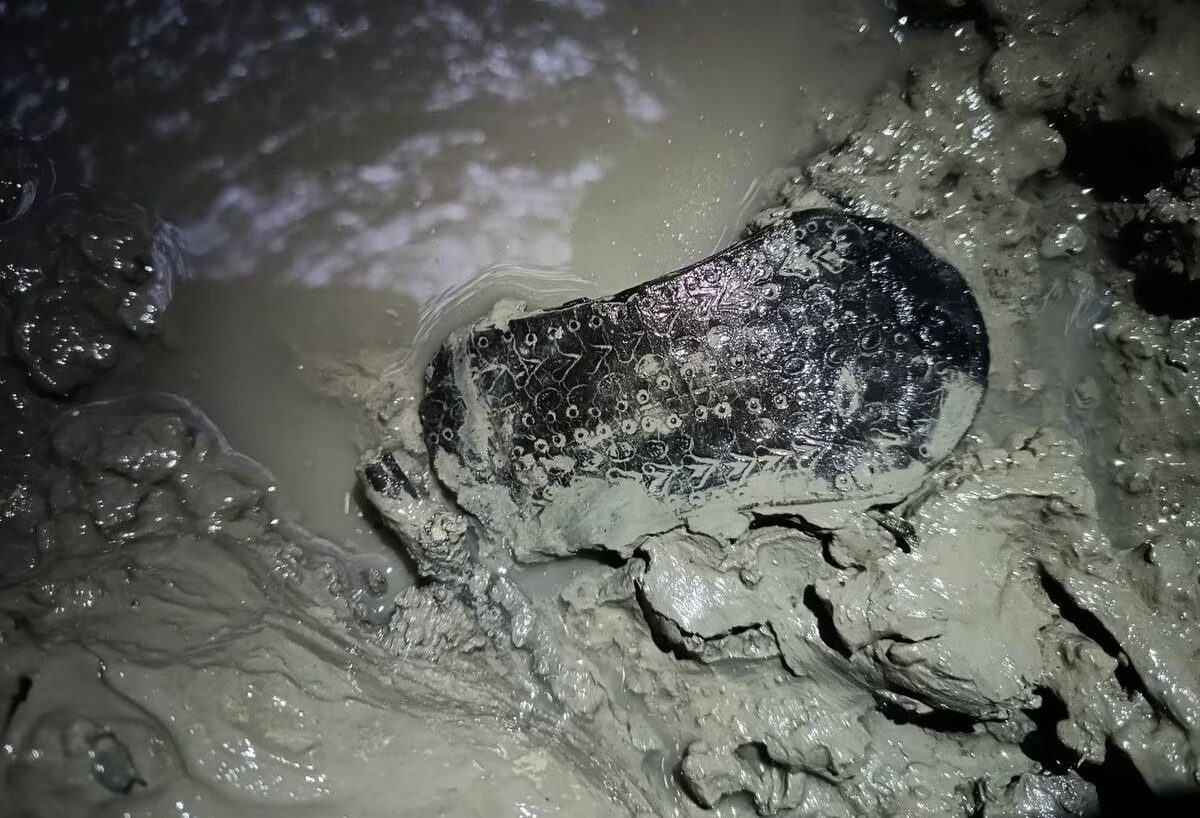
A 2,000-year-old Roman sandal was discovered during archaeological excavations at Lucus Asturum (modern-day Lugo de Llanera) in Asturias, northern Spain.
Between the first and fourth centuries A.D., the Roman city of Lucus Asturum served as a hub for communications and an administrative center in the north of the Iberian Peninsula.
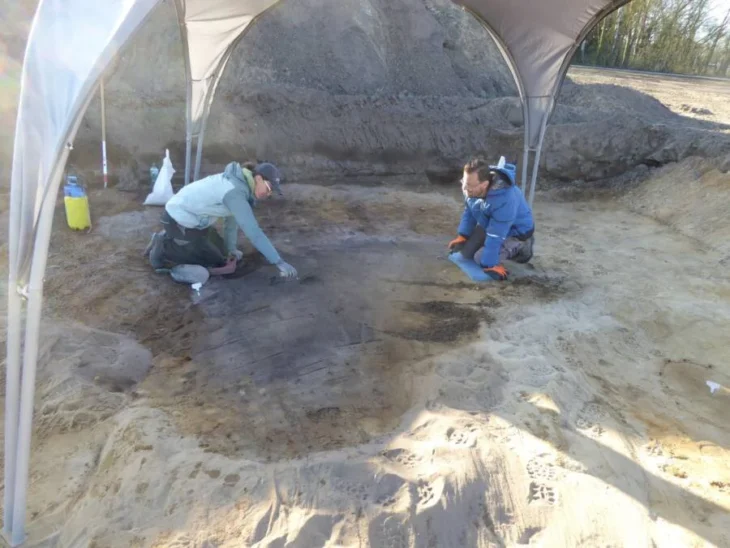
A team led by archaeologist Esperanza Martin discovered a large house with a central courtyard and a well in 2021. This summer, excavations at the site were resumed, and archaeologists decided to descend to the bottom of the well using a pulley system to avoid damaging the remains.
Inside, among many other Roman pieces, they found a sandal lost by a man who tried to clean the well 2,000 years ago. Despite the humbleness of the object, it is a unicum — an archaeological object without equal — because it is decorated with circles, ovals, and falciform figures. There are no more than 20 Roman sandals preserved in Hispania and this is the only one that is decorated.
