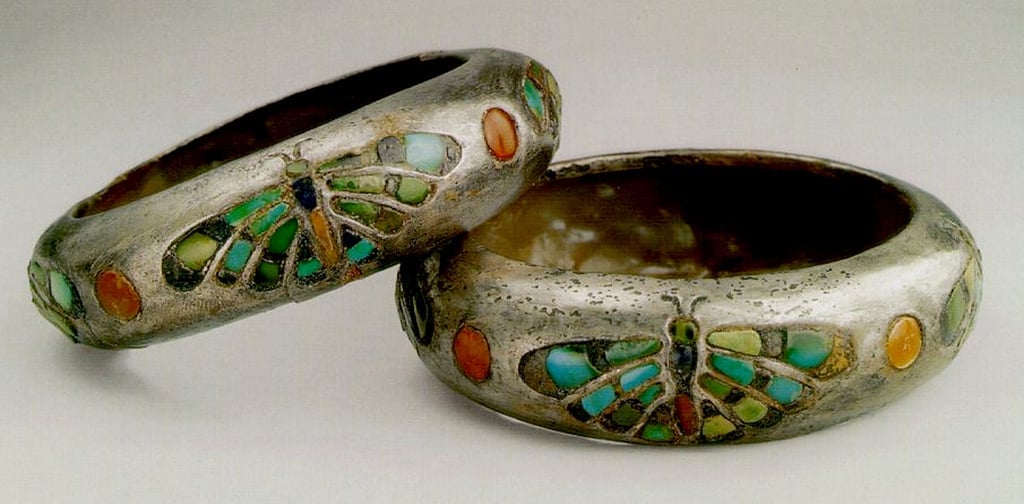
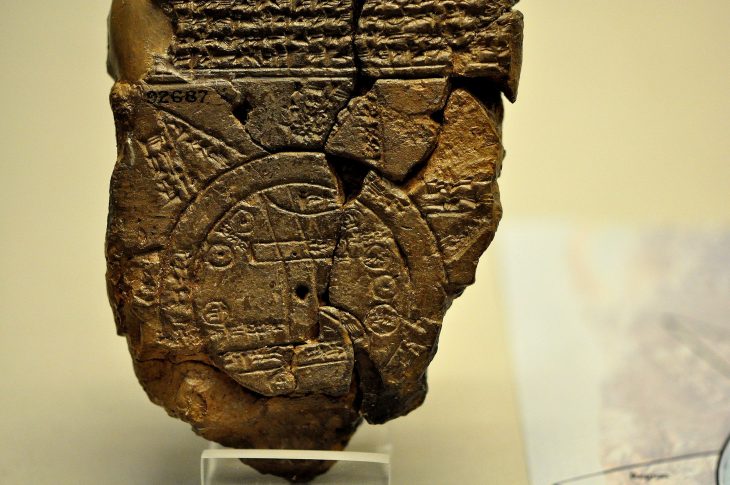
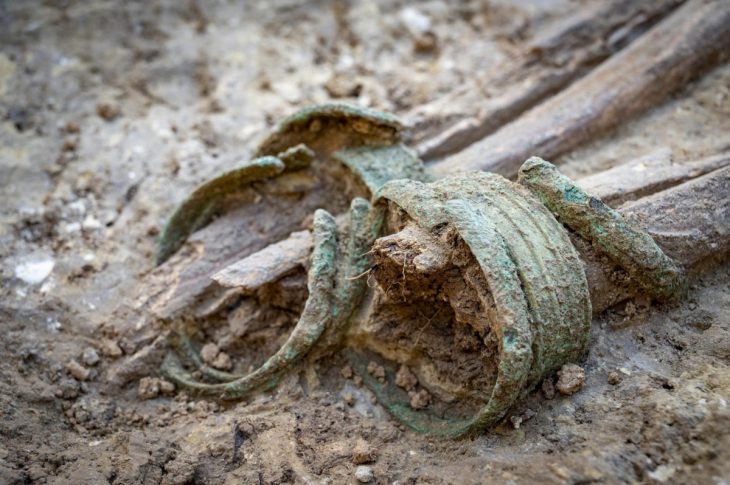
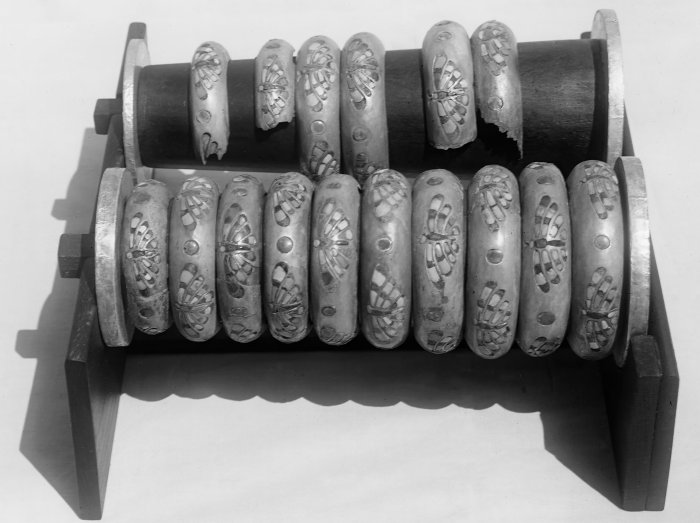
The discovery of silver bracelets in the tomb of Queen Hetepheres I, wife of Pharaoh Snofru and mother of Pharaoh Cheops, in 1925 came as a great surprise to researchers. Nearly a century later, however, the mystery seems to have been solved.
