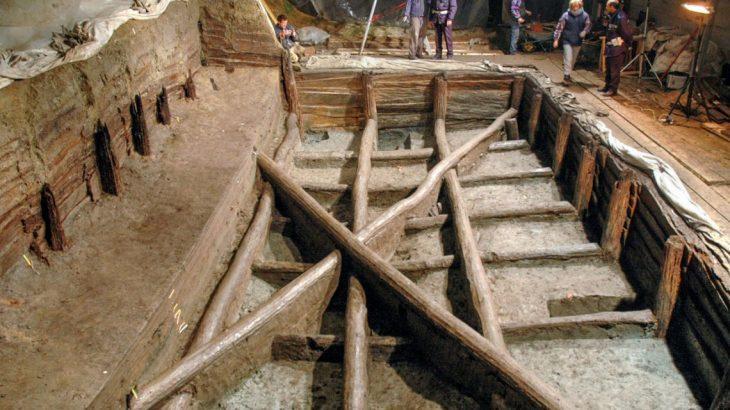
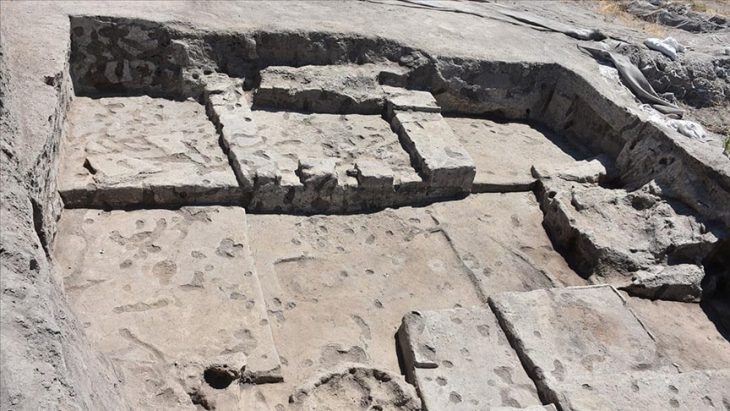
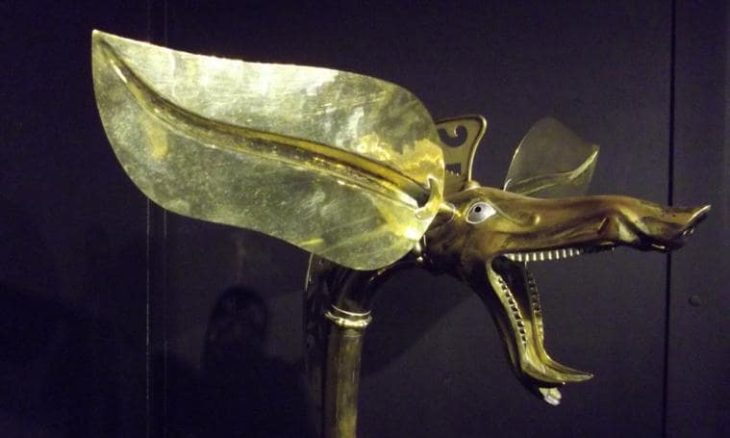
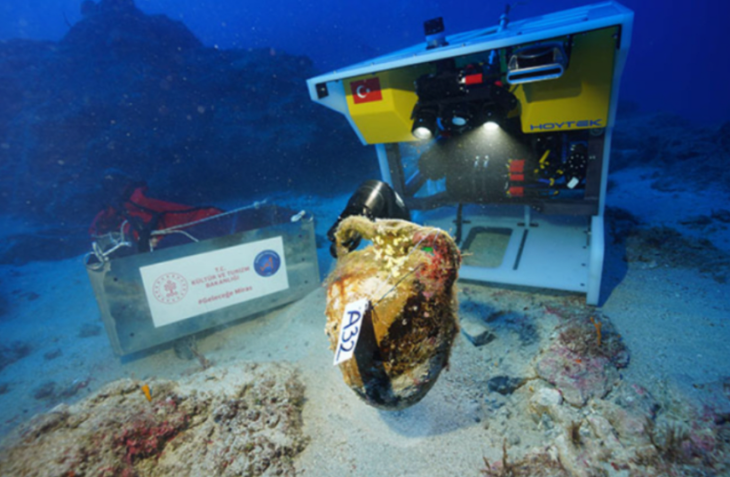
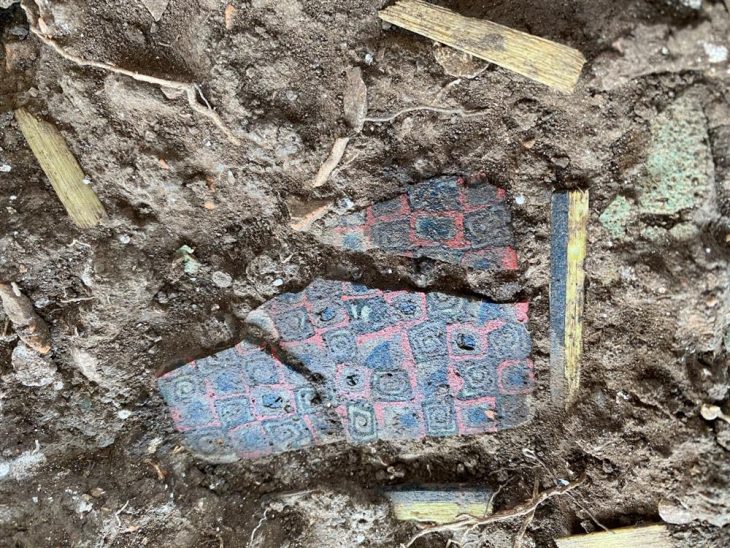
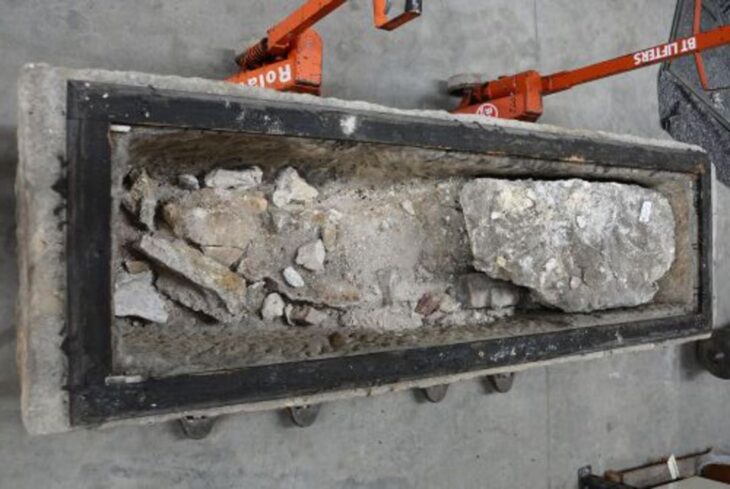
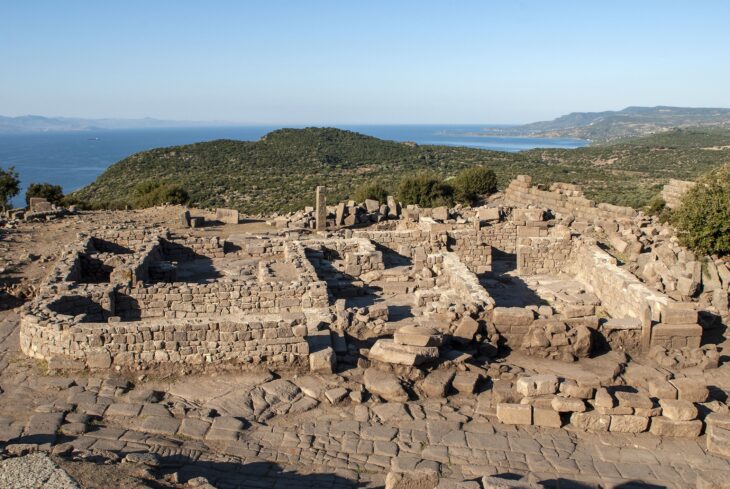
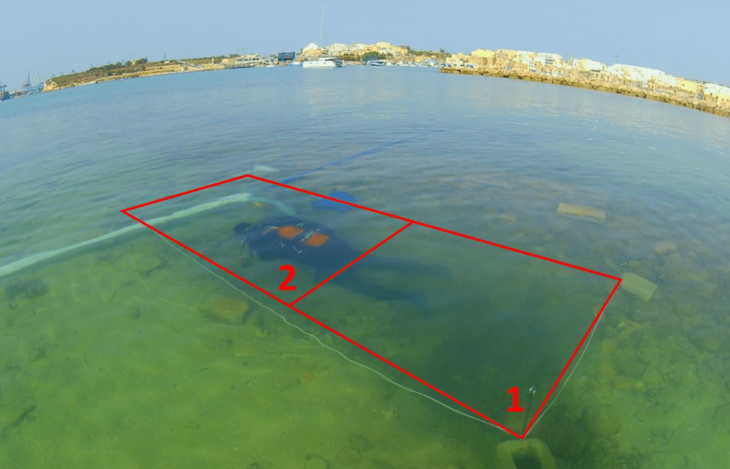
