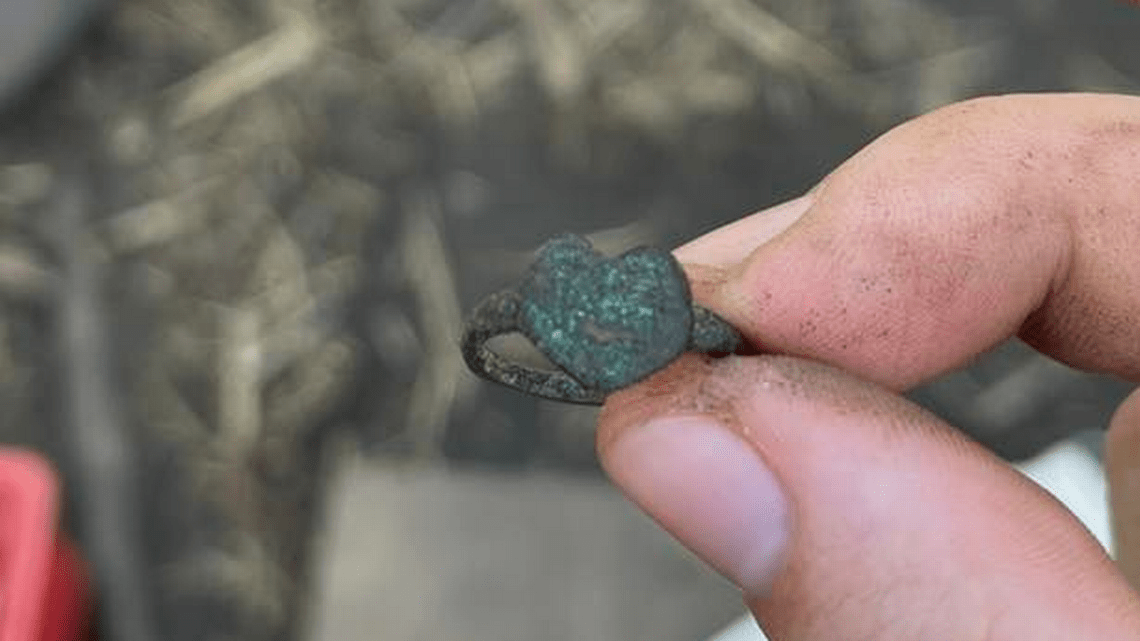
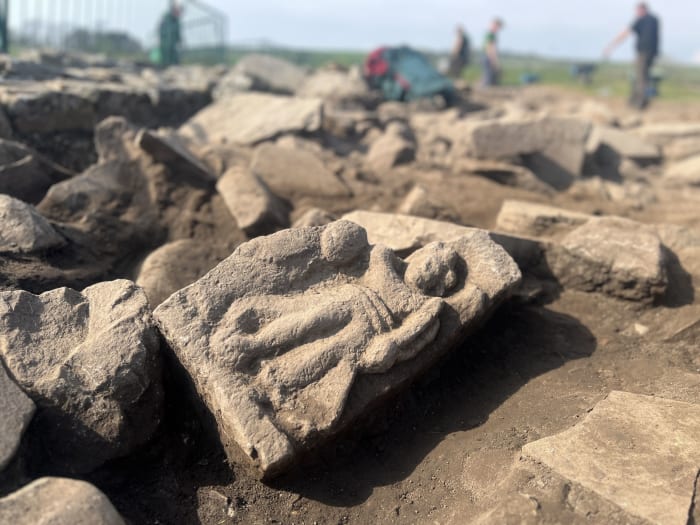
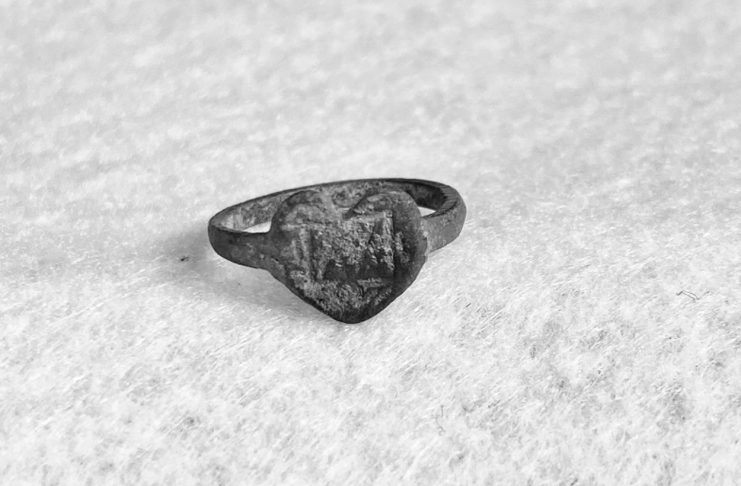
An archeology student from the Fort St. Joseph Archeology project at Western Michigan University has uncovered a unique heart-shaped Jesuit ring while excavating at Fort St. Joseph in the present-day town of Niles, Michigan, United States.
The ring has been dated to the 1700s and is thought to have been a trade trinket used when southwest Michigan was known as New France, according to experts.
Fort St. Joseph was built on land granted to the Jesuits by King Louis XIV in the 1680s, where Jean Claude Allouez built the Mission de Saint Joseph. The fort was built by the French in 1691 as a trading post to support the fur trade at Lake Michigan’s southern end.
Following the British victory over the French in the French and Indian War (the North American front of Europe’s Seven Years’ War), British forces took control of the fort and used it to supply their allies during the American Revolutionary War.
Until the United States’ victory in the Northwest Indian War and the signing of Jay’s Treaty in 1795, the British kept the fort under guard. After that, they abandoned it, allowing it to decay and become completely overrun by the forest.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Fort St. Joseph was rediscovered in 1998 after an archaeological survey led to excavations by archaeologists from Western Michigan University. Since then, excavations have continued at the site.
“Fort St. Joseph was occupied from the 1680s to the 1780s so the ring could have been lost at any point during that time frame,” according to Erika Hartley, field director and curatorial fellow at the Fort St. Joseph Archaeological Project.
“It was most likely manufactured prior to its arrival at the fort, but at this point it is hard to narrow down a specific date.”
In the official blog for the project, Kylie Krueger stated: “In New France, these iconographic “Jesuit” rings were used for trade and were likely an inexpensive form of jewelry. They were decorated with a variety of motifs that had religious and/or sentimental meanings.”
“Overall, “Jesuit” rings have been recovered from seventeenth- and eighteenth-century sites like Fort St. Joseph throughout New France. They appear to have been used during both the French and British occupation, with a higher concentration during the French period”, added Krueger.
The ring will be added to a collection fort artifacts at the Niles History Center, which houses the Fort St. Joseph Museum, Erika Hartley said.
Cover Photo: This “Jesuit ring” was found at the site of Fort St. Joseph, a former French stronghold dating to the 1680s in southwest Michigan. Western Michigan University photo.