Researchers have led the analysis of bracelets found in the tomb of Queen Hetepheres I. It is the first analysis of the collection in decades.
The bracelets discovered in the intact tomb of Queen Hetepheres I. (c. 2589-2566 BC), represent the largest and most famous collection of silver artifacts from ancient Egypt. As silver is rarely found in the Egyptian archaeological record until the Middle Bronze Age, the bracelets are a statement of royal privilege.
A new analysis of the bracelets shows that the silver used in them most likely comes from the mines of the Cyclades, a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea.
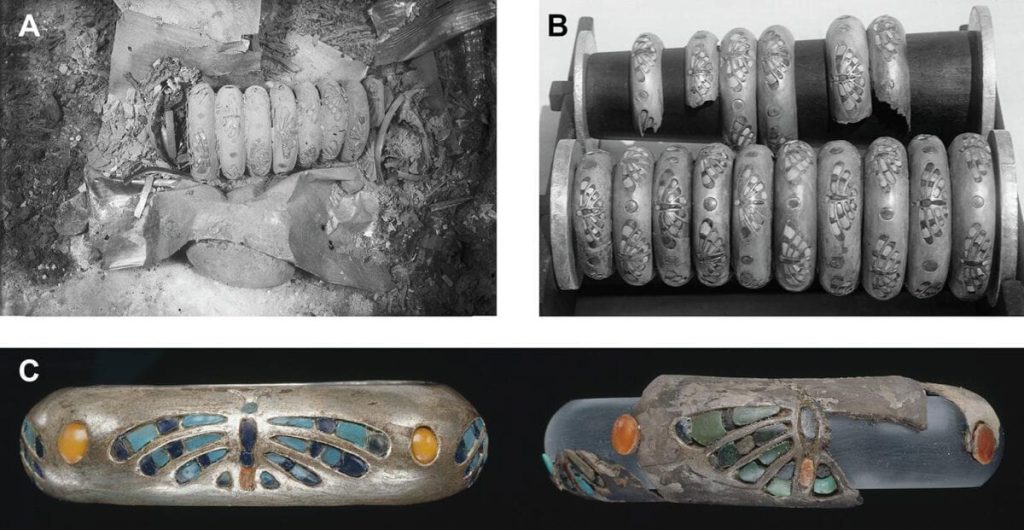
It is a special discovery. Because with that, the bracelets bear witness to the – as far as we know – the earliest trading activities between Egypt and Greece.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
With Egypt lacking domestic silver ore sources, experts had proposed that the Queen’s silver might have been partitioned from specific silver-rich gold ores, or it would have been imported from Byblos, in modern-day Lebanon. Still, the bracelets had not been recently analyzed, so each of these theories remained unproven.
A group of experts led by Karin Sowada (Department of History and Archaeology, Macquarie University, Sydney, Australia) analyzed samples of corroded bracelets from the collection, which is now housed at the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, and published their findings in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports.
According to the article’s abstract, the team used bulk XRF, micro-XRF, SEM-EDS, X-ray diffractometry, and MC-ICP-MS to obtain elemental and mineralogical compositions and lead isotope ratios, to understand the nature and metallurgical treatment of the metal and identify the possible ore source. It was found that the pieces consist of silver with traces of copper, gold, lead, and other elements. The minerals are silver, silver chloride, and a possible trace of copper chloride.

The source of silver (Ag) ores may be traced by examining lead (Pb) isotope ratios in the sample. Researchers actually compared the lead isotope composition of a sample, with those from a galena (PbS) database that included some 7000 localities located between the Atlantic Ocean and Iran. What came by surprise was that the lead isotope ratios are consistent with ores from the Cyclades (Aegean islands, Greece), and to a lesser extent from Lavrion (Attica, Greece), and were not partitioned from gold or electrum as previously proposed.
“Although similarities in Pb isotope composition occur in unlikely sources such as Samos and Tunisia, which are not known for Ag production,” according to the article, “the most significant ‘hits’ are from the Cyclades (Seriphos, which has more hits, Anafi, and Kea-Kythnos), and to a lesser extent from the Lavrion mines (district of Attica in central Greece).”
Historical sources tell of the import of silver in Egypt during the reign of Hetepheres’ husband, Sneferu, but the origins are not documented.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2023.103978
Cover photo: Egypt Museum