Archaeologists in China have produced distilled wine in a replica of a 2,000-year-old bronze vessel recovered from an emperor’s tomb, revealing that the technique of distilled spirits existed in China as early as the Western Han Dynasty (206 BC-AD 25). This result has pushed back the origins of China’s alcohol distillation technology by around 1,000 years.
The wine was made employing the same process believed to have been practiced at the time, including the use of taro.
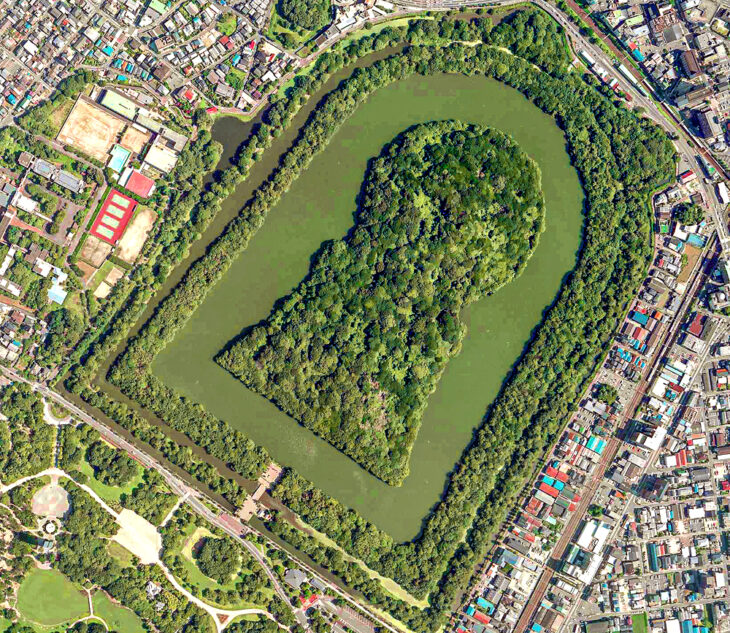
The bronze vessel was discovered at the tomb of Liu He, the deposed ninth emperor of the Western Han dynasty (202BC-AD9). It is one of the best-preserved tombs from that dynasty.
Liu ascended to the throne in 74 BC, installed by the minister Huo Guang. His reign was brief because, most likely as a result of misbehavior, he was overthrown after just 27 days. After that, he was exiled and made Marquis of Haihun. Since its discovery in 2011, Liu’s tomb in eastern China has yielded many artifacts.
Among the artifacts discovered are the oldest known painting of Confucius in China and 6,000 composite armor scales composed of iron, copper, and leather bound with lacquer.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
According to the renowned Chinese medical book Compendium of Materia Medica, also called Bencao Gangmu, which was written by Li Shizhen, a prominent pharmacist during the Ming Dynasty (1368–1644), the technology of alcohol distillation was first recorded in the Yuan Dynasty (1279–1368).
