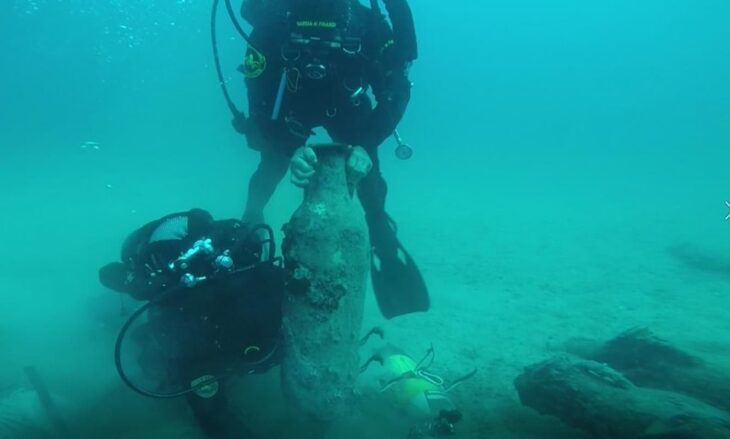
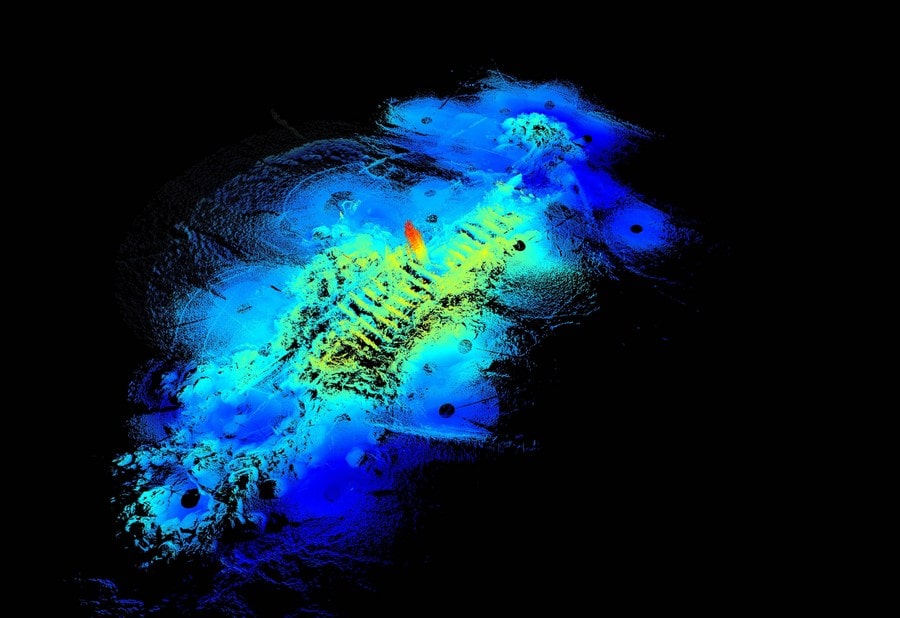
Rescue work has begun on a 160-year-old shipwreck in China, the largest and best-preserved wooden wreck ever discovered underwater.
This sunken ship, containing a large number of cultural relics, was a merchant vessel during the reign of Emperor Tongzhi (1862-1875) in the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911), the country’s last imperial dynasty.
Named Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck, the ship was found submerged at a depth of 5.5 meters below the seabed in the waters of Hengsha shoal in the northeast of Hengsha Island in Shanghai’s Chongming District.
