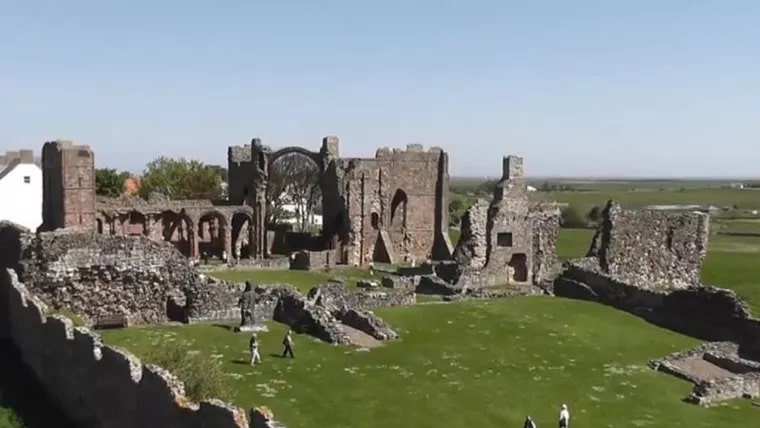
On the island of Lindisfarne, just off the coast of Northumberland, known in England as the “Holy Island“, archaeologists have uncovered the oldest prayer beads ever found in England.
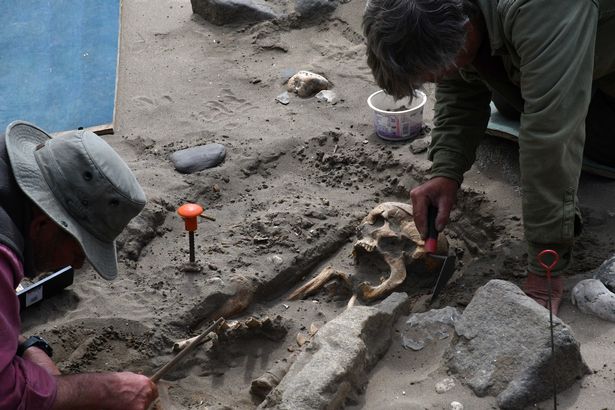
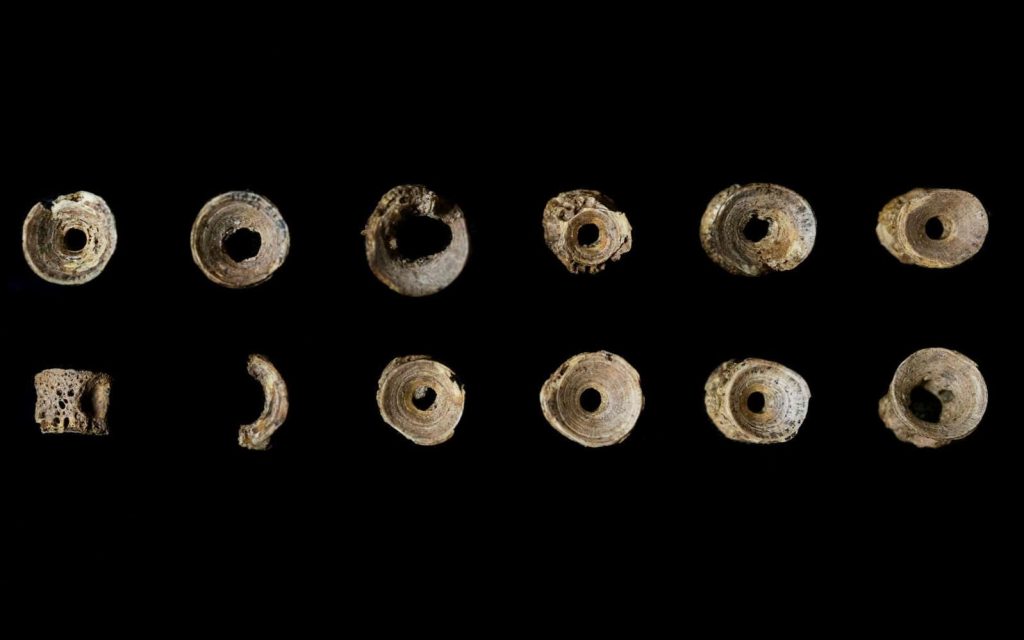
Fashioned out of salmon vertebrae in the 8th or 9th century, the necklace is the only artifact ever found in a Lindisfarne grave.
