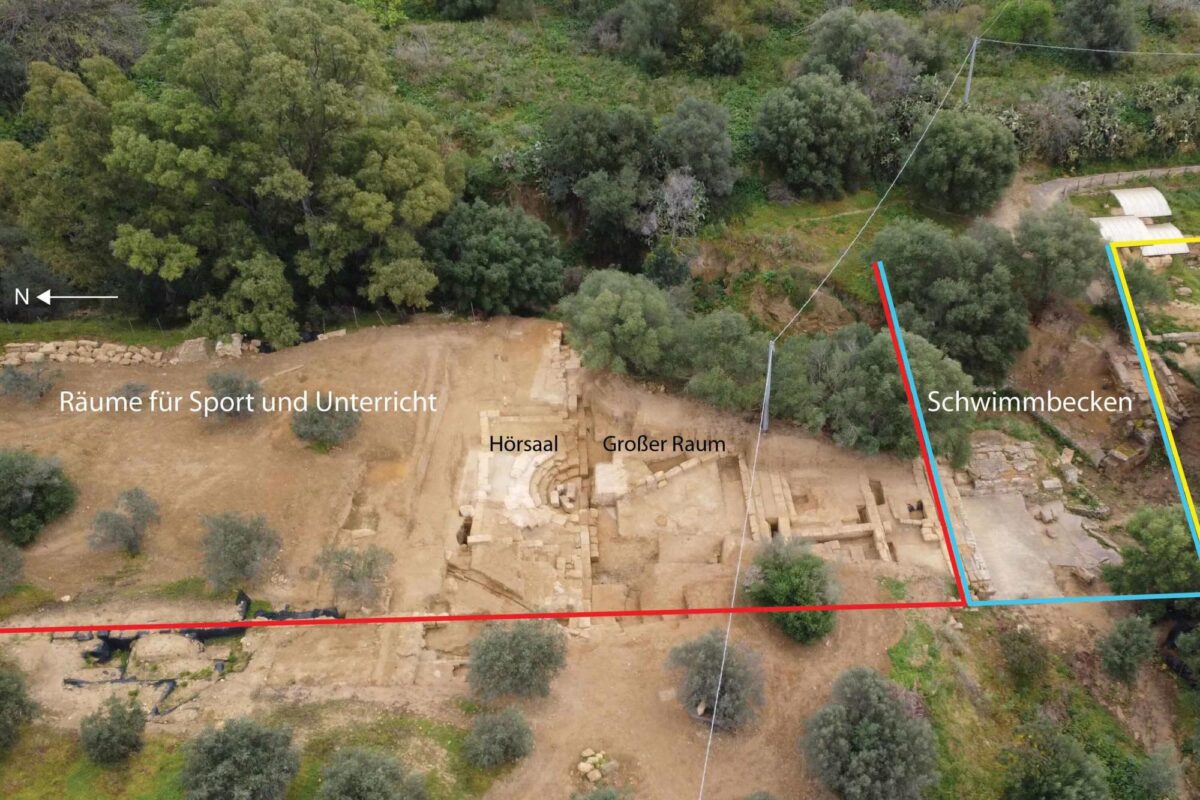
In a remarkable archaeological breakthrough in southern Sicily, an international team of researchers has uncovered an extraordinary ancient classroom that offers profound insights into the educational practices of Ancient Greece. This significant discovery, located in the historic town of Agrigento, was made in March 2025 by a team from Freie Universität Berlin, led by Professor Monika Trümper and Dr. Thomas Lappi, in collaboration with the Politecnico di Bari and the Parco Archeologico Valle dei Templi di Agrigento.
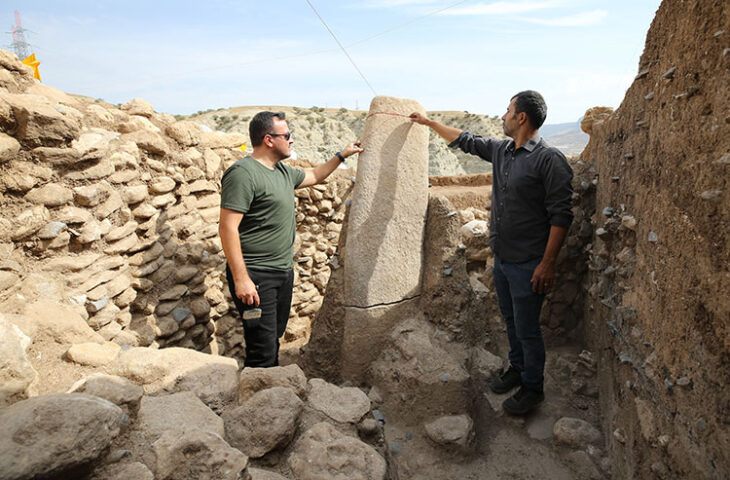
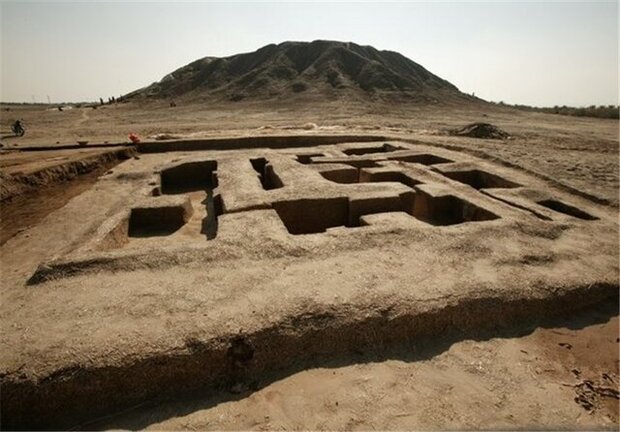
The excavation revealed a roofed semicircular auditorium, an integral part of a vast Greek gymnasium, which served as a multifunctional space for both physical and intellectual training. This ancient classroom, capable of seating approximately 200 individuals, is unique in its design and functionality, marking a significant advancement in the educational architecture of its time. Unlike other known gymnasiums, the Agrigento auditorium, dating back to the second century BCE, showcases a sophisticated approach to education that combined athletic prowess with scholarly pursuits.
