The hegemony of wealth to the poor, arising from the ruler, elite structure, property ownership, unjust acquisition, and distribution of resources, which began to be seen with the transition to settled life, became more evident in the Ancient Age.
The structure, which constitutes the political and economic structure of the Roman Empire, separated people with a sharp line within the society. The citizen Roman was always advantageous over the individual belonging to the other lower class. This sharpness was not only seen in the lower part but even in itself. Even the diet of the wealthy Roman is a phenomenon that shows this sharpness.
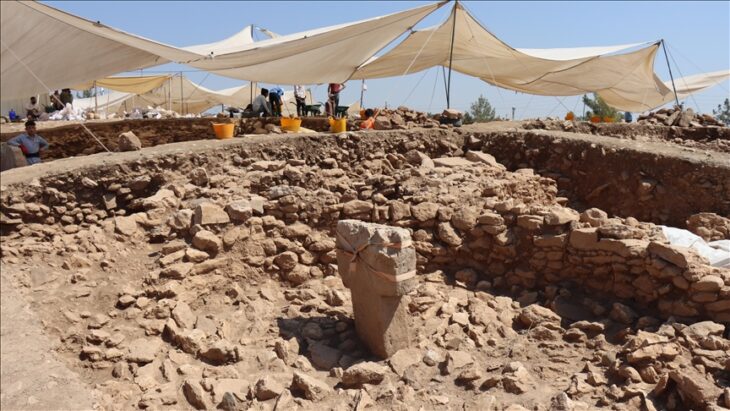
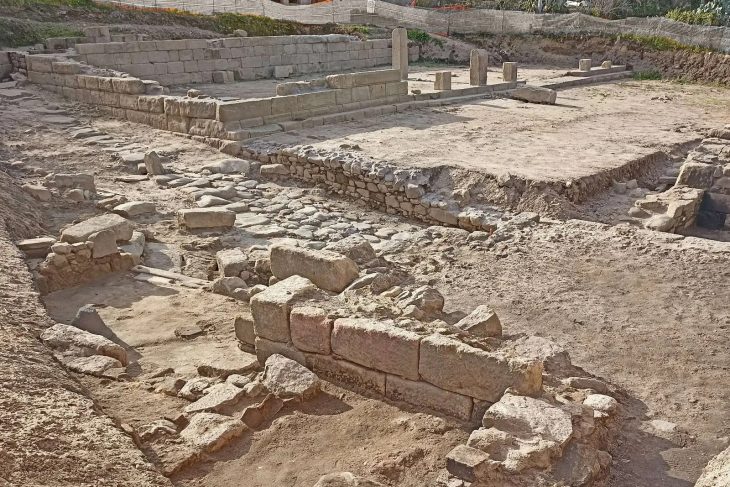
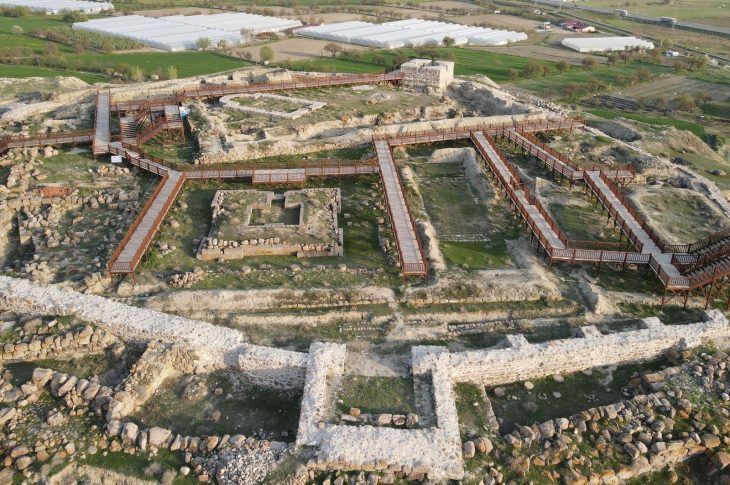
Nutrition of the people of the Ancient City of Pergamon helps distinguish the rich from the poor
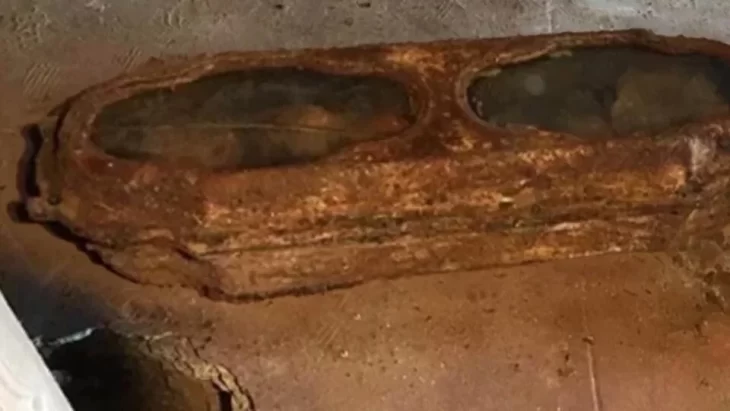
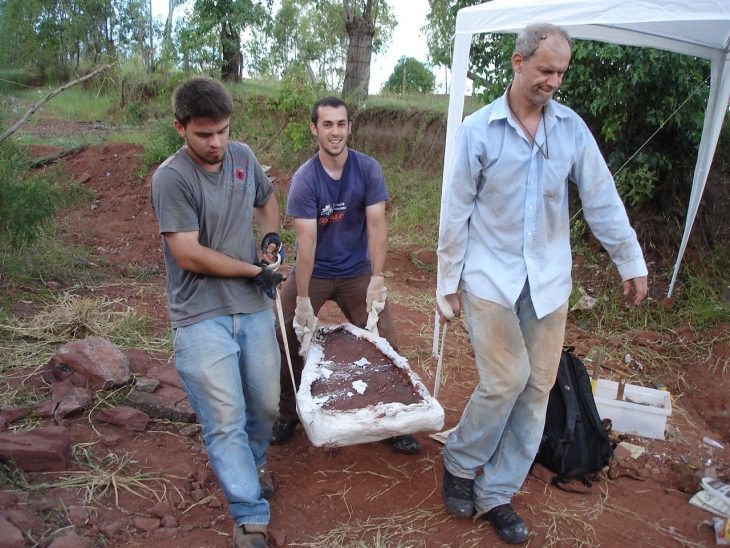
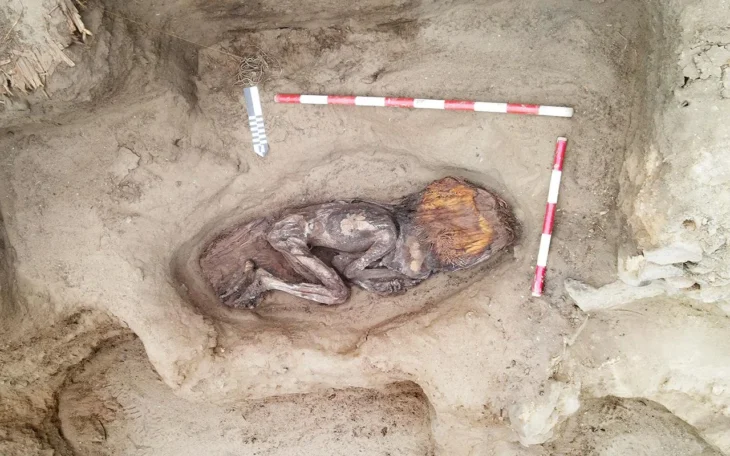
Research on the skeletons unearthed in the ongoing excavations in the Ancient City of Bergama, which is on the UNESCO World Heritage List, helps to understand the health conditions, diseases, and eating habits of the city people.