The reason why the sandal is well preserved is the silt at the bottom of the well. Since this silt creates an anaerobic system that prevents the proliferation of microorganisms, it is in a good state of preservation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
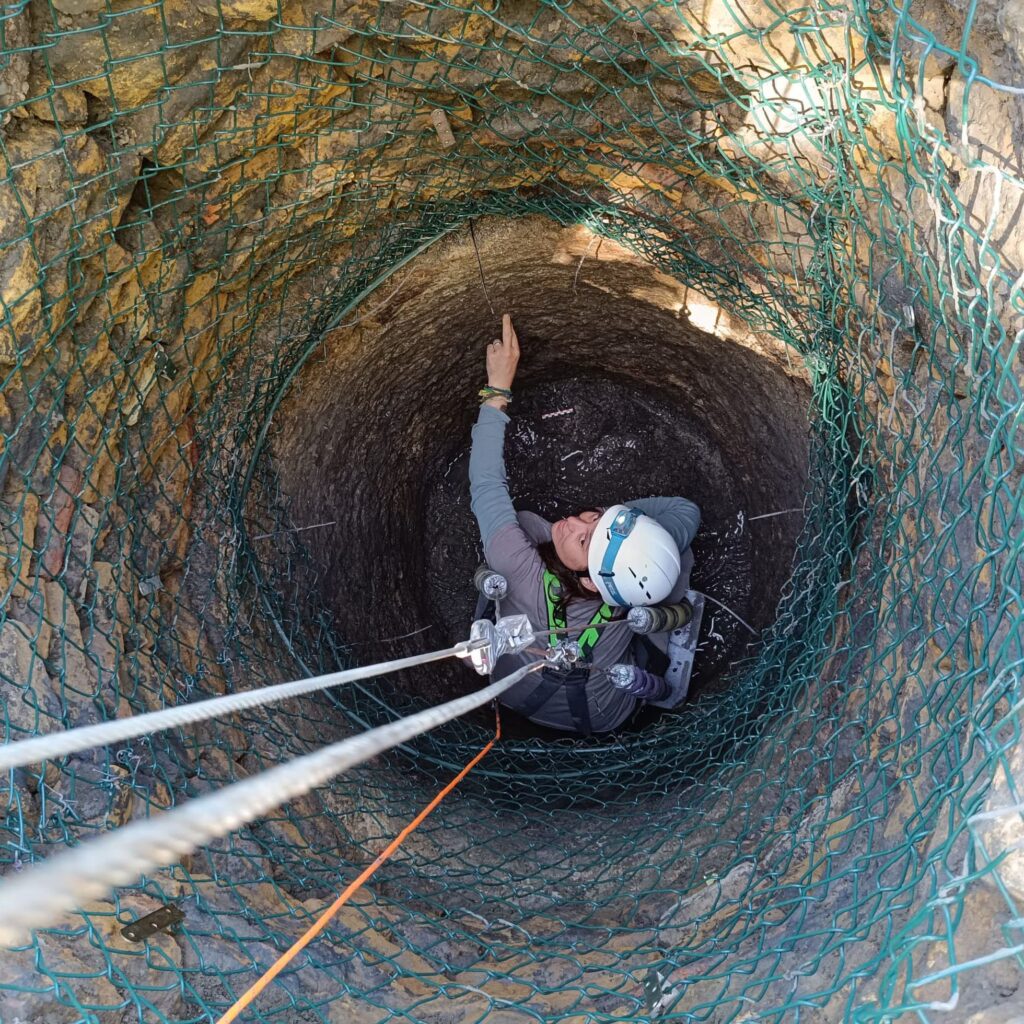

“The remains we found, due to the anoxia generated by the high water table in the area, are in an exceptional state,” says archaeologist Esperanza Martín.
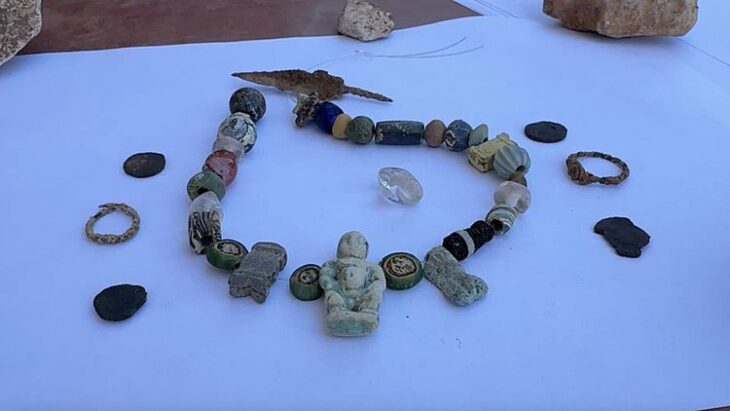
“The silts have created an anaerobic environment thanks to the plasticity of the clays that compose them, so the organic materials have been perfectly preserved.” At a depth of about three meters, the specialists extracted part of the wooden cover of the well, a tiled floor for the decantation of silts, several jars, seeds, chestnuts, pine nuts, mollusks, the remains of domestic and wild fauna, an acetre, or bronze, cauldron, a small metal ring and the sandal, among other objects. “It is almost complete and retains the cutting notches to hold it in the upper leg area. It is more than likely that it was lost by someone who came in to clean [the well] when it got caught in the silt. It is a unique object as it is decorated.”
The footwear is currently refrigerated to prevent degradation until it can be restored and displayed in the Asturian Archaeological Museum. The sandal will thus tell visitors the story of how, 2,000 years ago, a rather well-dressed individual descended into a well in Lucus Asturum to extract the mud that was contaminating his home’s water supply.
Cover Photo: The Roman sandal discovered in Lugo de Llanera, Asturias. ESPERANZA MARTÍN
















Yes , Keep it Coming ,We want More