Archaeologists from Germany and Kurdistan have discovered a 3,400-year-old Mittani Empire-era city on the Tigris River.
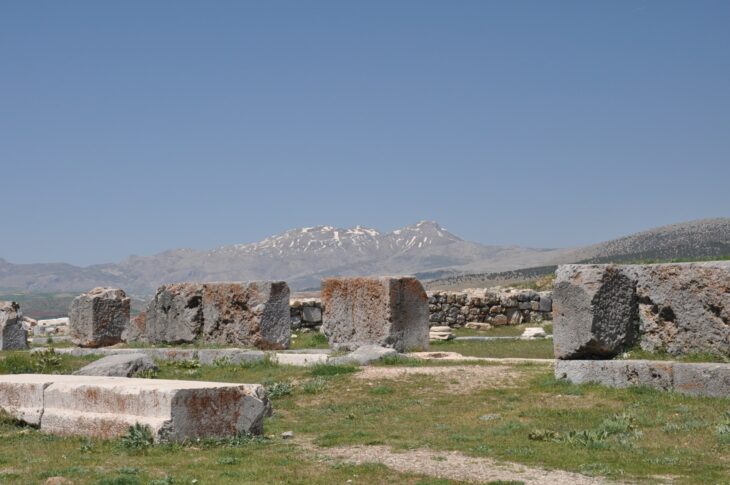
The ruins emerged on the waters of the River Tigris during a severe drought. The water level was significantly reduced in the Mosul Dam reservoir, and that is when the settlement appeared.
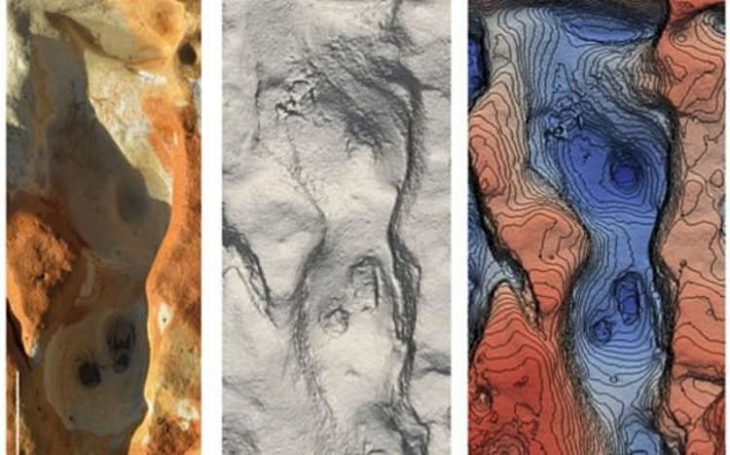
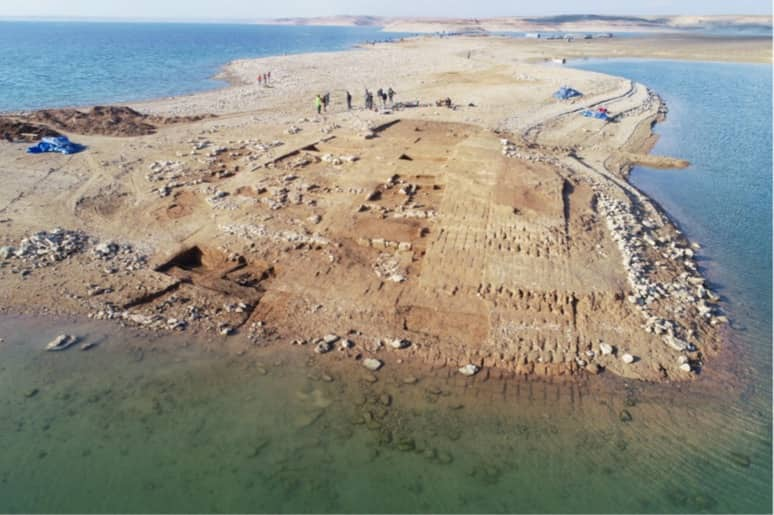
The extensive city with a palace and several large buildings might be ancient Zakhiku, which was an important location in the Mittani Empire (ca. 1550–1350 BC).
