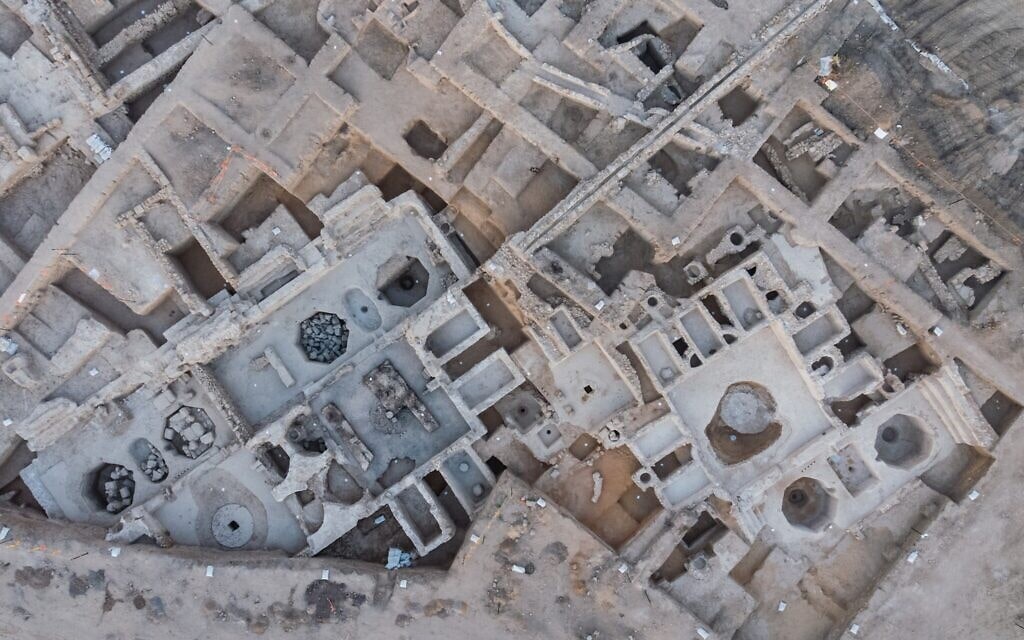
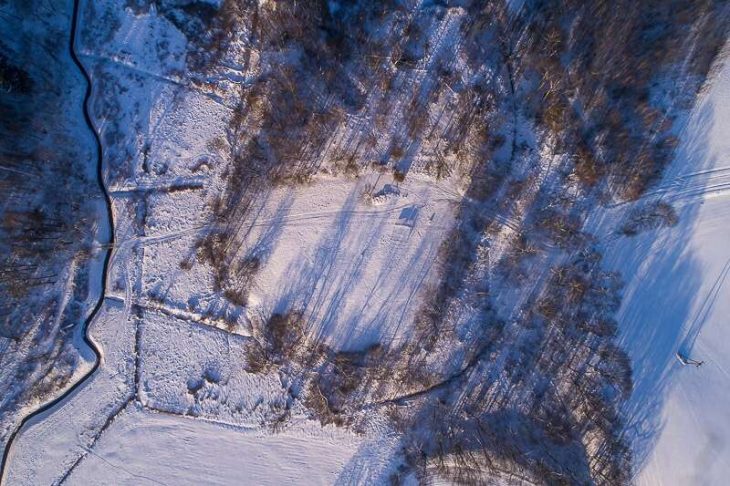
Archaeologists say they’ve discovered the world’s largest known Byzantine-era winery in the city of Yavne, south of Tel Aviv.
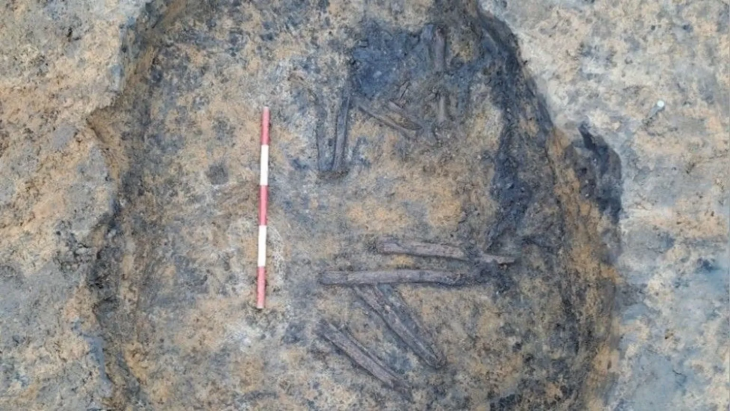
The Israel Antiquities Authority said the factory contains five wine presses, warehouses for maturing and bottling the wine, and kilns for burning the clay amphorae in which the wine was stored.
