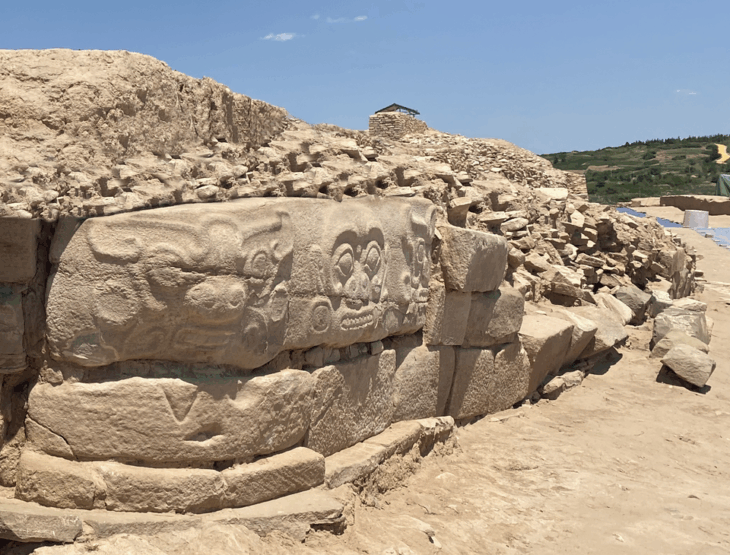
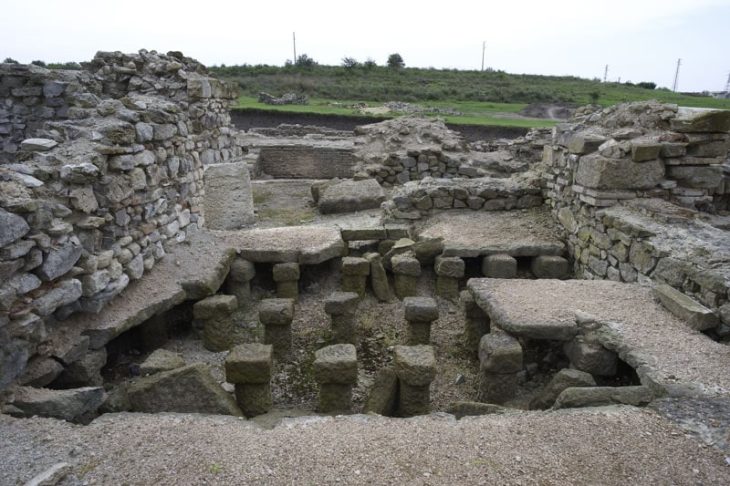
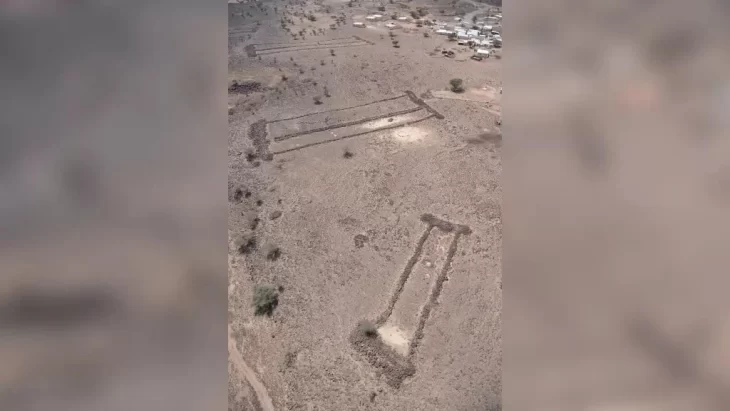
Sogmatar, Şanlıurfa is 53 kilometers from Harran. It is located in Yağmurlu village, where there are important springs in the Tek Tek mountains.
Tek Tek Mountains, which have important Neolithic centers such as Karahantepe, Harbetsuvan, and Kurt Tepesi, also have a cult center belonging to the Moon God Sin.
The region is a cult center dedicated to the Moon God Sin in the Tektek Mountains region of the Harranians during the Abgar Kingdom Period.
