In the center of Falster, southeast of Denmark, a man with a metal detector has made an important discovery. The discovery is so important that it could help write a few chapters for Danish history or at least the local history of Falster.
While Lennart Larsen was out on a rainy day and searching for anything of historical value, he suddenly heard a faint beep in his equipment, and when he checked the ground, he discovered small, interesting objects, unlike anything he had seen before.
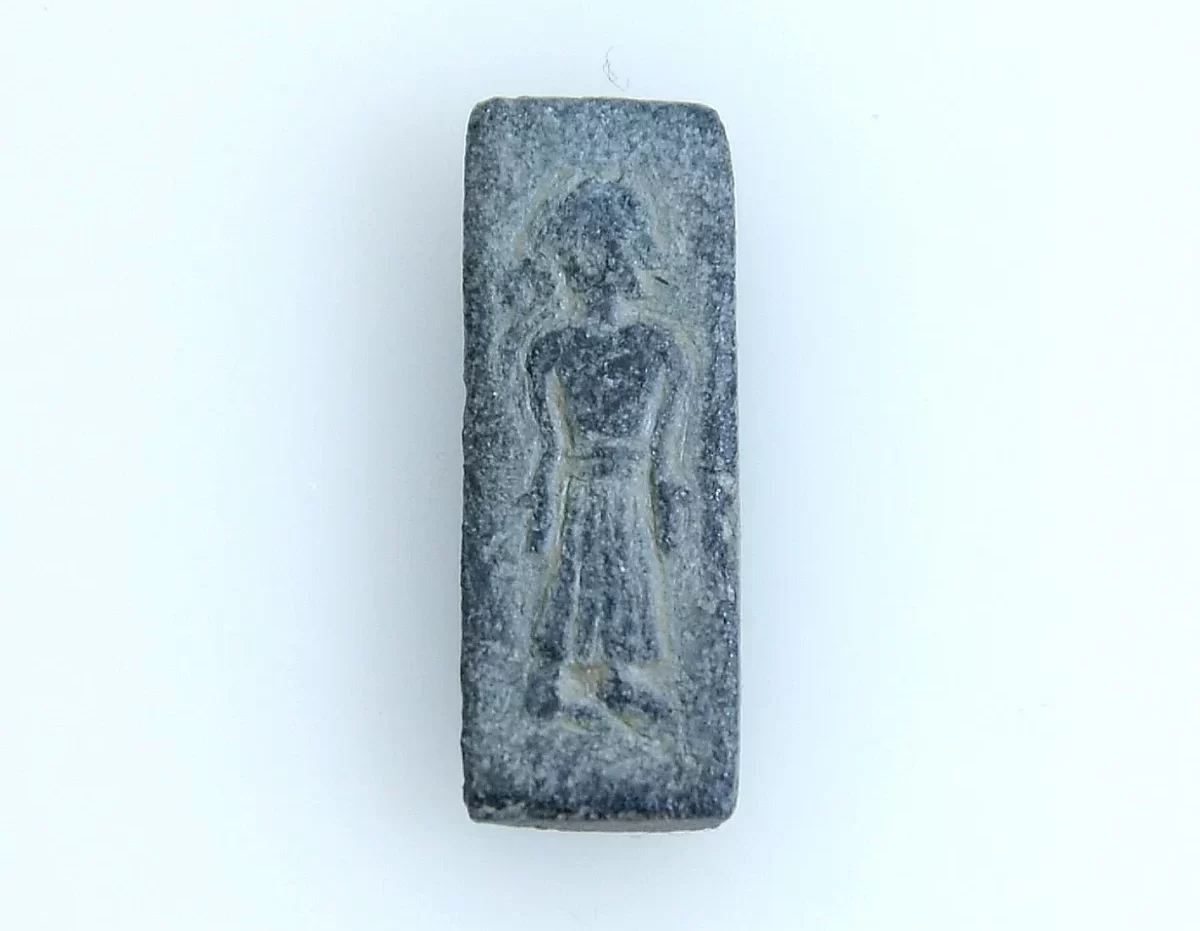
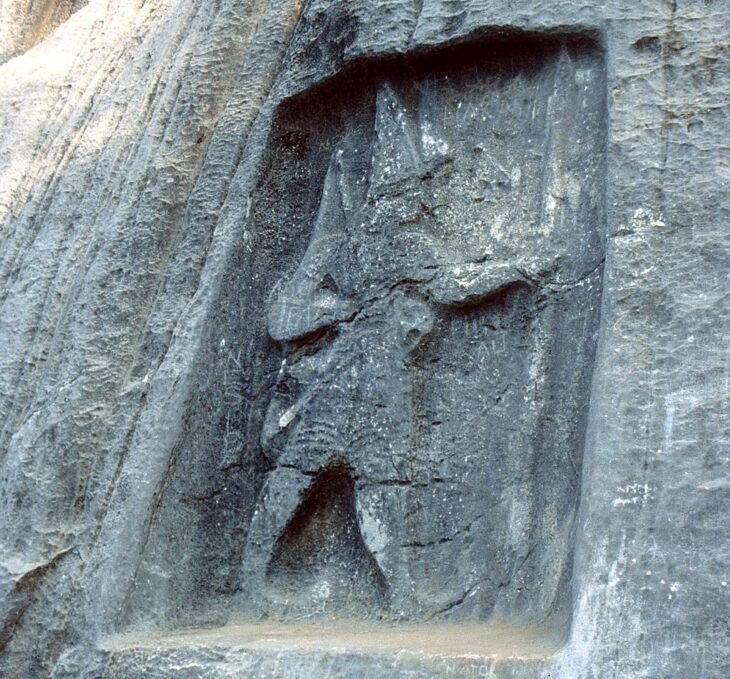
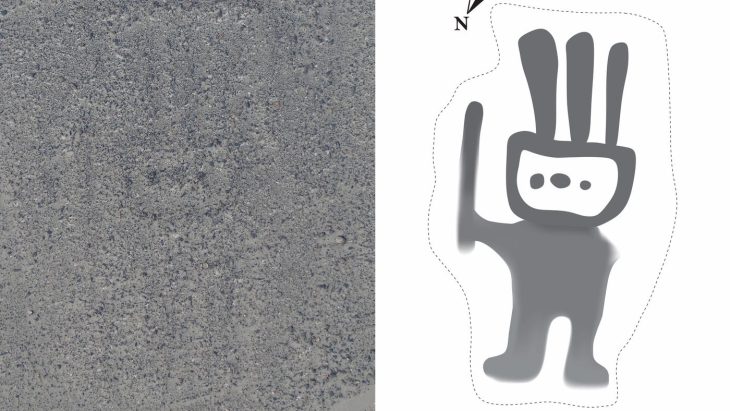
A faint beep has indeed revealed a special stamp in the ground – a so-called Patrice – that was used to make gold images, which are believed to be gifted to the gods.
The Museum Lolland-Falster has been informed. The only two-centimeter-long object in Falster’s soil may be a trace of a former royal power on Falster, the museum said.
“This indicates that we are standing in a place that has meant some trade and probably also had some form of cultic activity. And although it’s a bit wild to say, it could also indicate that it was once a center of power on Falster,” museum inspector and archaeologist Marie Brinch from the Lolland-Falster Museum told Tv2 Øst.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