The site has been dated back to the Byzantine era, around the 4th-5th century CE, and is the largest such complex known to exist from the period.
The winery, dating back 1,500 years, is believed to have produced one of the finest white wines of the Mediterranean at the time. It was widely praised in Byzantine-era literature and known as Vinum Gazetum or Gaza wine because it was exported from the ancient port city near modern-day Gaza.
They estimate the winery produced between two to three million liters of wine a year.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
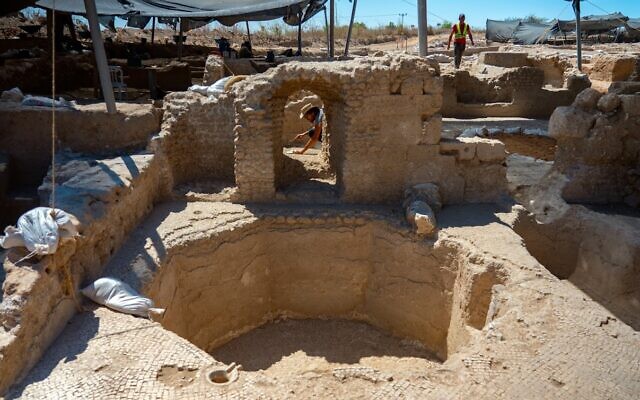

According to the excavation’s directors, the magnitude of the site and its ability to produce such a huge amount of wine using manual production methods was unexpected.
“The proportions here are incredible,” said Elie Haddad, an Israel Antiquities Authority archaeologist who co-directed the two-year dig.
“A calculation of the production capacity of these winepresses shows that approximately two million liters of wine were marketed every year, while we should remember that the whole process was conducted manually”
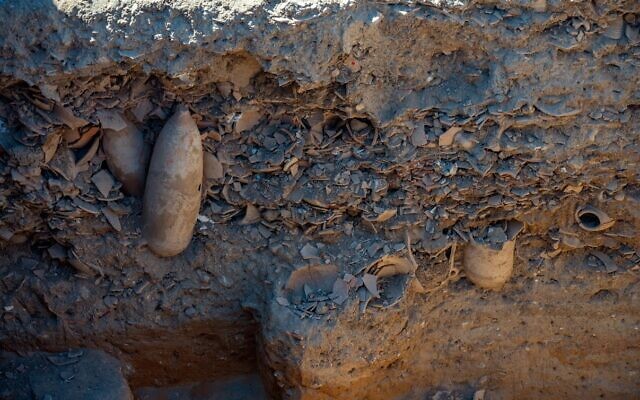

Each winepress found covers an area of about 2,400 square feet. Around the treading floor, where grapes were crushed by foot, were compartments for fermenting the wine and large octagonal vats that collected the wine.
The IAA said that “Gaza and Ashkelon Wine” was considered a quality wine brand of the ancient world, with a reputation that went beyond the immediate vicinity of the winepresses. The archaeologists said the wine was marketed through the ports of Ashkelon and Gaza — hence its name — and then transported throughout the Mediterranean Basin.
The dig also unearthed even more ancient wine presses about 2,300 years old, pointing to a longstanding tradition of winemaking in the area.
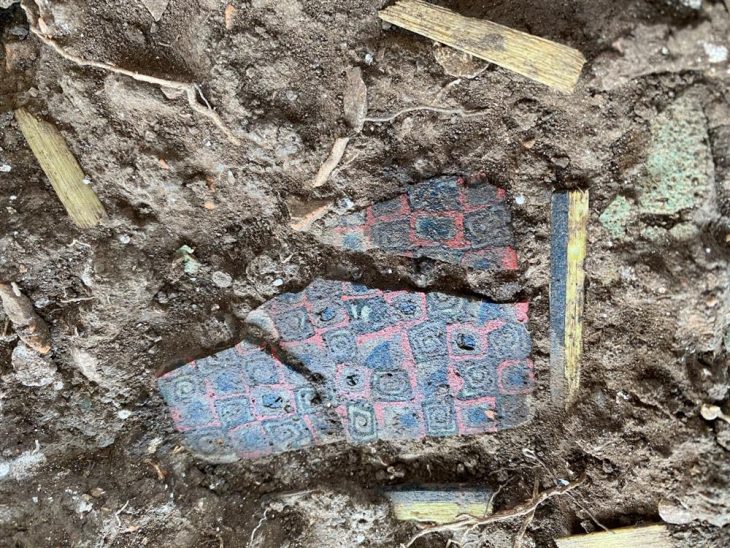
The winery’s owner is unknown, but archaeologists believe the huge, elaborate conch-shell embellishments indicate the owners were rich.
Cover Photo: Aerial view of the Byzantine winepress uncovered in Yavne (Asaf Peretz/IAA)