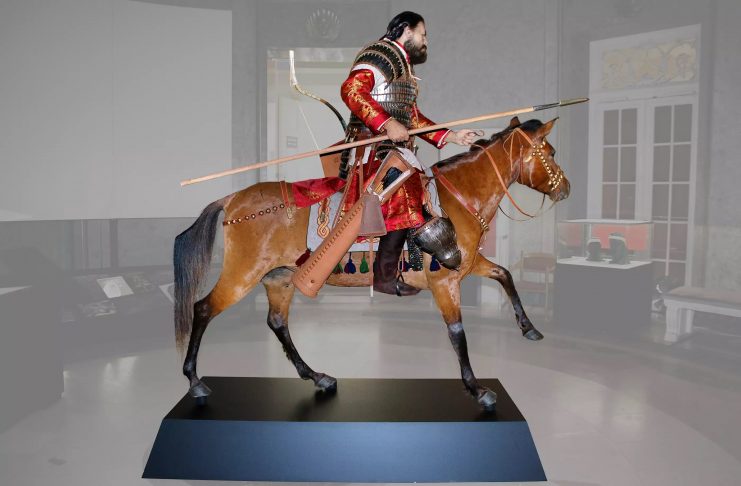
Ruled much of Central and Eastern Europe for 250 years, the Avars were less well known than Attila’s Huns, but undoubtedly more successful.
In the AD 560s, the Avars established an empire centered on the Carpathian Basin.
The Avars, we know that they came from Central Asia in the sixth century CE, But the question of who exactly they were has occupied ancient and modern historians ever since.
They are primarily known from Byzantine historical sources, who documented and questioned the sudden appearance of Avars in Europe. Modern historians have wondered whether they were a well-organised migrant group or a mixed band of fugitives.
Archaeological research has pointed to many parallels between the Carpathian Basin and Eurasian nomadic artefacts (weapons, vessels, horse harnesses), for instance a lunula-shaped pectoral of gold used as a symbol of power. We also know that the Avars introduced the stirrup in Europe. Yet we have so far not been able to trace their origin in the wide Eurasian steppes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
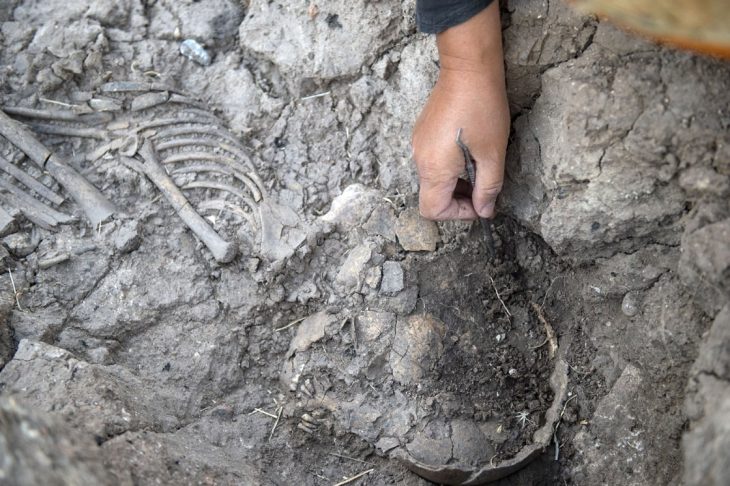
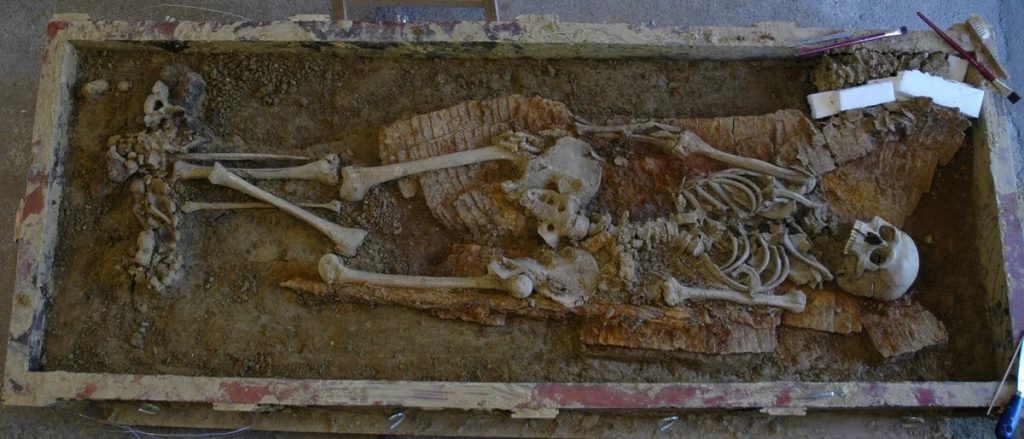
Now, a multidisciplinary research team of geneticists, archaeologists, and historians, including researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, obtained and studied the first ancient genomes from the most important Avar elite sites discovered in contemporary Hungary.
The study included the eight richest Avar graves ever discovered, overflowing with golden objects, as well as other individuals from the region prior to and during the Avar age. “We address a question that has been a mystery for more than 1400 years: who were the Avar elites, mysterious founders of an empire that almost crushed Constantinople and for more than 200 years ruled the lands of modern-day Hungary, Romania, Slovakia, Austria, Croatia, and Serbia?”, explains Johannes Krause, senior author of the study.

Fastest long-distance migration in human history
The Avars did not leave written records about their history and these first genome-wide data provide robust clues about their origins. “The historical contextualization of the archaeogenetic results allowed us to narrow down the timing of the proposed Avar migration. They covered more than 5000 kilometres in a few years from Mongolia to the Caucasus, and after ten more years settled in what is now Hungary. This is the fastest long-distance migration in human history that we can reconstruct up to this point,” explains Choongwon Jeong, co-senior author of the study.
Guido Gnecchi-Ruscone, the lead author of the study, adds: “Besides their clear affinity to Northeast Asia and their likely origin due to the fall of the Rouran Empire, we also see that the 7th-century Avar period elites show 20 to 30 percent of additional non-local ancestry, likely associated with the North Caucasus and the Western Asian Steppe, which could suggest further migration from the Steppe after their arrival in the 6th century.” The East Asian ancestry is found in individuals from several sites in the core settlement area between the Danube and Tisza rivers in modern day central Hungary. However, outside the primary settlement region we find high variability in inter-individual levels of admixture, especially in the south-Hungarian site of Kölked. This suggests an immigrant Avars elite ruling a diverse population with the help of a heterogeneous local elite.
These exciting results show how much potential there is in the unprecedented collaboration between geneticists, archaeologists, historians and anthropologists for the research on the ‘Migration period’ in the first millennium CE.
This research is a part of HistoGenes, an ERC-funded project investigating the period of 400 to 900 CE in the Carpathian Basin from a multidisciplinary perspective.
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
Cover Photo: Ilona C. Kiss