An ancient city dating back to the Mittani Empire-era over 3,400 years ago has resurfaced in the Tigris River in Kurdistan Region’s Duhok province, a local official confirmed.
Speaking to reporters on Monday, Bekas Brifkani, head of the Duhok Archaeology Directorate, told reporters that the re-emergence of the city happened due to drought which has significantly affected the water level in the Tigris River.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

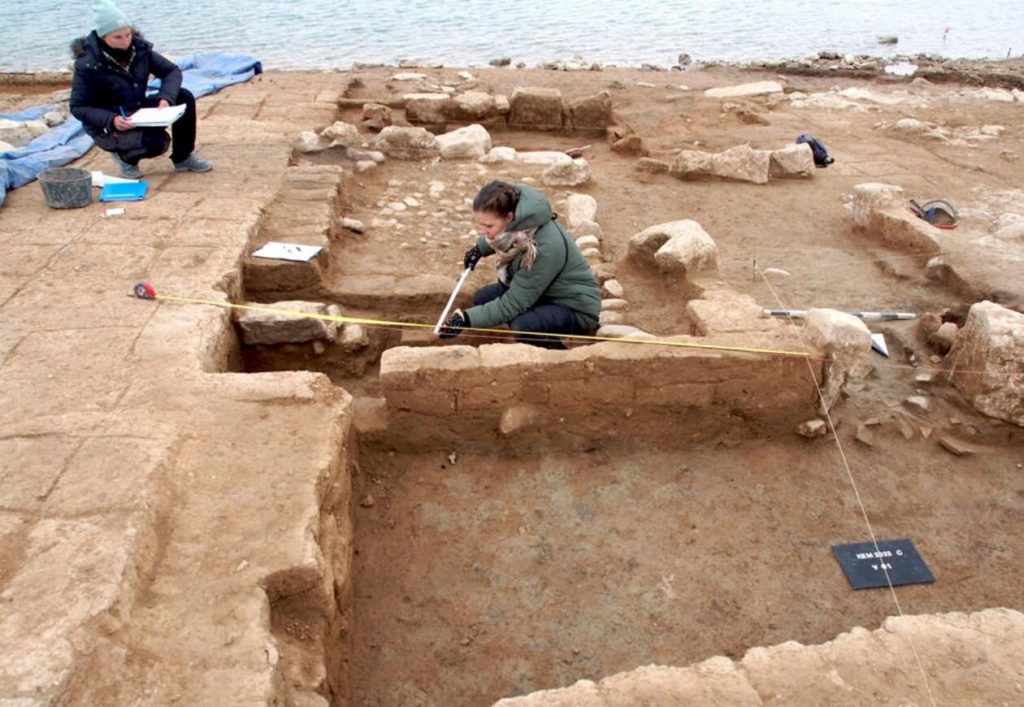
“After the water level continued to decrease, the remnants of the city resurfaced, which includes a massive settlement with a large number of buildings and antiquities,” Brifkani revealed, noting that they have so far found nearly 200 clay tablets inscribed with Cuneiform texts.
In the first stages, funding for the work was obtained at short notice from the Fritz Thyssen Foundation through the University of Freiburg. The German-Kurdish archaeological team was under immense time pressure because it was not clear when the water in the reservoir would rise again, according to a report by idw.
The team did not get much time as the water level kept increasing in the Tigris. Nevertheless, the researchers were able to map the city in a very short period of time. A gigantic fortress with walls and towers, a monumental, multi-story storage building, and an industrial complex were discovered in addition to a palace, which had already been recorded during a brief campaign in 2018.