The gymnasium, originally established in Akragas—Agrigento‘s ancient name—around 580 BCE, was not merely a venue for physical exercise but a comprehensive institution aimed at cultivating well-rounded citizens. The newly discovered auditorium features eight stepped rows of seating surrounding a central performance area, reminiscent of a theater, emphasizing the importance of public speaking and intellectual discourse in the educational curriculum.
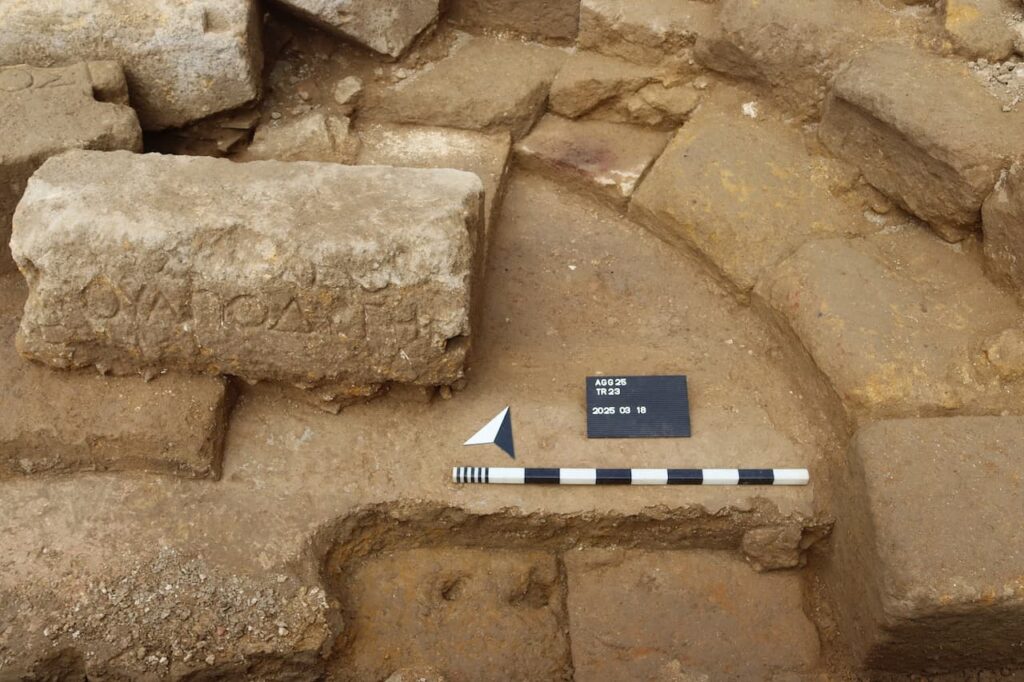
In addition to the architectural marvel, the excavation team uncovered two inscribed blocks of white limestone in the auditorium’s orchestra area. These inscriptions, meticulously engraved and highlighted with red pigment, reference the gymnasiarchos, the director of the gymnasium, and detail a renovation project funded by a local citizen dedicated to the deities Hermes and Heracles. This epigraphic evidence, dated to the late 1st century BCE, is one of the few surviving records from Agrigento, providing invaluable insights into the social and cultural dynamics of the time.
The significance of this discovery extends beyond its architectural and epigraphic elements. It highlights the enduring legacy of Greek education and culture, even after the city came under Roman rule. The gymnasium continued to serve as a vital educational hub, preserving its Hellenic traditions and practices amidst the political changes of the era.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
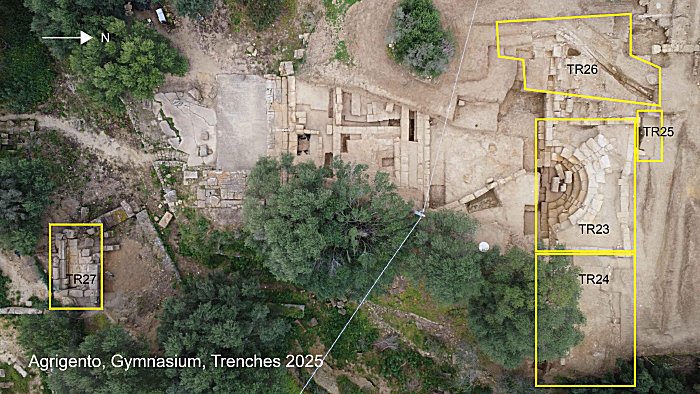
As the research team prepares for further excavations in 2026, they aim to uncover additional rooms dedicated to teaching and training, as well as more inscriptions that could illuminate the daily lives of the citizens of ancient Agrigento. This ongoing exploration promises to enrich our understanding of the vibrant educational landscape that once thrived in this remarkable Greek colony.

The discoveries in Agrigento not only enhance our knowledge of ancient educational systems but also underscore the city’s historical significance as a center of learning and culture in the western Mediterranean. With its unique architectural features and rich inscriptions, the gymnasium of Agrigento stands as a testament to the sophisticated educational ideals of Ancient Greece, offering a fascinating glimpse into a civilization that valued both mind and body.
Cover Image Credit: Aerial view captured by drone showcasing the gymnasium unearthed during excavations in Agrigento, with the auditorium (Hörsaal) prominently positioned at the center. Credit: Thomas Lappi – Monika Trümper / FU Berlin, Institut für Klassische Archäologie.