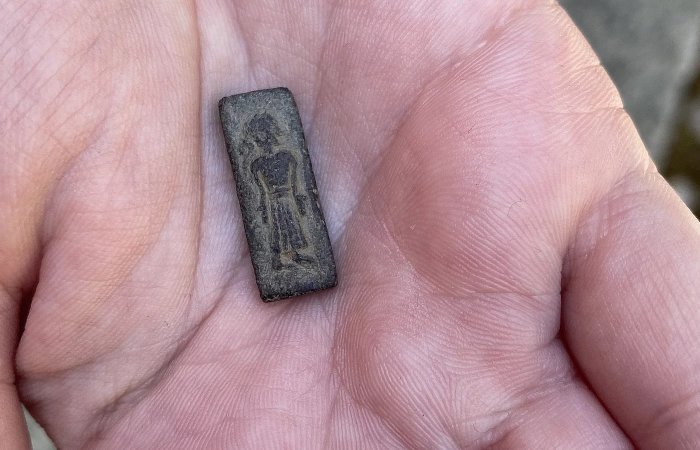

She emphasizes that the discovery was made in an area with names dating back to the Viking Age or even earlier and that the marshland was discovered in an area that had been sacrificed to the gods in the century preceding the stamp’s creation.
Archaeologists have before come across several signs of activity from the Iron Age and the Viking Age have been found, including an enormous shipyard and a large castle from the Viking Age at Falster. However, only a small number of discoveries have been made that can demonstrate where the island’s wealthy elite resided in the years prior to the beginning of the Viking Age. The new find may help to shed light on that.
Researchers have determined the tiny objects are stamps from the era just before the Viking Age. They were created between the years 500 and 700.
According to Margrethe Watt of the National Museum, who collects and researches ancient gold coins and stamps, these are extremely rare. There have only been 28 stamps discovered in the entire Nordic region, including the one from Falster, and it is a very unique stamp. South of the Baltic Sea, no stamps or gold coins have been discovered.