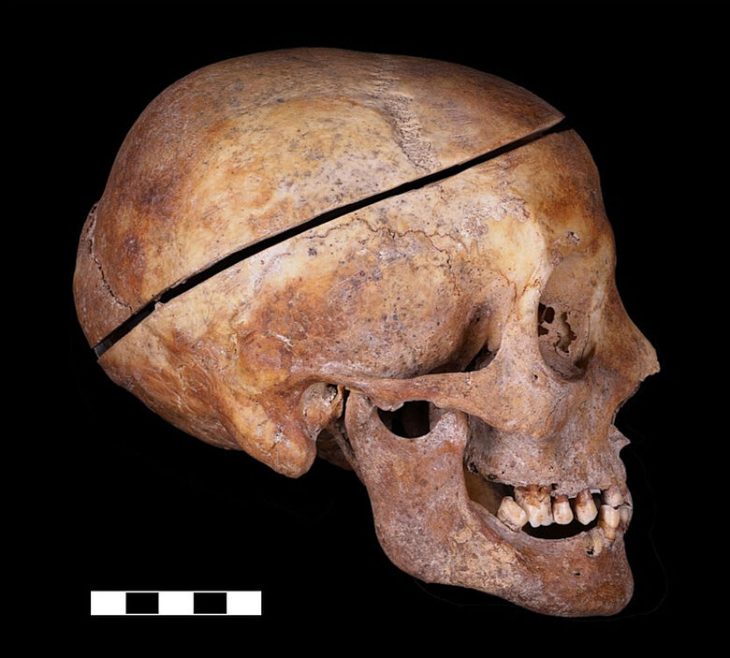
The excavations in Cavuştepe castle continue with the excavations in the necropolis this year. Two new tombs from the Urartian period were unearthed in the necropolis. The tombs reveal a different burial type used by the Urartians.
The palace was built during the reign of King Sarduri II in 764-735 BC, the lower section was built around the 7th century and included a temple, kings tower, workshops, storehouses, cisterns, and even a harem.
Under the chair of professor Rafet Çavuşoğlu of the Van Yüzüncü Yıl University’s (YYÜ) Faculty of Letters Archaeology Department, archaeological investigations at Çavuştepe Castle and the necropolis around the castle continue.