In the Sogmatar Cult center; There is a cave where the moon god Sin is worshiped (Pognon Cave), and a hill (Sacred Hill- Turkish: Kutsal Tepe) on the slopes of which there are reliefs of the god and inscriptions engraved on the ground. Also, there are 6 square and round planned mausoleums, the inner castle, and many rock tombs carved into the main castle.
Although the Ancient City of Sogmatar is dated to the 2nd century AD, researches show that the history of the city dates back to 2000 BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Sogmatar was founded by the people who fled from the region due to the intense attacks of the Parthians (Iranians) in the Urfa region, especially in 165 AD, and preserved its cult center feature until the Islamic Period.
Although the name of the moon god in Mesopotamian civilizations varies from culture to culture, it is mostly seen as “Sin” and “Nanna”.
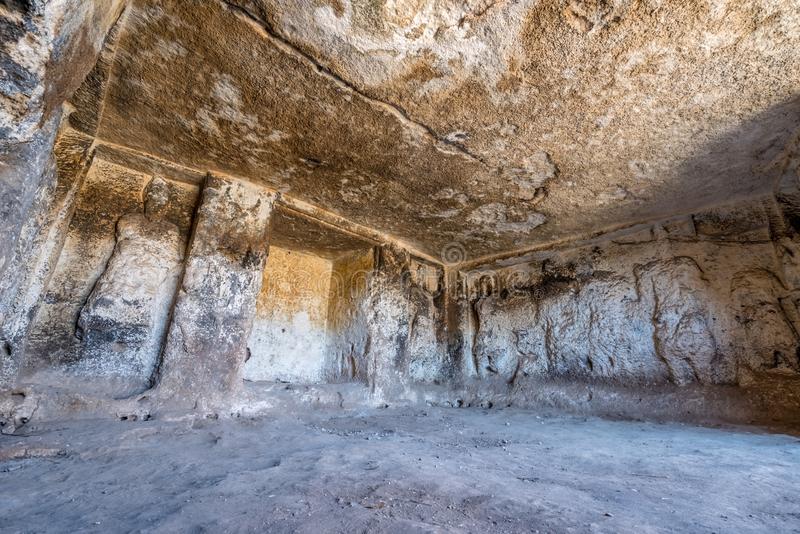

The Sumerians called their moon gods Nanna, Nannar, or Suen.
Sometimes they used to combine two different names. In later periods, the Akkadians of Semitic origin named the moon god Sin. Besides these names, Asimbabbar, Namraşit, and Inbu were among the words used to characterize Nanna-Sin.
The Sumerians used descriptions for Nanna-Sin such as the brightness of the moonlight, the bull, and Enlil’s young bull, and depicted him as a bull and a lion-dragon. In addition, the symbol of this god consists of a crescent. The moon god Sin was very important to the Sumerian city of Ur. But in the following periods, the city of Harran became an important center for Nanna-Sin. A triple god system was established in Harran with Nanna-Sin, Utu and Inanna.
Nanna-Sin, who was accepted as the patron god of the city of Ur, is mentioned in the Sumerian Pantheon as the son of Enlil. In the Sumerian texts, it is described that Nanna-Sin judged the dead in the underworld. It is said that he is the god who determines the time. One of the most important features attributed to Nanna-Sin is that he acted with great vengeance in the face of the wrong deeds of the kings living on earth and was an important power in punishing them.

Although the moon is called “Sin” with its crescent shape, “Nanna” at the full moon is gradually it took the form of “Asimbabbar” with its growing state. The moon god Sin is known as the most important god of all Semitic tribes. When it is in the form of a crescent, it is masculine, when it is in the full moon female, it is identified with the bull when it is in the form of a crescent.
Deities associated with the 7 planets (Sin, Shamash, Ishtar or Atargatis, Mara, Samyaya or Ares, Girgis, Bel, and Nabu or Nabig) and their families (Ningal, consort of Sin, Nusku, and consort of fire god) Sadarnunna) dominated the Harran pantheon from the Assyrian and Babylonian periods to the Islamic Period.
The moon god Sin is constantly at the top of the pantheon of gods. The name of the moon god Sin is included in the treaties and agreements made between the kingdoms in Harran since the Assyrian and Babylonian periods. It is even written that some treaties were made in the famous Sin Temple in Harran.