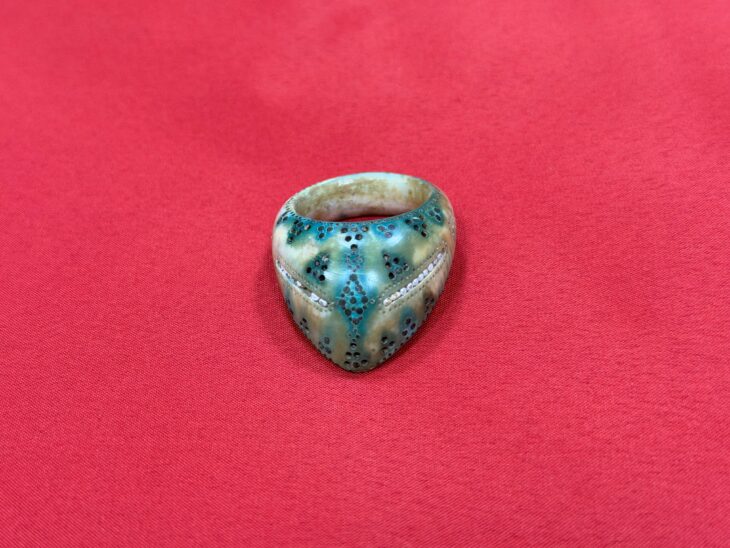
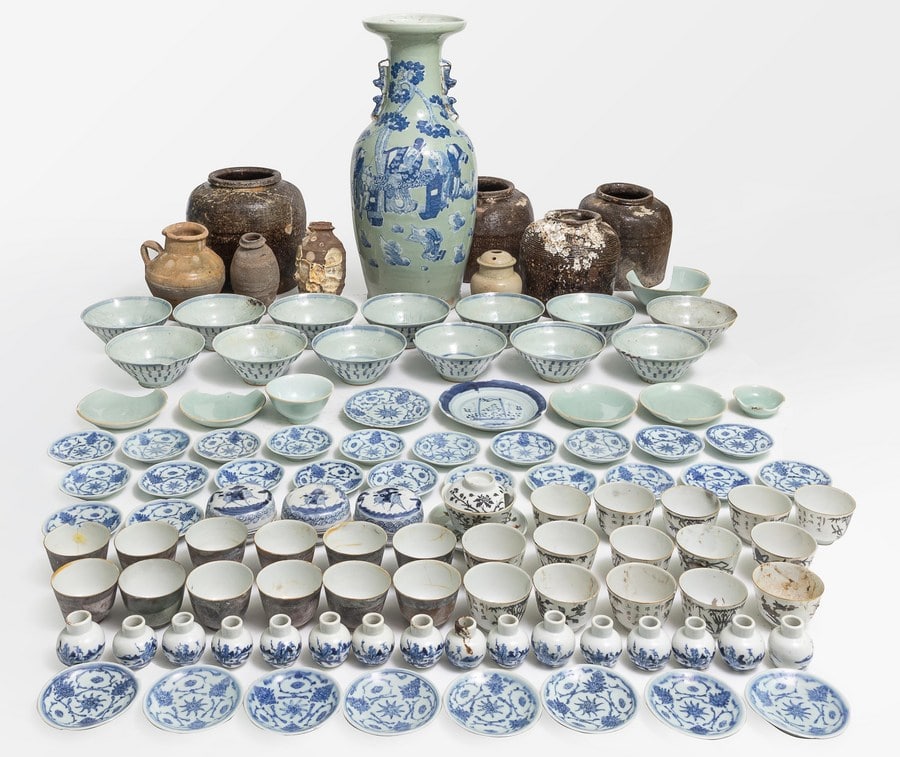
Archaeological investigations show that the ship is about 38.5 meters long and 7.8 meters at its widest in the middle. It has 31 cabins and is loaded with exquisite cultural relics such as porcelain made in Jingdezhen, a world-famous “porcelain capital” located in east China’s Jiangxi Province. Between July and September last year, big wares, including porcelain works of the Yuan Dynasty (1271–1368) and a 60-centimeter-high blue and white porcelain vase, were found.

The ship is probably a sand vessel with a flat bottom, widely used for water transportation in Shanghai during the Ming (1368-1644) and Qing dynasties, according to Zhai Yang, deputy director of the Shanghai Cultural Heritage Protection and Research Center.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In 2015, an underwater archaeological investigation in the Hengsha area of Chongming Island detected a sunken iron vessel via sonar scanning technology, which was named the Yangtze No. 1 Ancient Shipwreck. As archaeologists expanded the scanning scope, the wooden vessel was found north of the warship.
The whole salvage work is scheduled to finish by the end of this year or September as hoped, according to Fang Shizhong, director of the Shanghai Administration of Cultural Heritage.
“But it depends on weather, hydrology conditions and there are some uncertainties during the salvage process,” he added.
Cover Photo: Handout photo shows a sonar scan taken in 2021 of Yangtze No. 2 Ancient Shipwreck. /Xinhua