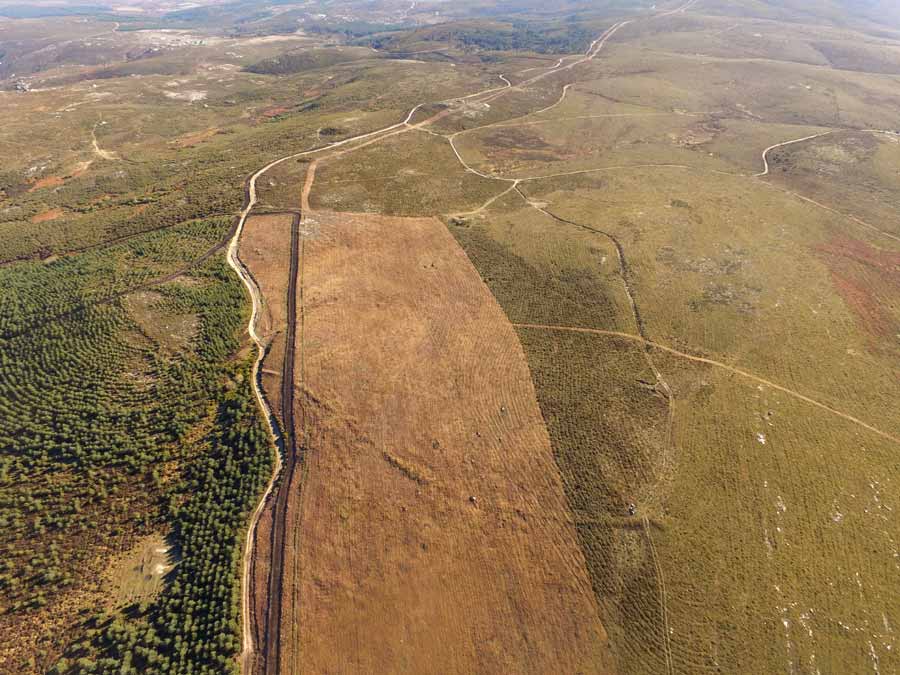
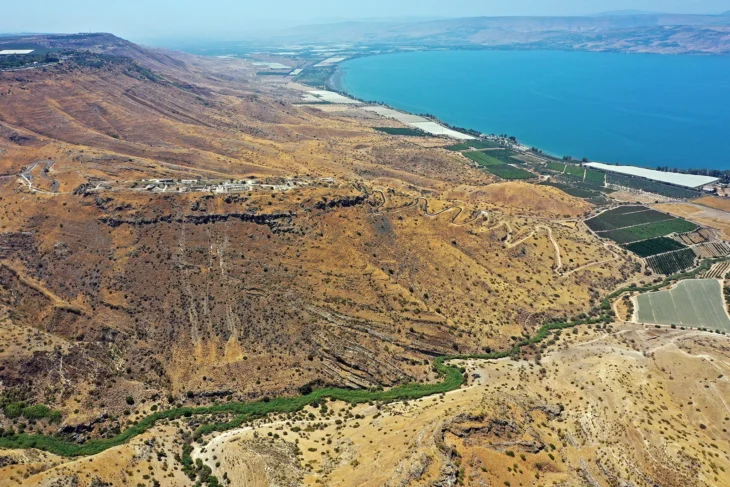
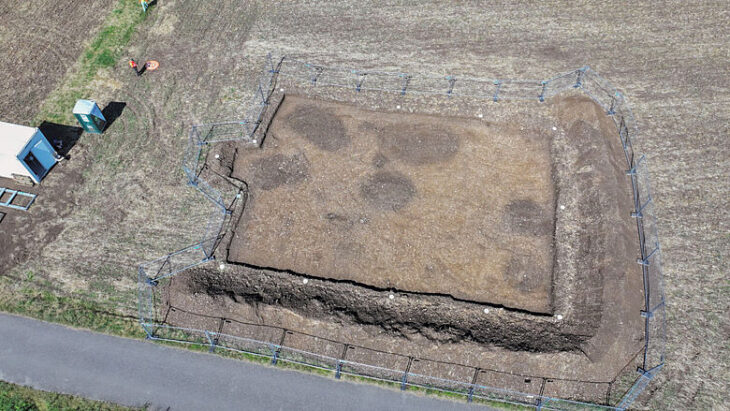
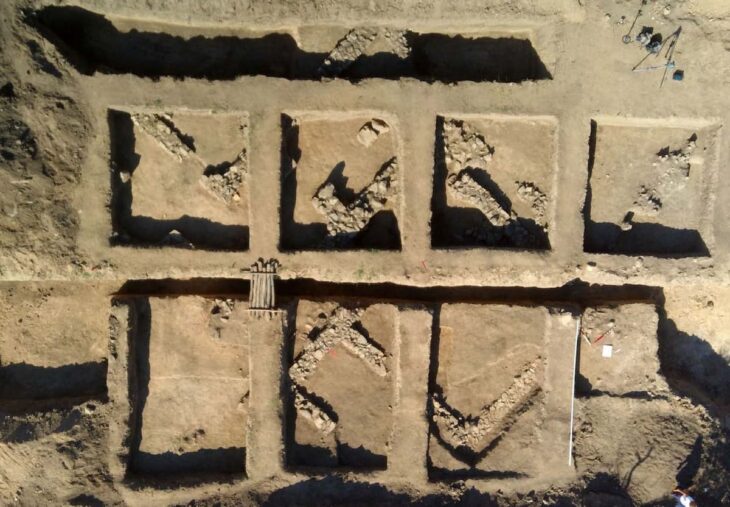
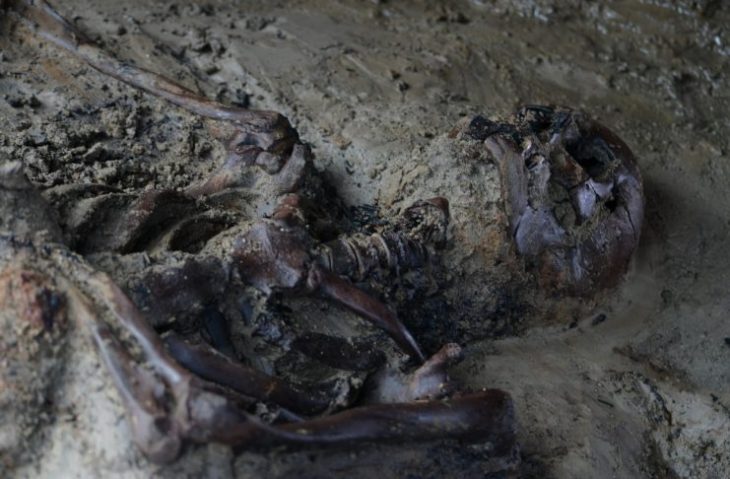
A camp used by 10,000 Roman soldiers sent to conquer northwestern Iberia has been discovered in the Portuguese city of Melgaço.
