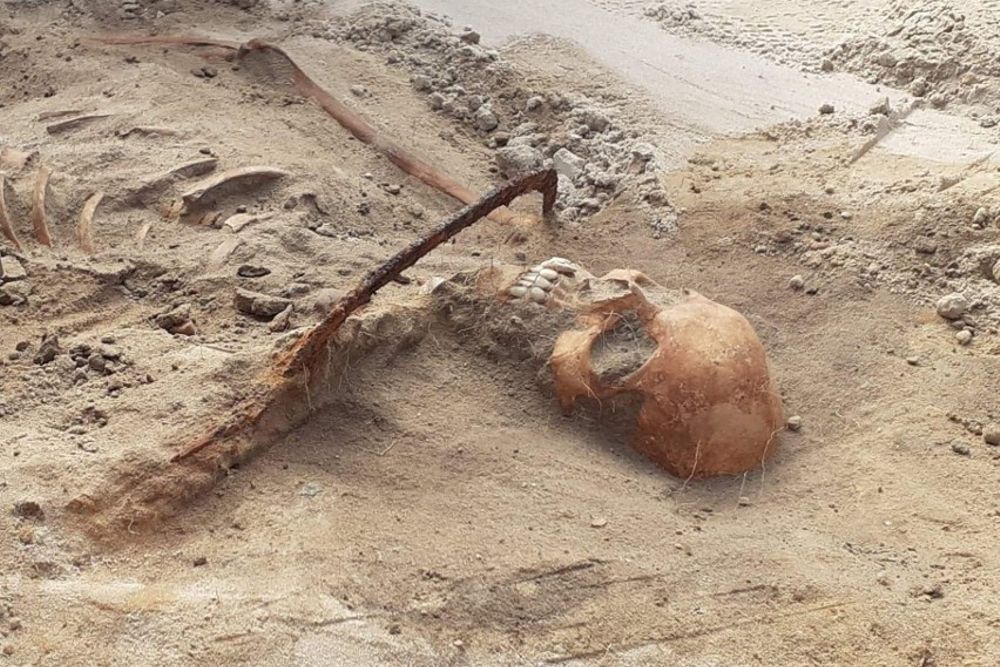
A skeleton of what archaeologists believe may have been a 17th-century female vampire has been discovered near Bydgoszcz in Poland.
The team of researchers from Toruń Nicholas Copernicus University found that the body in the village of Pień had a sickle placed around its neck to prevent her from returning to mortality, as well as a padlock on the big toe of her left foot.
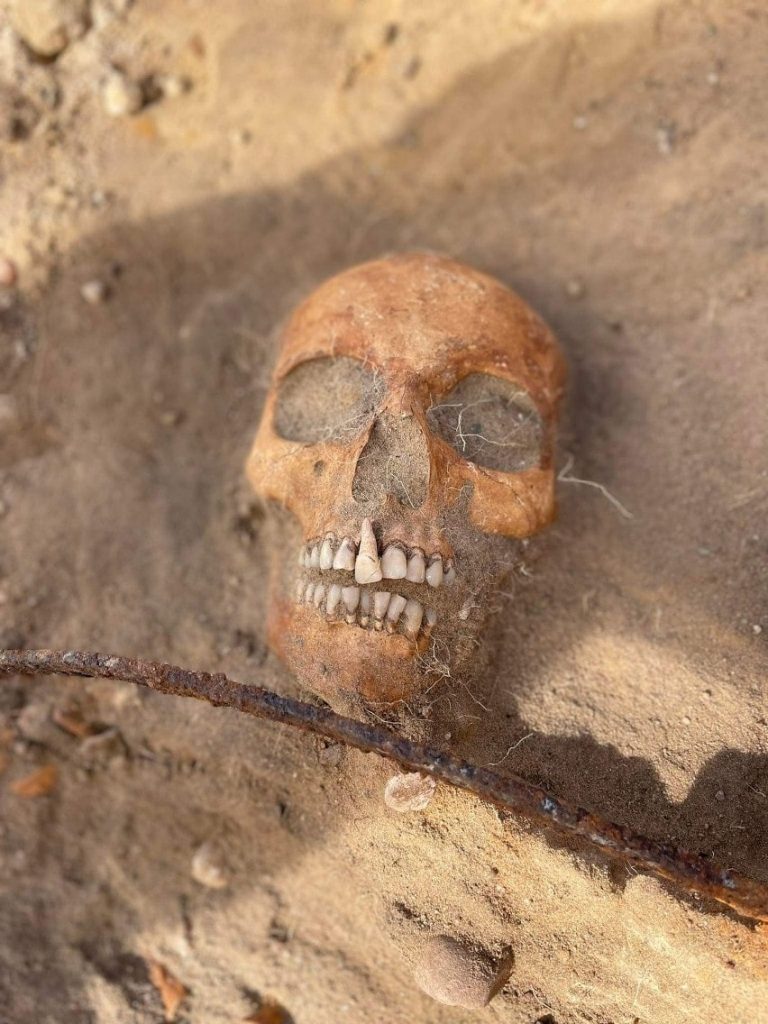
Researchers also discovered the skeletal remains had a silk cap on its head, indicating she had held a high social status and had a protruding tooth.
