannic Wars (A.D. 166–180). This turbulent period saw the Roman army clashing with Germanic tribes such as the Marcomanni, and nomadic Sarmatians from regions now within modern-day Russia and Eastern Europe. The conflict led to the construction of numerous military installations along the Danube, including this newly excavated tower, which formed part of a network safeguarding vital river crossings and trade routes.
According to Dr. Marko Dizdar, director of the Institute of Archaeology in Zagreb and lead researcher on the project, “The watchtower was built in a strategic location, at one of the crossings over the Danube River. From this position, there was excellent visual control of a large area, and it was naturally protected on three sides by deep ravines.”
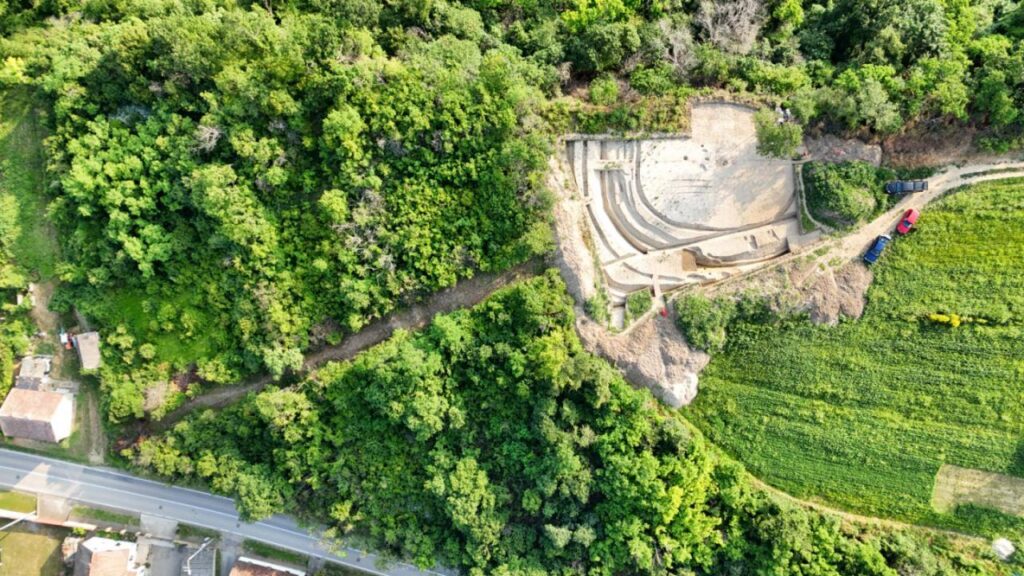

Layers of History Beneath the Surface
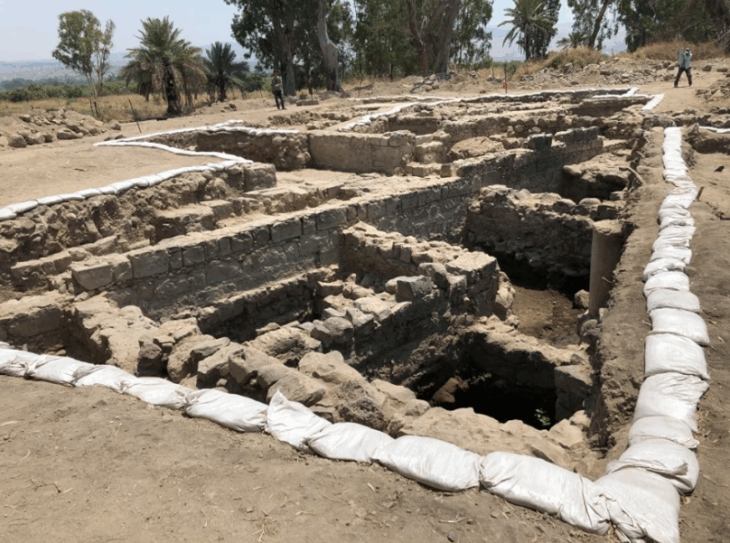
Excavation of the Mohovo site began in earnest in April 2025 following years of geomagnetic surveys conducted between 2003 and 2023. These noninvasive techniques had suggested the presence of multiple Roman military structures across at least ten locations in eastern Croatia. However, the Mohovo tower marks the first systematically researched Roman watchtower on the Croatian Limes, confirming long-held assumptions about the region’s defensive role.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Measuring approximately 130 by 100 feet (40 by 30 meters), the tower was fortified by deep defensive ditches and surrounded by a wooden palisade. At its center stood a wooden building, likely used by the Roman soldiers stationed there. Dizdar notes that the site underwent three construction phases, indicating repeated upgrades or repairs, and that by the 4th century A.D., it may have been replaced by a smaller fortification equipped with a tower.
