Scientists have recreated the Eastern Mediterranean silver trade across a time span that includes the conventional dates of the Trojan War, Rome’s birth, and the destruction of Solomon’s Temple in Jerusalem.
During the Late Bronze and Iron Age eras, silver originating from the north-eastern Mediterranean, as far away as the Iberian Peninsula, was used as a trade token across the Mediterranean.
A group of scientists and numismatists from France, Israel, and Australia discovered geochemical evidence for pre-coinage silver commerce persisting throughout the Mediterranean during the Late Bronze and Iron Age eras, with only minor interruptions.
In a presentation at the Goldschmidt Conference organized by the Washington-based Geochemical Society, Dr. Liesel Gentelli said “Even before coinage, there was international trade, and Hacksilber was one of the commodities being exchanged for goods.”
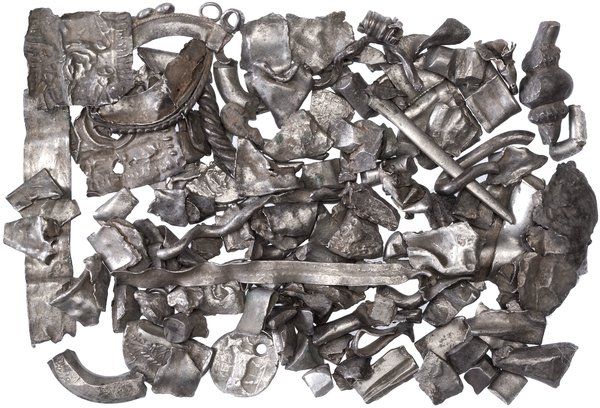
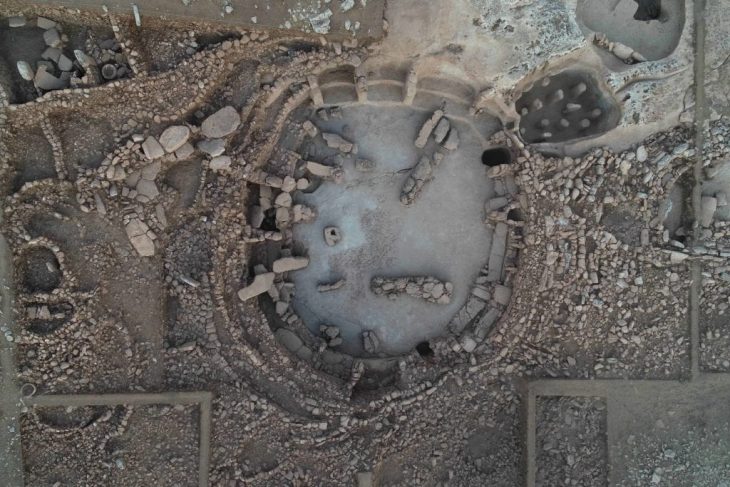
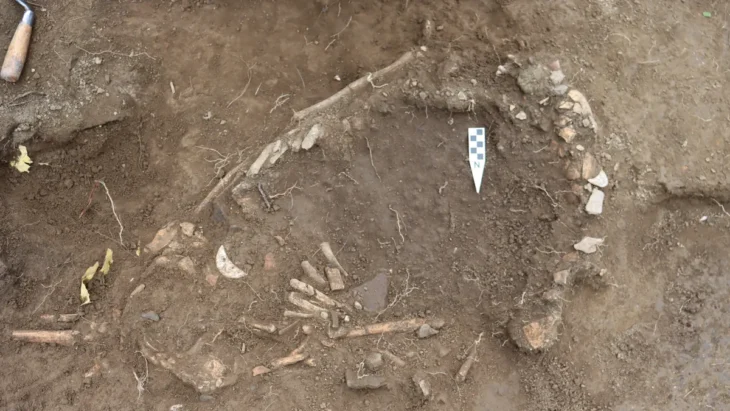
Hacksilber is an irregularly cut silver bullion consisting of broken bits of silver ingots and jewelry that was used as a form of payment in the southern Levant from the early second millennium to the fourth century BCE. Its worth was established by weighing it on scales against specified weights in local and international transactions. It has been discovered in archaeological excavations in the region usually stored inside ceramic containers and it had to be imported because there was no silver to be mined in the Levant.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
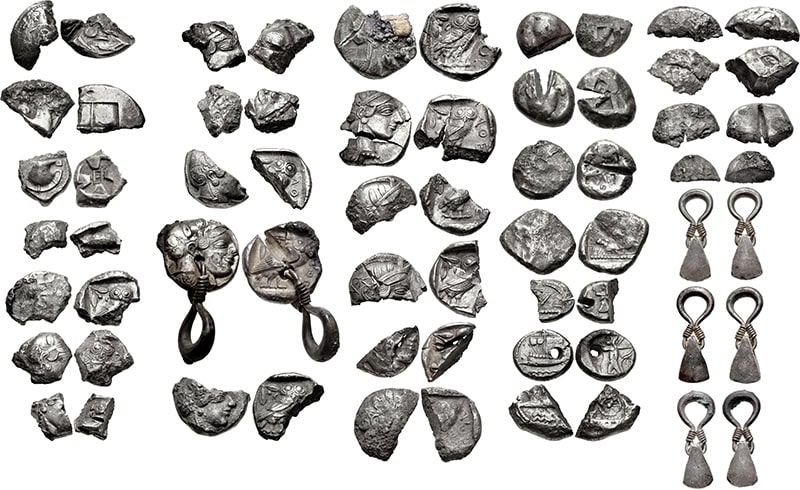

The researchers utilized high-precision isotopic analysis to pinpoint the mineral origins of the minute lead traces discovered in silver Hacksilber.