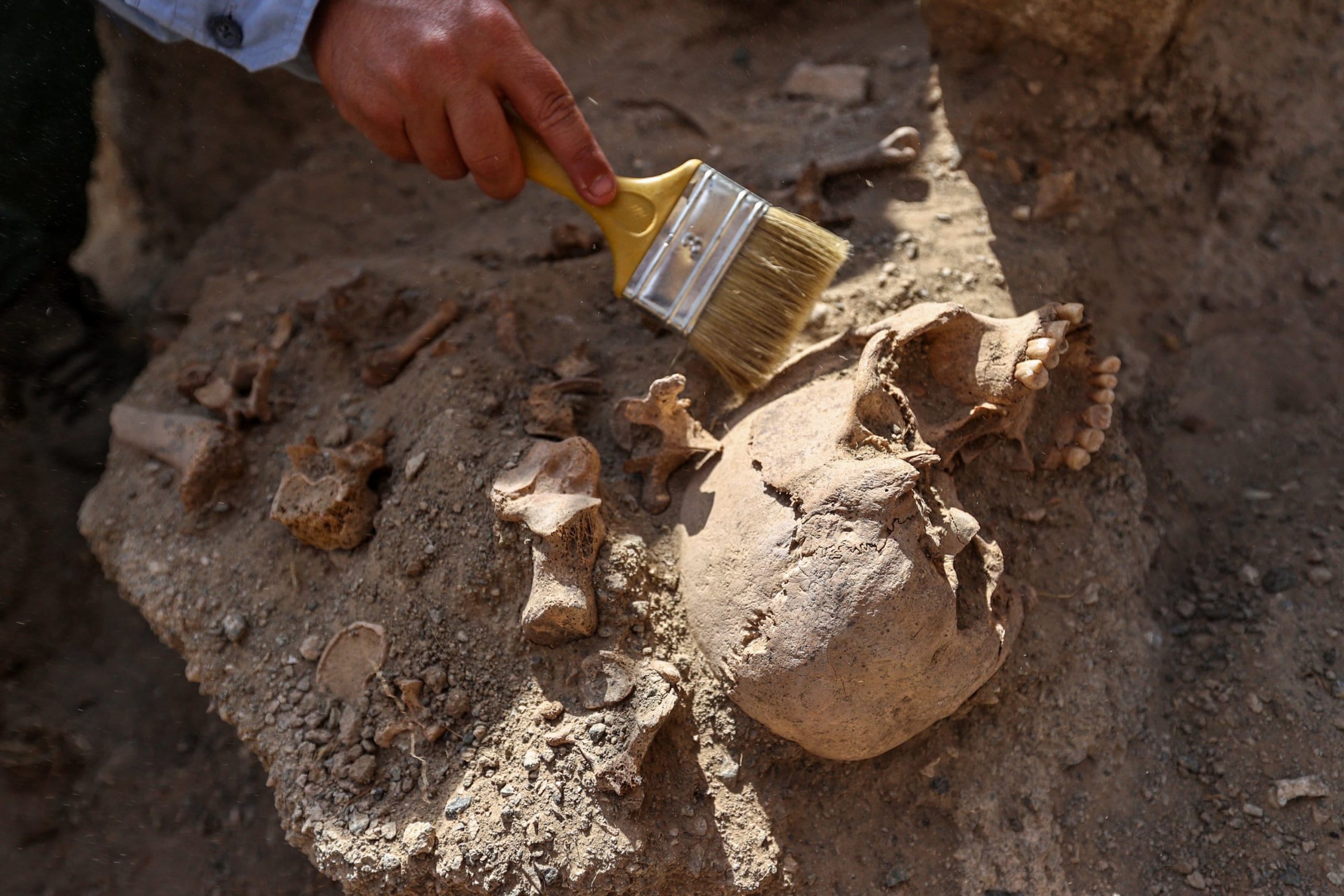
The two newly unearthed graves in these areas provide information about the burial traditions and lifestyles of Urartians. While one of them belongs to an adult, the other is a grave of a child.