Artifacts recovered from the site include military equipment, ceramic vessels, and brooches, all pointing to active Roman presence well into the 3rd century A.D. The discovery not only confirms the area’s military function but also demonstrates the architectural evolution of Roman frontier defense.
A Beacon in the Defensive Network
The Mohovo watchtower likely operated as part of a visual communication network, positioned to relay messages quickly to nearby outposts in Sotin and Ilok, about 12 kilometers away. With other towers located roughly 2 to 3 kilometers apart, soldiers could send warnings across the frontier in the event of an enemy advance.
“This system allowed the Romans to mobilize forces rapidly in response to threats,” said Dizdar. “Crossing the ditches around the tower would have been highly demanding for attackers, buying precious time for defenders to react.”
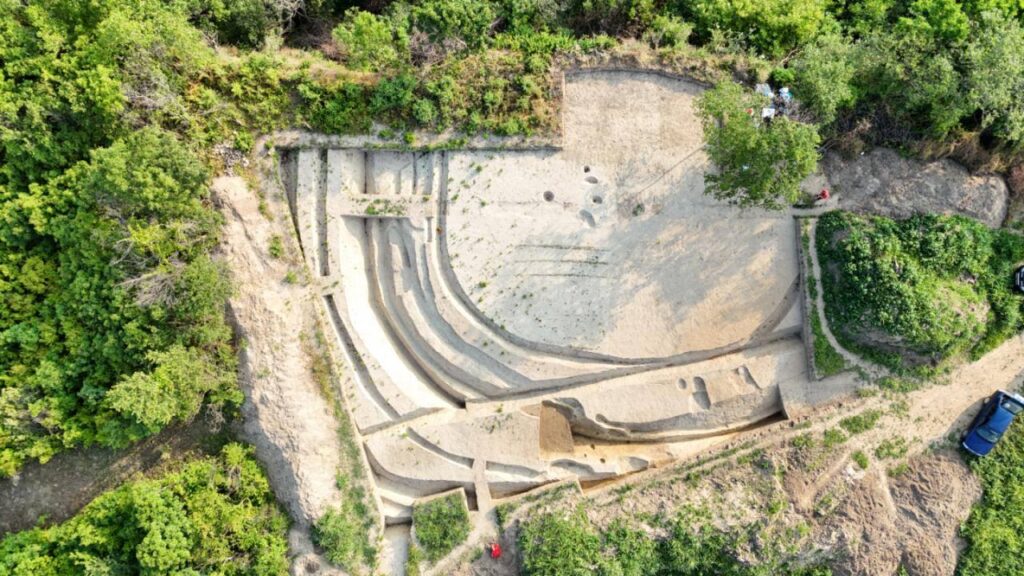

Preserving a Multilayered Heritage
Interestingly, the site at Mohovo holds even deeper historical significance. In addition to Roman remains, archaeologists have uncovered traces of Copper Age, Bronze Age, Iron Age, and medieval settlements — a testament to the area’s long-standing importance as a crossroads of civilizations.
The Croatian team’s work is part of a broader initiative to protect and promote the Danubian Limes as a potential addition to the UNESCO World Heritage list. The discovery underscores not only the Roman Empire’s vast military reach but also the cultural continuity that shaped the region over millennia.
Unlocking the Empire’s Military Legacy
The excavation of the Roman watchtower in Mohovo offers a rare glimpse into the empire’s complex border security systems and the daily lives of soldiers stationed far from Rome. As research continues, archaeologists hope to better understand how these frontier structures evolved in response to shifting political and military landscapes.
With further digs planned to investigate the transformation of the site in the 4th century, the Mohovo tower stands as a remarkable monument to Roman engineering, strategy, and resilience — and a silent sentinel of an empire once determined to hold the line against the world beyond.
Cover Image Credit: Institute of Archaeology in Zagreb