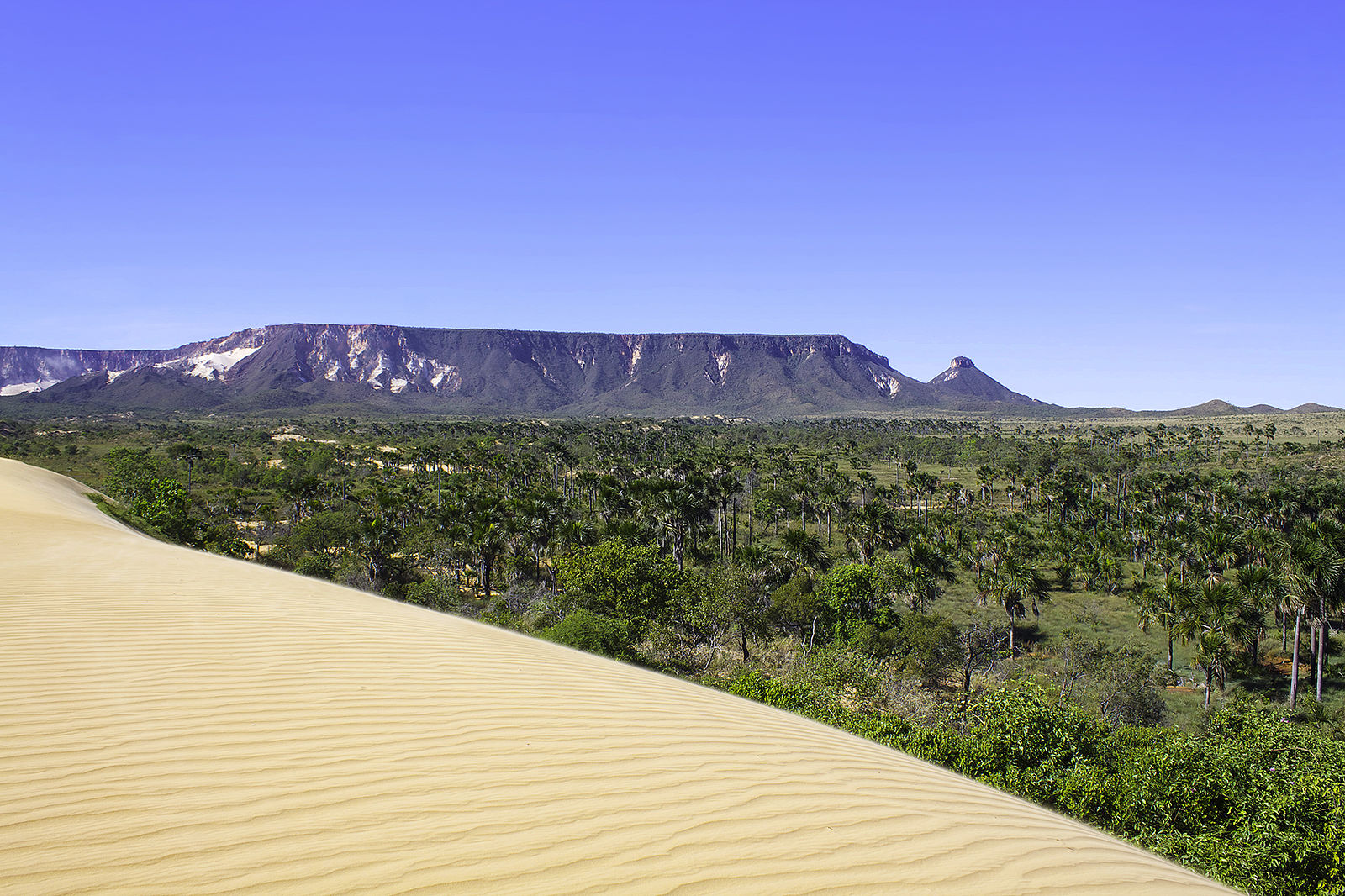
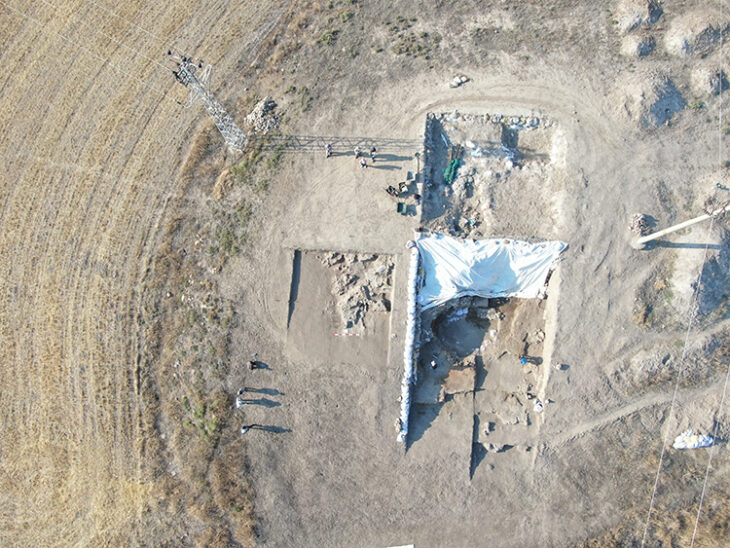
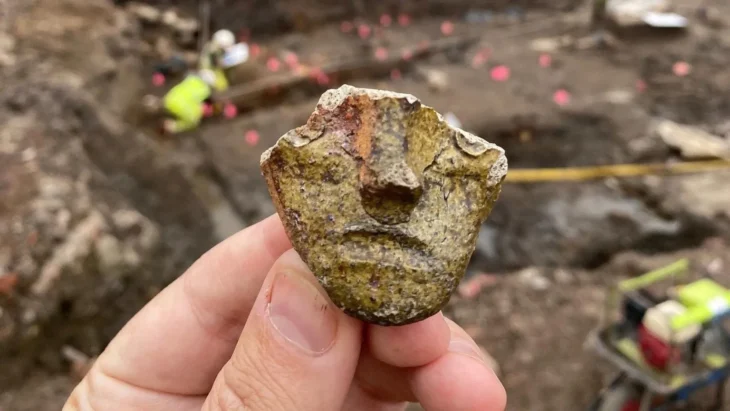
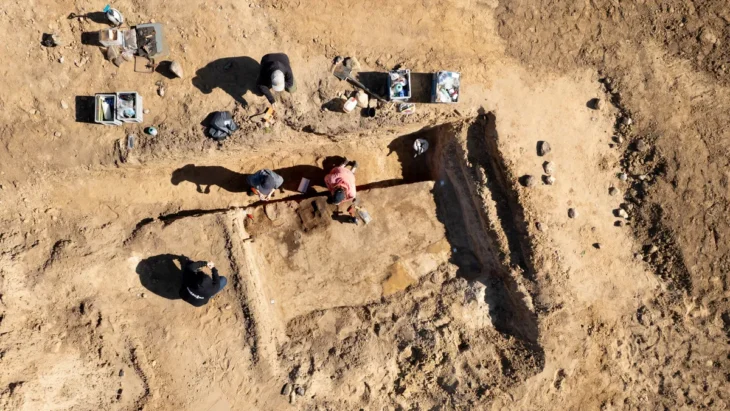
Archaeologists at Brazil’s National Institute of Historical and Artistic Heritage (Iphan) discovered 16 new archaeological sites while surveying a large area in Jalapão, in the eastern part of the state of Tocantins.
According to a press statement by Brazil’s Ministry of Culture, the sites feature rock art—including human and animal footprints, engraved symbols, and figures representing celestial bodies—thought to have been made around 2,000 years ago.
Rômulo Macedo, an archaeologist, has been leading a team that has been looking for undiscovered sites in the region since 2022. These 16 sites represent only the most current research.
However, Macedo said in a statement that human activity like vandalism and deforestation, along with natural disasters like wind erosion and forest fires, pose a threat to the recently found sites. As part of its efforts to preserve the sites, Iphan is undertaking conservation and educational projects in the region to protect the sites.
The discovery has been added to an archaeological complex of sites within the Jalapão region, where human occupation has been documented as far back as 12,000 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