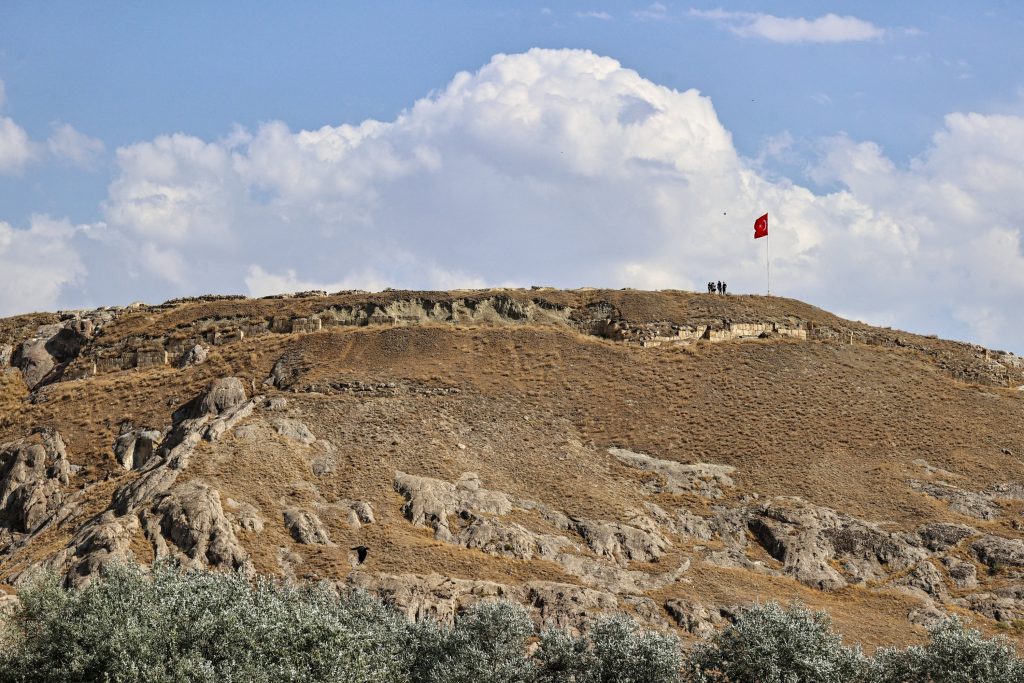

In the tombs examined by archaeologists, it was determined that the valuable grave goods of the deceased were not in place and their bones were in a different area.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Excavation head professor Rafet Çavuşoğlu told Anadolu Agency (AA) that they are mostly working on conservation and protection in the area.
Noting that they have been excavating in the necropolis area of the castle since 2017, the professor stated that they have reached very important archaeological data in terms of Urartian archeology and burial traditions here.
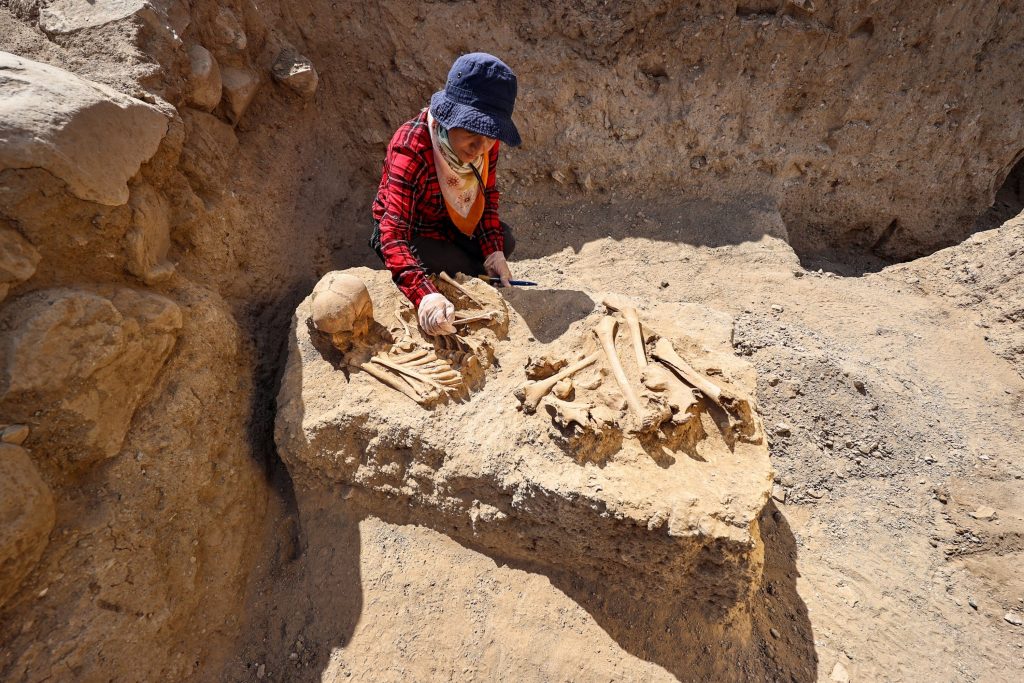