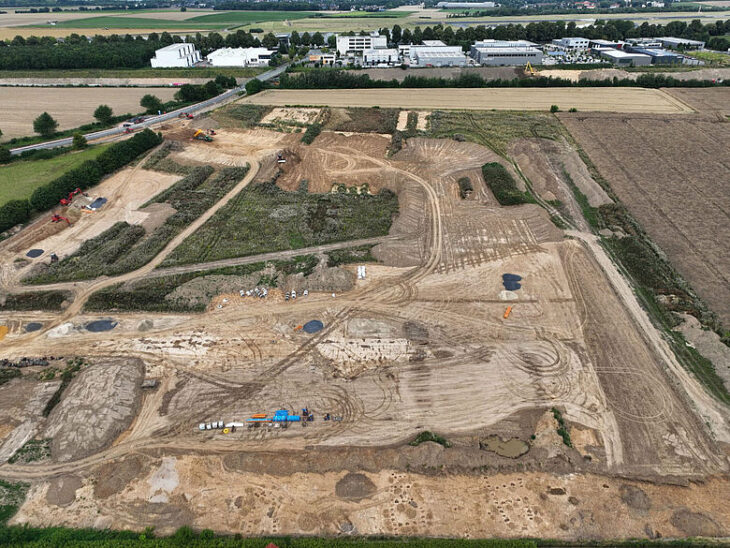
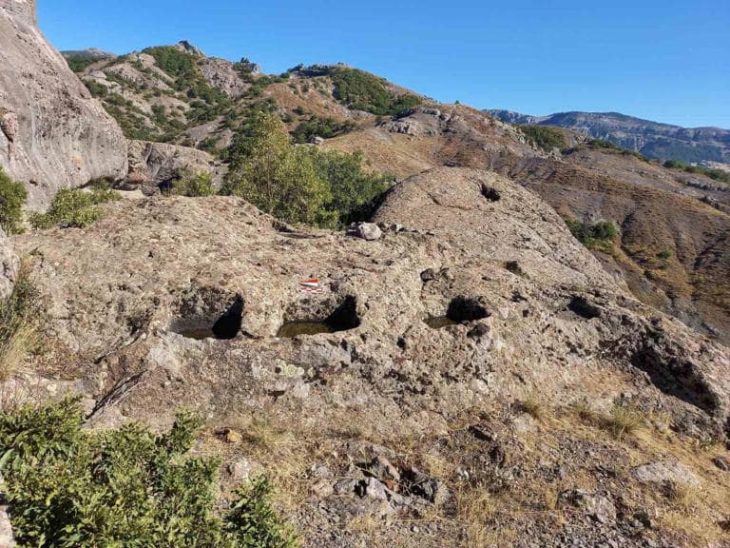
The researchers examined Hacksilber from 13 distinct sites in the southern Levant, modern-day Israel, and the Palestinian Authority ranging from 1300 BCE to 586 BCE. The discoveries came from “En Gedi, Ekron, and Megiddo” (also known as Armageddon). They compared their findings to ore samples and discovered that the majority of the Hacksilber came from the Southern Aegean and Balkans (Macedonia, Thrace, and Illyria). Some were also found to come from as far away as Sardinia and Spain.
Liesel Gentelli (École normale supérieure de Lyon, France) said: “Previous researchers believed that silver trade had come to an end following the societal collapse at the end of the Late Bronze Age, but our research shows that exchanges between especially the southern Levant and the Aegean world never came to a stop. People around the Eastern Mediterranean remained connected. It’s likely that the silver flowed to the Levant as a result of trade or plunder.
According to the scientists, silver shortage occurred during the time of the Bronze to Iron Age transition, about 1300-1100 BCE, and certain hoards from this era exhibit abnormally high copper content, which would have been added to compensate for the absence of the grey metal.
“We can’t match our findings on the silver trade to specific historical events, but our analysis shows the importance of hacksilber trade from before the Trojan War, which some scholars date to the early 12th century BCE, through the founding of Rome in 753 BCE, and up to the end of the Iron Age in 586 BCE, marked by Nebuchadnezzar’s destruction of Solomon’s Temple in Jerusalem,” Gentelli pointed out.
The researcher also said that these events were followed by a gradual introduction of coins, first as finds of several archaic coins, and later a transition to a monetary economy in the southern Levant circa 450 BCE which made the trade of hacksilber less relevant.
Gentelli stated that this study reveals the ongoing and important economic role played by Hacksilber in the Bronze and Iron Age economies.