The researchers said the find was a first for Poland and the discovery was unique.
The unfortunates marked as witches or vampires from time immemorial were feared even after apparent death. People went very far to prevent a return from the tomb.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Professor Dariusz Poliński, the Nicholas Copernicus University, who headed the team said that this example of the anti-witchcraft practice was unusual.
Professor Dariusz Poliński said: “Ways to protect against the return of the dead include cutting off the head or legs, placing the deceased face down to bite into the ground, burning them, and smashing them with a stone.”
However, in this instance, a different technique that had never before been used on Polish soil—a sickle positioned across the neck—was used.
“It was not laid flat but placed on the neck in such a way that if the deceased had tried to get up most likely the head would have been cut off or injured,” explained Poliński.
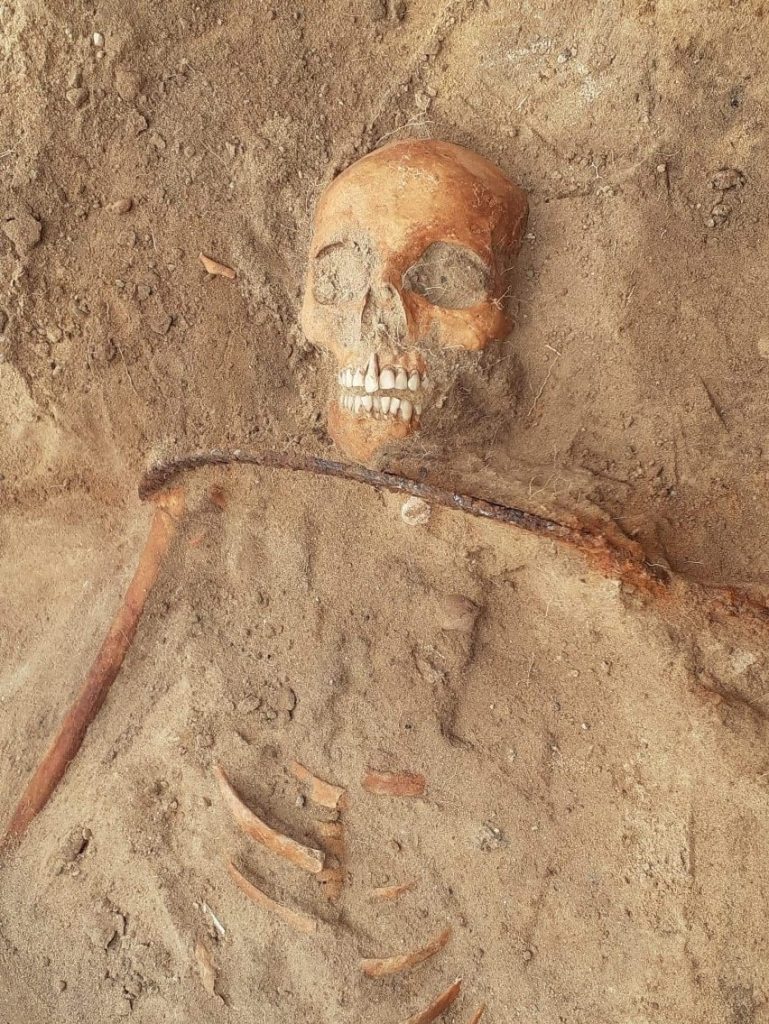

Another object in the grave was a closed padlock on the left foot’s big toe. According to Professor Poliński, “This symbolizes the closing of a stage and the impossibility of returning.”
Archaeologists noted that the woman was buried in an unusual manner and with great care, which is surprising given traditional anti-vampiric customs. She had a silk cap on her head, which was very pricey in the 17th century and, according to archaeologists, indicates high social status.
The woman’s protruding front tooth is another eye-catching feature. This has led to speculation that her unusual appearance led superstitious locals in the 17th century to label her a witch or vampire.