Emphasizing that the latest graves gave them new information about the burial customs of the Urartians, Çavuşoğlu said, “Previously, there were cist graves, chamber tombs, normal graves that are buried in the ground, and urn tombs in the necropolis area. We have encountered a new type of tomb now. In this type, the dead bodies are buried near a platform.”
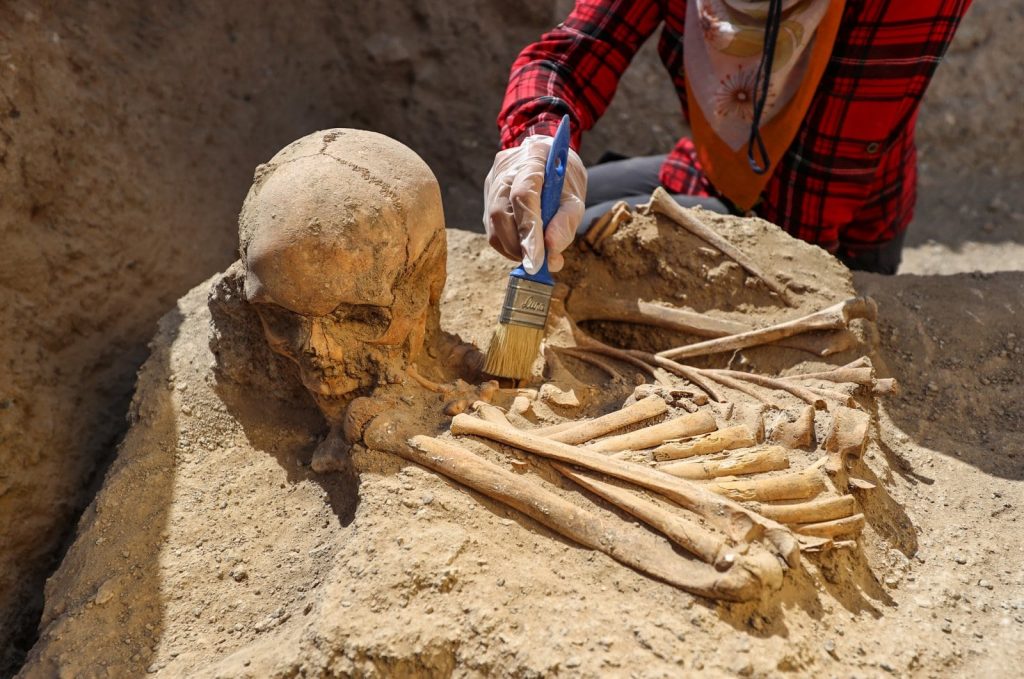

“We usually found the belongings of individuals in the graves in this site. However, the latest adult grave did not have anything with it and his/her corpse was found in a mixed state. For example, we found the head of the corpse next to the feet. This indicates that it was destroyed. We think that the tomb was opened by someone to take the jewelry.”
Çavuşoğlu said that the next work on the site will provide much clear information.