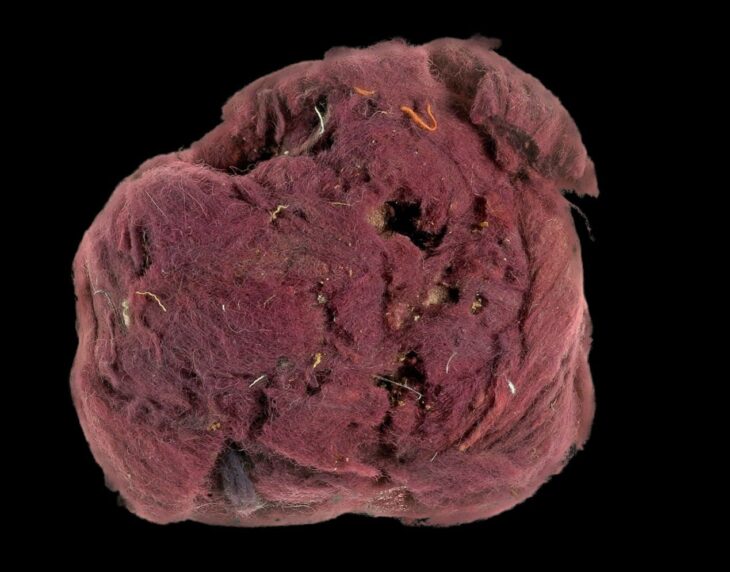
Of particular interest is the discovery of five ceramic vessels that contained an archive of over 100 cuneiform tablets. They date to the Middle Assyrian period. Some clay tablets, which may be letters, are even still in their clay envelopes. The researchers hope this discovery will provide important information about the end of the Mittani-period city and the beginning of Assyrian rule in the region.
“It is close to a miracle that cuneiform tablets made of unfired clay survived so many decades under water,” Prof. Dr. Peter Pfälzner from University of Tübingen said.

Another archaeologist Ivana Puljiz of the University of Tübingen putting light on the importance of the discovery said that the Mittani Empire is among the least researched empires of the Ancient Near East. The information on the existence of this particular empire is so little that historians don’t even know the capital of the Mittani Empire.
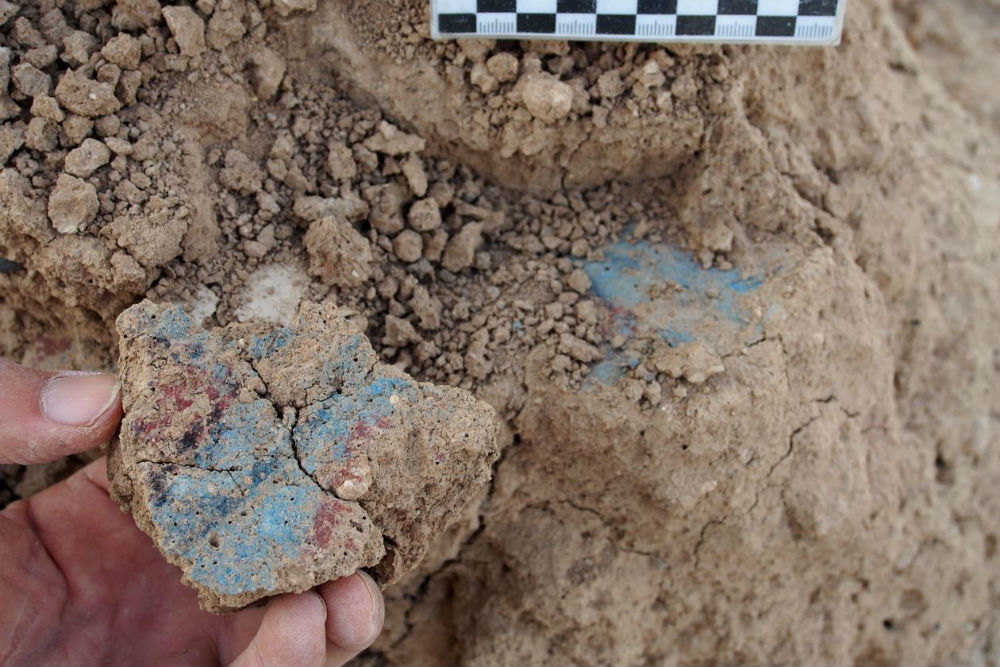
Archaeologists also discovered wall paints in bright shades of red and blue.
Puljiz mentioned that in the second millennium BC, colorful murals were the prime feature of palaces in the Ancient Near East but they never found any so well-preserved. So, discovering wall paintings in Kemune is no less than an “archaeological sensation”, she mentioned further.
Researchers hoping to find more about the Mittani Empire, which ruled over sections of Syria and northern Mesopotamia, thanks to this finding.