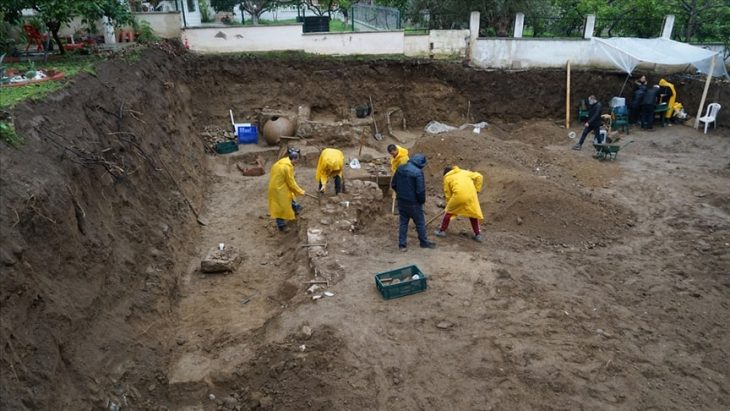
Archaeologists first discovered early medieval graves near Bydgoszcz in 2005-2009, when they found high-value grave goods such as silver jewelry, semi-precious stones from a necklace, a bronze bowl, and silk clothing fragments. They returned this year in the hopes of finding more. When they failed to do so, they focused on a nearby, agriculture-damaged, 17th-century cemetery.
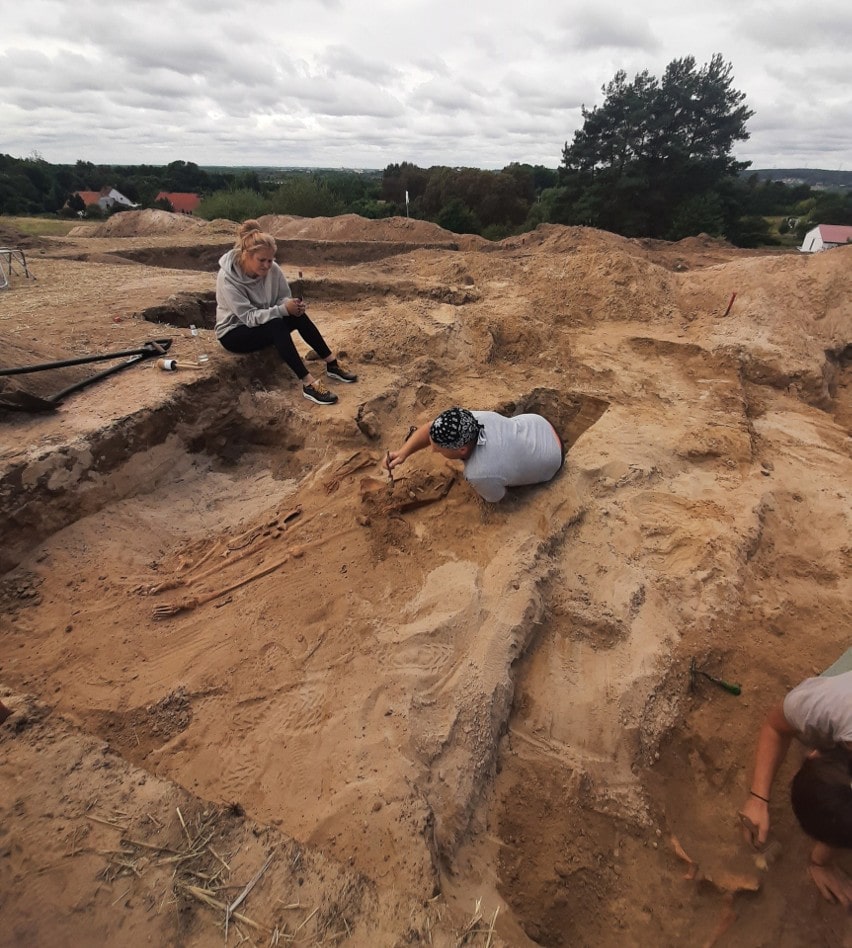

The area in the danger was examined by the archaeologists. They discovered the intriguing grave—which they immediately recognized as an anti-vampiric burial—during the course of their work.
The unearthed remains from Pień have been taken to Toruń, where they will undergo a detailed examination.
Despite the fact that this is the first instance of anti-vampire burial using a sickle across the neck in Poland, numerous other vampire suspects have been located.
Under Rynek Gówny in Kraków, a number of skeletons with severed heads were discovered in 2008.
2014 saw the discovery of a body in Kamie Pomorskie that had all of his upper teeth knocked out by having a piece of brick forced into his mouth. Additionally, his leg was drilled to prevent him from emerging from the grave.
Cover Photo: Mirosław Blicharski/Aleksander Poznań