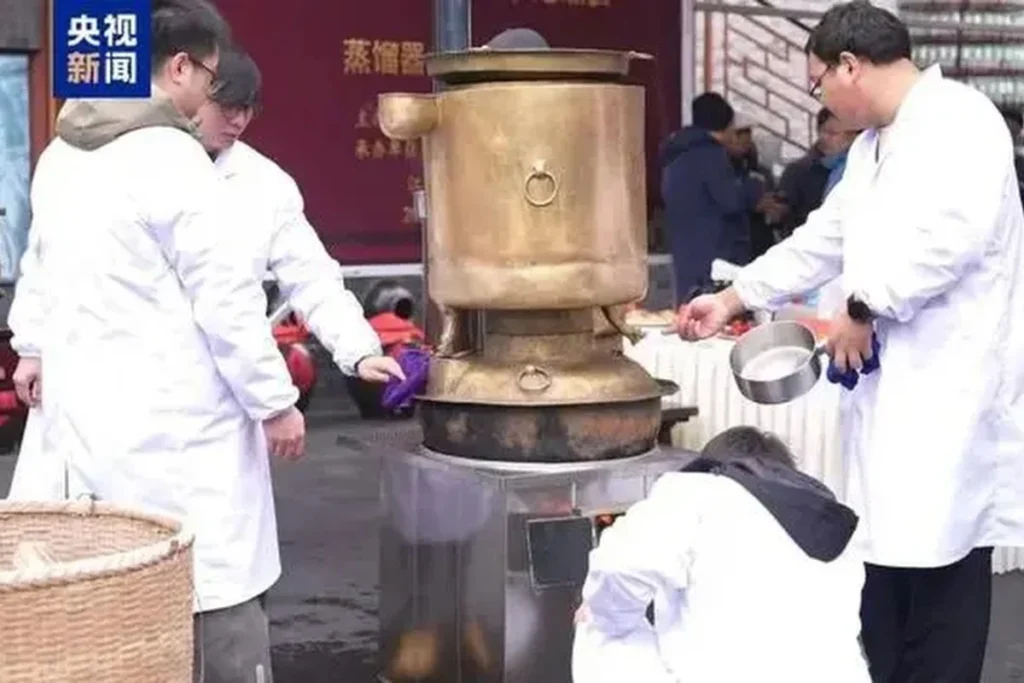

The discovery was made by a research team from the historical and cultural heritage conservation research center affiliated with Zhengzhou University in Central China’s Henan Province.
“This discovery has recreated the product from the Western Han dynasty—from raw materials to production process and the instrument used,” said Zhang Zhongli, an archaeologist with the State Administration of Cultural Heritage and the project manager for the tomb excavation.
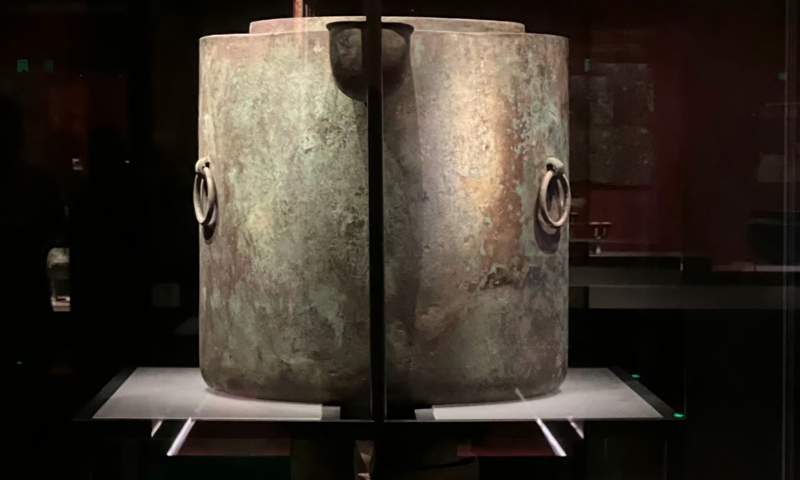
The center has made a replica of a distiller excavated from the tomb of the Marquis of Haihun, East China’s Jiangxi Province. Made of bronze, the unique distiller was discovered in the tomb’s wine storage chamber. It consists of three parts: a main pot known as the “heavenly pot,” a cylindrical vessel, and a cauldron.
However, this kind of ancient distiller could be used not just for filtering alcohol, but also for “purifying and distilling cinnabar substances and flower dews,” said Yao Zhihui.
Yao added that the possibility of the distiller being used for “purifying and distilling cinnabar substances and flower dews” can be “ruled out” according to parameters such as the ware’s design and the excavation site residue analysis.
The team’s replica device was on a 1:2 scale of the original. The team used raw liquid materials such as beer and yellow wine to test the ware’s functionality. The results showed that the design achieved a “distillation efficiency of over 70 percent” and successfully maintained “the flavor and alcohol concentration of the spirits.”
Cover Image Credit: A distiller excavated from the tomb of the Marquis of Haihun, East China’s Jiangxi Province. Photo: Sina Weibo