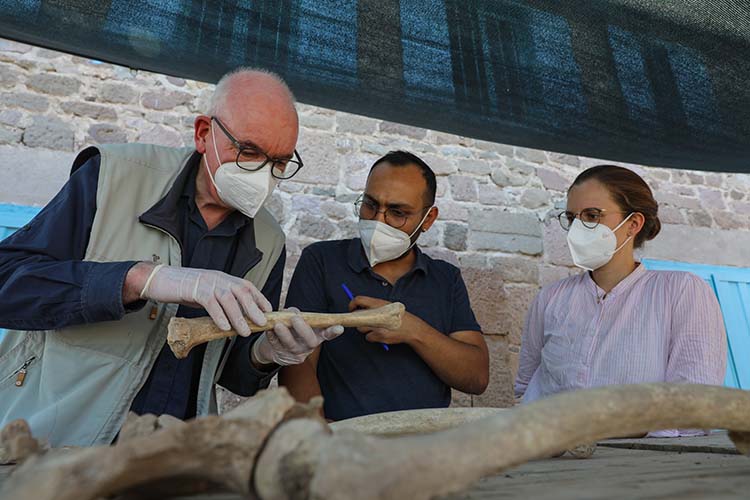

Working on the skeletons unearthed from 2 necropolises in the ancient city, also known as Pergamon, Ludwig Maximilians University of Munich, Prehistoric Protohistoric and Roman Archeology Specialist Prof. Dr. Wolf Rüdiger Teegen’s international articles also give clues about the dietary habits and diseases of the ancients.
Professor Wolf Rüdiger Teegen told Anadolu Agency (AA) that he has been working on fossil and bone remains andIn this context, he said that he has been in Bergama for about 11 years.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Explaining that they conducted research on 300 skeletons and bone remains in the region, Teegen said that their work also covered the Roman and Byzantine periods.
Teegen stated that they primarily focused on “gender” and “age” in their reviews: “In some skeletons, it is impossible to determine gender. Age determination is much more possible. We see a typical age distribution. This is also true for Roman and Hellenistic times.
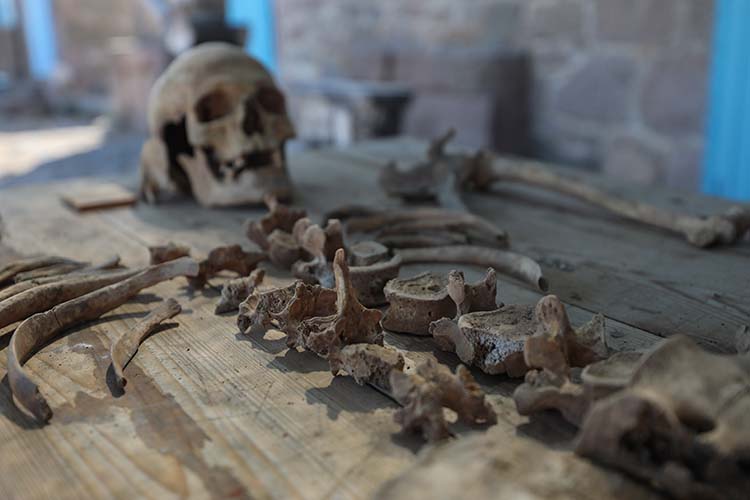

We found that people predominantly died between the ages of 20 and 40. The death rate at older ages is lower. Particularly the median age at death among women is lower due to factors such as pregnancy and childbirth,” he said.
He underlined that they rarely come across causes of death other than blunt trauma, as diseases with symptoms such as fever or diarrhea do not leave any traces on the skeleton.
The most frequent health problems include abscess and tooth loss, he said, adding: “These diseases also played an important role in childhood and youth.”
Prof. Dr. Wolf Rüdiger Teegen stated that they also benefited from the teeth in terms of the eating habits of the period, “we see that a carbohydrate-rich diet was common, such as bread and porridge.”
“A certain group could eat meat regularly. The number of people who ate a lot of meat was low because meat-eating was dependent on social status,” he explained.
“From the researches, we know that beef is cheaper than pork. The pork was very popular during the Roman Empire. The most expensive meat was rabbit meat at that time,” he said.