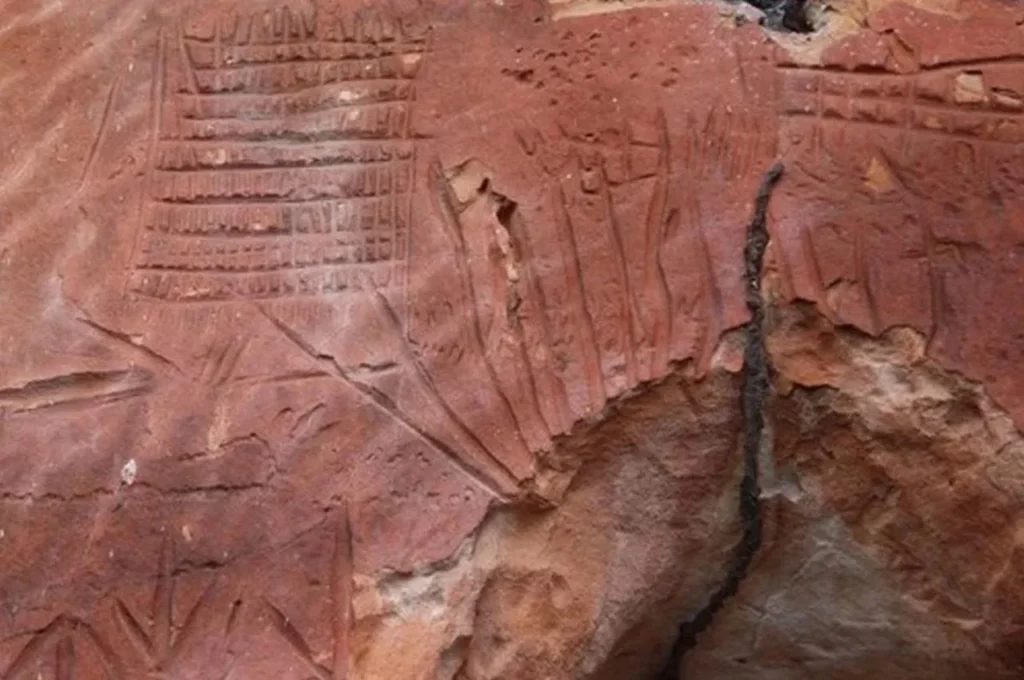

There are many sites in the state that Iphan registered, and many of them are now a part of a larger archaeological complex in Jalapão. These areas include pre-colonial archaeological sites that were established before the arrival of European colonists, as well as evidence of human settlements dating back 12,000 years.
Furthermore, the presence of archaeology-related structures emphasizes the region’s importance as a meeting point between the Amazon Forest and the Cerrado biome of Central Brazil.
As infrastructure development in the Amazon states accelerates, Tocantins has seen a significant increase in archaeological research as part of environmental licensing. This has made it possible to collect data from archaeological sites that were not previously explored.
In this case, archaeological work is done by companies dedicated to preserving heritage in areas impacted by economic activities. Two key actions are prioritized: organizing and sharing information about discovered assets, and incorporating archaeological considerations into environmental licensing procedures.
Cover Photo: Gabriel Castaldini