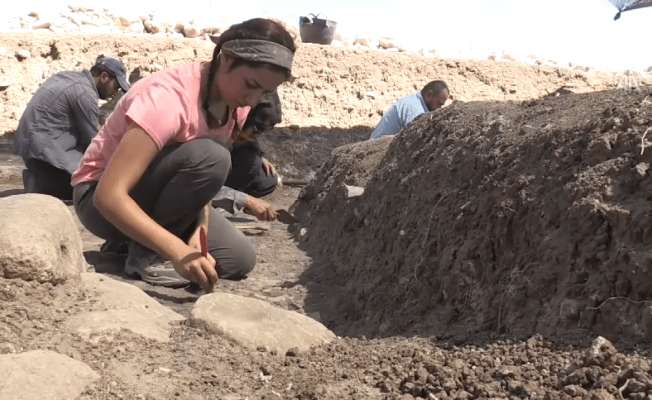
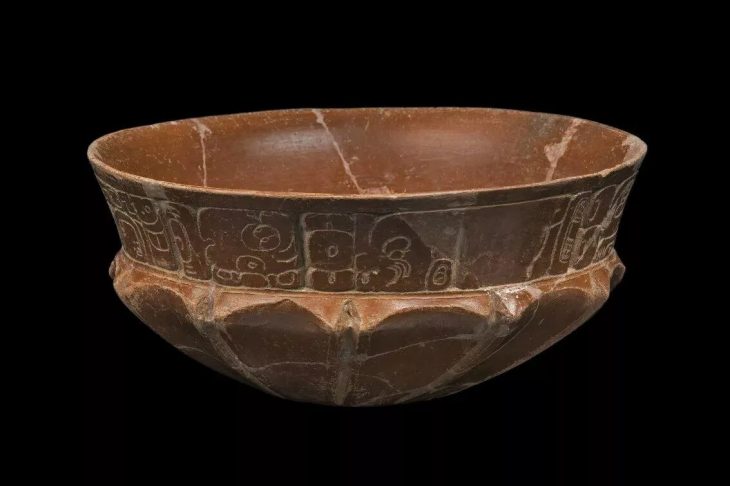
A new study suggests that pre-colonial people in Brazil gathered during the summer months to feast on migratory fish and share alcoholic drinks. An international team of scientists analyzed pottery fragments dating back between 2300 and 1200 years, discovered around the Patos Lagoon in Brazil.
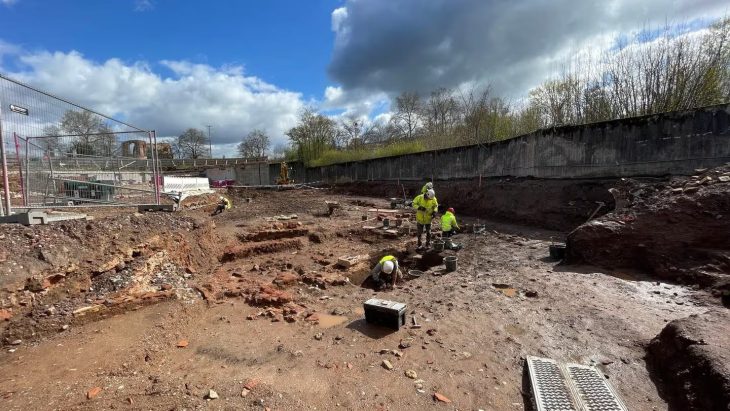
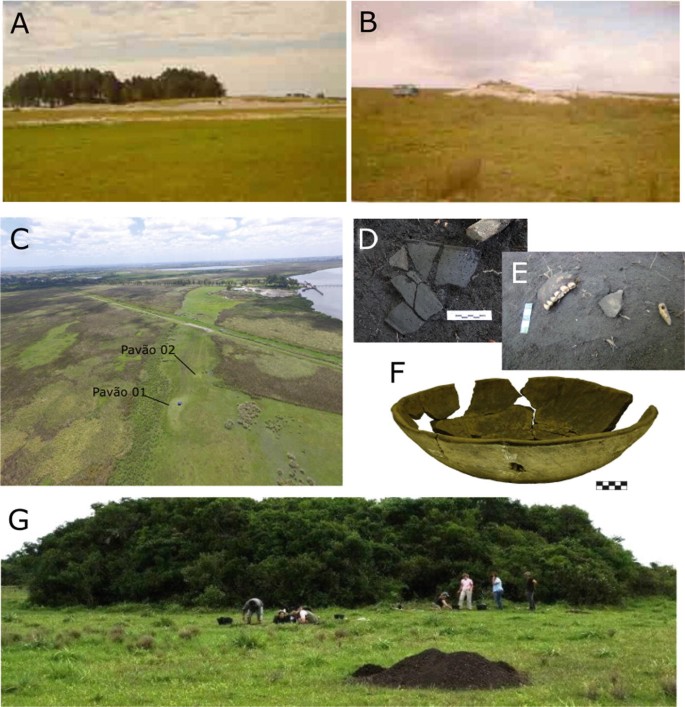
The shores of the lagoon are characterized by settled earthen mounds known as “Cerritos,” built by the pre-colonial ancestors of Pampean Indigenous groups, including the Charrua and Minuano. The researchers identified some of the earliest evidence of alcoholic drink production in the region, with advanced analysis revealing traces of beverages likely made from tubers, sweet corn, and palm. Other pottery fragments contained evidence of fish processing.
This discovery strengthens the belief that pre-colonial people may have gathered around these mounds, which held symbolic significance as burial sites, territorial markers, and monuments, to celebrate and feast on seasonally abundant fish. Previous isotope analysis of ancient human remains from the area indicated that the inhabitants had diverse diets, suggesting that people may have traveled to the lagoon from a wider region.
Dr. Marjolein Admiraal, the lead author of the study, emphasized that seasonal gatherings at the mounds were important cultural events, bringing together dispersed communities to exploit and celebrate the return of migratory fish, such as the Whitemouth croaker, which likely required collective effort to process. “We see examples of such practices around the world, often related to the seasonal abundance of migratory species. These events provide excellent opportunities for social activities, such as funerals and marriages, and hold great cultural significance,” she stated.
Professor Oliver Craig from BioArCh at the University of York added, “Through detailed chemical analysis, we were able to determine what products were present in the Cerritos pottery vessels and how people prepared these products, through heating, storage, and potentially fermentation. This brings us one step closer to understanding the culinary role of different foodstuffs in past societies.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery sheds new light on the lifeways of these pre-colonial groups, highlighting the multifaceted purposes of the Cerritos and their role in the social and economic life of the mound builders. Co-author Rafael Milheira from the Universidade Federal de Pelotas in Brazil noted, “The Cerritos are a combination of ritual and domestic places, and their elevated design may have been influenced by the local environment; these places were likely important to the people and raising them above potential erosion by seasonal high waters would have protected them.”
André Colonese from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, a co-author of the research, emphasized, “This study reinforces the power of molecular archaeology in unlocking information from common artifacts, such as pottery sherds, that was previously inaccessible through conventional archaeological methods. Moreover, a key message from the paper is that preserving the Cerritos as unique Pampean cultural heritage is of high priority if we want to learn from past societies how to sustainably live in such a dynamic environment.”
As research continues, these insights into the Cerritos and their cultural significance offer a glimpse into the early traditions and social practices of the Pampean Indigenous groups, enriching our understanding of prehistoric life in southern Brazil.
Cover Image Credit: Public Domain