This discovery is by far the largest and oldest Roman military fortification excavated in Galicia and northern Portugal.
To date, the oldest Roman camp in Galicia and northern Portugal-excavated by the same team-is Penedo dos Lobos (Manzaneda, Orense), where coins can be found, and the paddock is called Canta The Breen War (29-19 years) was linked to BC), and Emperor Octavius used it to end the process of conquering Spain. Lomba do Mouro was built 100 years earlier than Penedo dos Lobos.
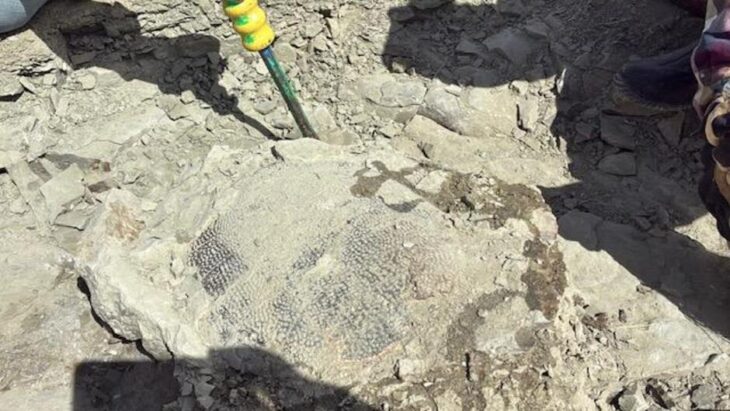
Experts analyzed a fragment of the sediment from the wall foundations using the optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating technique. This made it possible to determine the date when the quartz crystals were last exposed to sunlight and when they were buried under the walls. The foundations of the enclosure wall date from around the second century BC.
Around 10,000 Roman troops crossing the Laboreiro Mountain between the Lima and Minho rivers built the camp at Lomba do Mouro. It was built rapidly and was intended to be a temporary fortification, used for a day or weeks at most the warmer months.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
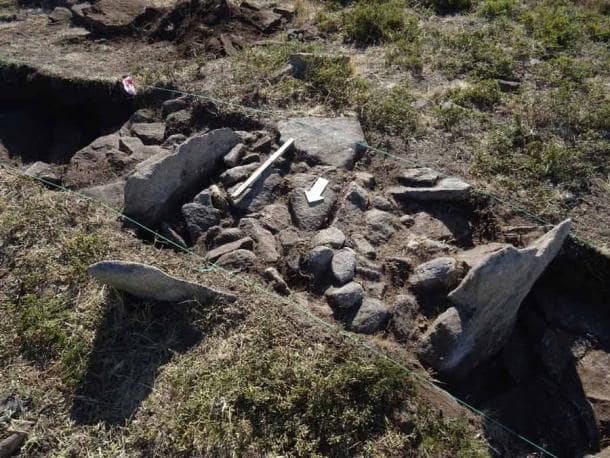

For protection, the army was crossing high ground. According to written accounts, they fought during their journey, but they also established some tentative agreements with the local populace. Temporary camps are difficult to locate since little archaeological evidence is left behind — owing to their transient nature and the fact that they were frequently demolished on purpose when the Roman Army left.
Dr João Fonte, from the University of Exeter, a member of the research team, said: “Written sources mention the army crossing different valleys, but until now we didn’t know exactly where. Because of the temporary nature of the site, it’s almost impossible to find without using remote sensing techniques, and radiocarbon dating wouldn’t have been accurate because plant roots creep into the structure.”
“We have found numerous military camps in the Northwest of the Iberian Peninsula in recent years, but their dating is very complex. As they are temporary enclosures, there is very little material or organic evidence in them that would allow a scientifically valid dating to be obtained, until now.”
In 137 BC, the Roman consul Decimus Junius Brutus entered Galicia with two legions, crossing the Douro and Lima rivers and reaching Minho. The dating of the walls along with the large dimensions of the fenced fence supports the hypothesis that the camp could have been erected by the contingent associated with those times, although due to the degree of uncertainty of dates it is difficult to establish a direct association with the episode of the Decimus Junius Brutus campaign.
The research is funded by the European Commission through a Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant (grant contract 794048).