The name of the temple built in the name of the god Sin in Harran is E.HUL.HUL. The first information about the Sin Cult, which is known to have a very old history, was revealed in a letter obtained from Mari, which was dated to about 1776 BC. Accordingly, it is understood that a decision was made to make peace in the Sin Temple in Harran. Thus, it is understood that Sin in Harran had an important position in the first half of the second millennium BC and that his name was heard more thanks to the presence of Sin.
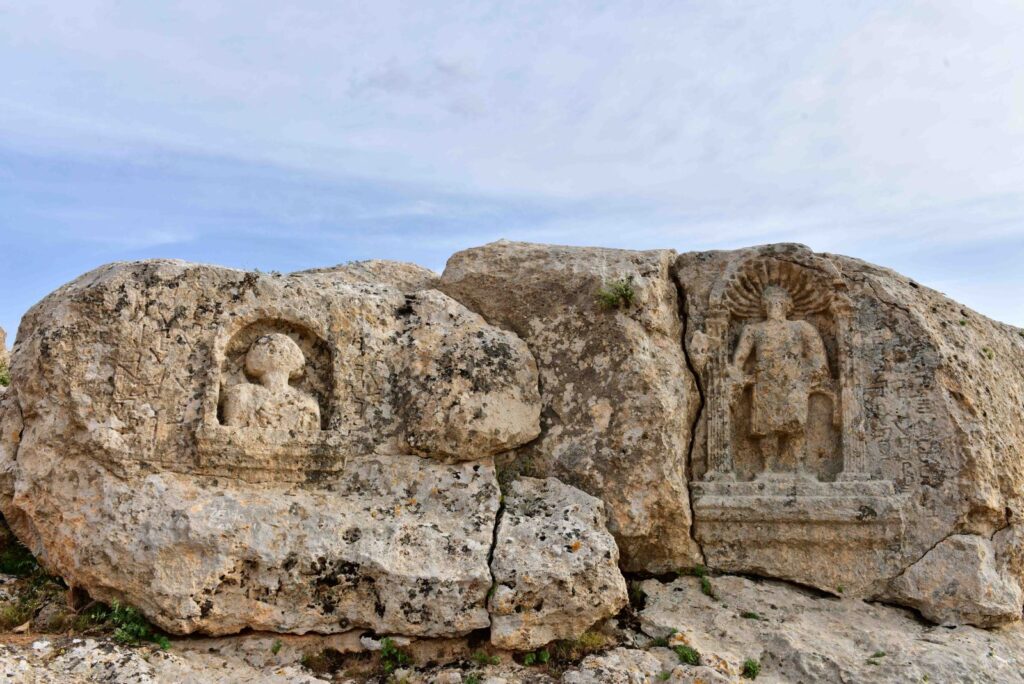

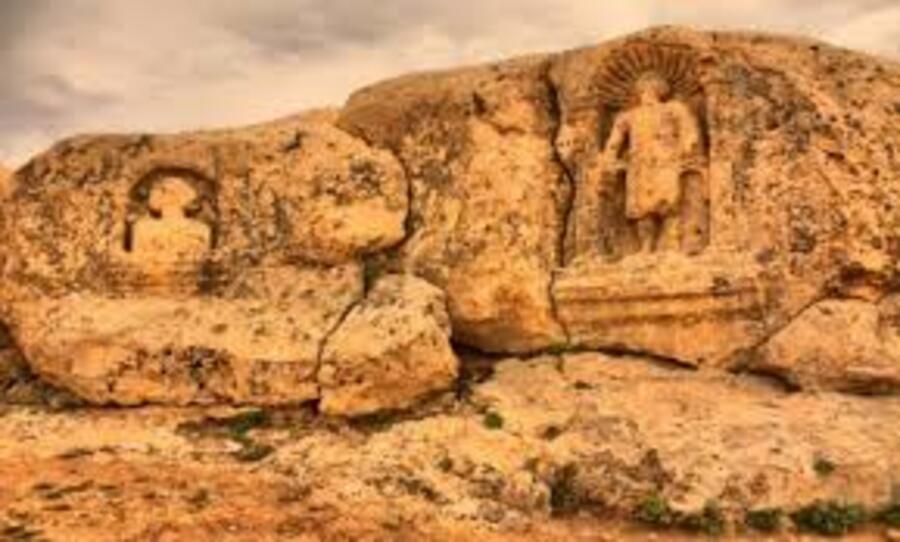
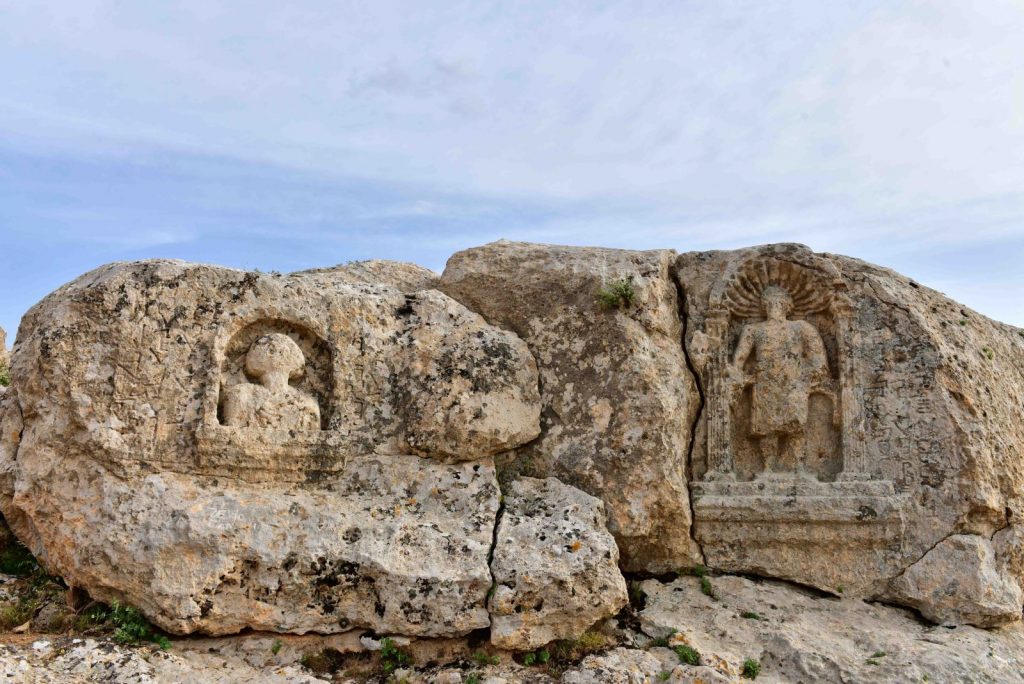
The two reliefs on the northern end of the hill, south of the mound at the entrance of Soğmatar, are quite striking. This hill is mentioned as a sacred hill in an inscription. The relief on the right is of a man depicted from the front and is in a frame with an arch, two quadrangular columns, and two steps. Rays radiate above his head
To the right of the relief is an inscription in Syriac. In the inscription; “God commanded this image to Ma’na on the thirteenth day of Adar (March) 476 (AD 165). is written.
The other relief is a bust in a rock-cut niche to the right of this relief. Behind the shoulders of the bust, a crescent with its ends upwards draws attention. There is an inscription on both sides of the bust.
In the first of these inscriptions; “Šila’s son Šila made this image for the god Sin, in memory of the life of Adona’s son Tirdat and his brothers,” In the second inscription; “I am God…. I see him. I see him and him I’m looking. I am God Sin”. On the left side of this bust.

In the inscription, the title of God is mentioned. The inscription; says, “May the son of Kuza Zakkai and his children be remembered before God”. It is clearly understood that this bust is the god Sin, due to the name Sin in the inscription and the crescent motif.
In addition, human reliefs and inscriptions can be seen on the south, north, and west walls of the cave, which was identified by Pognon, the French Ambassador to Aleppo, in the early 1900s and is called the Pognon Cave today. The presence of the crescent, which is the symbol of Sin, on the top of the head of one of these reliefs, reveals the presence of Sin in the Soğmatar sanctuary.
In Soğmatar, the name “Maralahe” is mentioned in two inscriptions and “Maralahe, the king of the gods” in one inscription. Maralahe, as the name of the moon god Sin in Old Akkadian and Aramaic known.
Source: Süheyla İrem MUTLU, Yusuf ALBAYRAK, “Harran ve Soğmatar’da Sin kültünün varlığı“, Karadeniz, no: 37