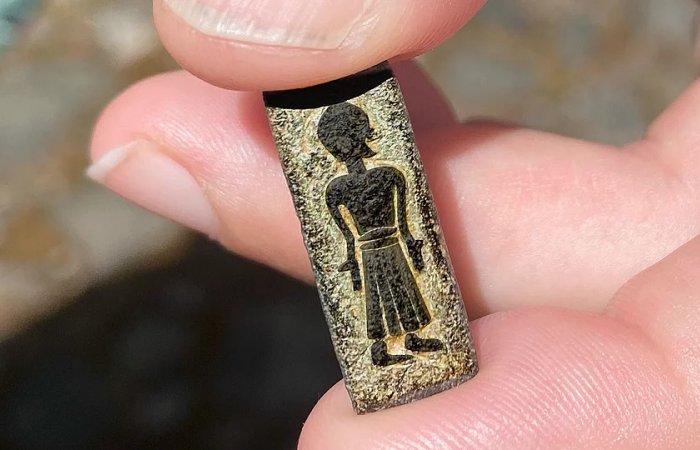

“The stamps are all very special. We only find them in the most important places of residence – those that we call the central places in the technical language. These are the places that we associate with the greatest magnates or kings. That’s the league we’re in here. And this stamp is at the same time very much for itself in its style,” she says.
“On the stamp from Falster, you can see a person in fine clothes, standing with their hands at a very special angle. The hands are down, and the palms are visible. It is something that we know in both Christian and pre-Christian cultures as either a sign of submission or a revelation. It is also a symbol that we see in many churches today, Watt explains.
Neither the god nor the king were shown as weak or flawed in any way. And you don’t see that on the stamp from Falster either.
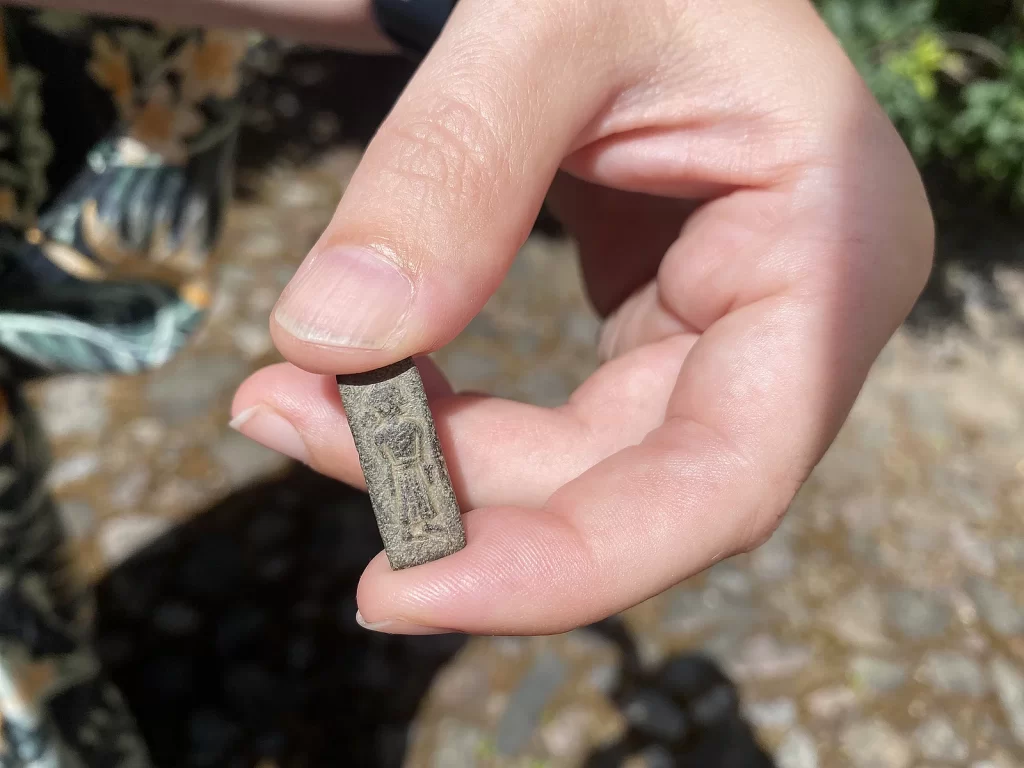

“This means that it is either a royal figure who submits to a god – or that it is a god who reveals himself to a human being,” she says.
“It is actually difficult to see if it is a man or a woman who is depicted. You would see that by the fact that there is a tuft of hair on the back of the piston. But it may well appear that there is, she says, and emphasizes that it requires further investigations to determine whether this is the case.
As there may be more finds in the ground at the site, Museum Lolland-Falster does not yet want to publish where the find was made – but states that it was made in central Falster.
Cover Photo: Museum Lolland Falster