Fish, a significant early Christian emblem, were arranged in a group around the neck of one of the oldest bones, presumably, that of a monk interred at the renowned early medieval monastery.
Lindisfarne is also the birthplace of the Lindisfarne Gospels, one of the most celebrated illuminated books in the world. The Lindisfarne Gospels, the most remarkable text to survive from Anglo-Saxon England, were written there by monks, yet there have been few tangible finds at the site.
The Holy Island of Lindisfarne, a religious center founded in the 7th century by King Oswald of Northumbria, is famously the location of the first Viking raid of Britain in 793 A.D. The Vikings came back numerous times over the next century and the last of the monks left in 875, taking the exquisite Lindisfarne Gospels, written and illuminated by the monk Eadfrith around 700 A.D., with them.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
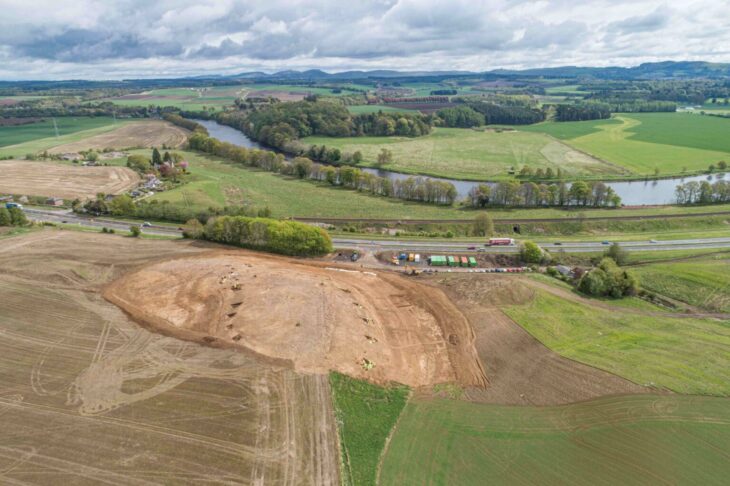
Following the Norman invasion, a monastery was established on the island, although little of the Anglo-Saxon monastery survives, and there have been no significant excavations until lately. Dr. David Petts of the University of Durham joined with the crowdsourcing platform DigVentures in 2014 to seek funding for an archaeological study of the Anglo-Saxon priory site. Since then, excavations at the site have been crowdfunded. (You may contribute to the 2022 fundraising here.)

The prayer beads may have been used for personal devotion, according to Dr. David Petts, the project co-director and a Durham University specialist in early Christianity, The Telegraph said.
“We think of the grand ceremonial side of early medieval life in the monasteries and great works like the Lindisfarne Gospels. But what we’ve got here is something which talks to a much more personal side of early Christianity,” he said.
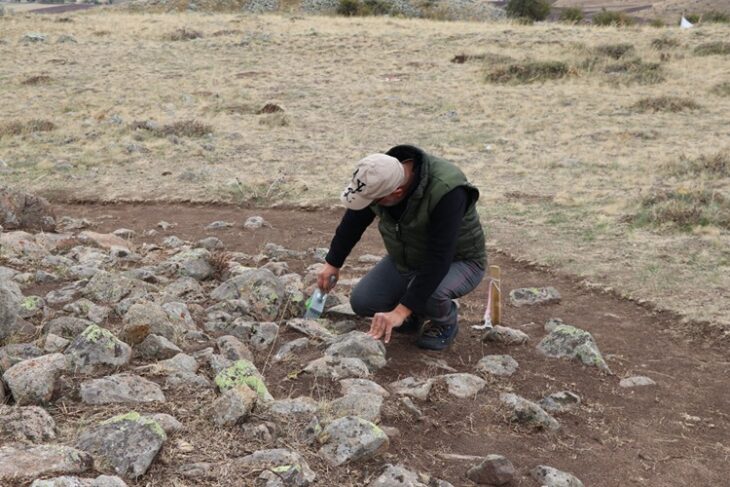
Petts noted that the beads were recognized by Marina Chorro Giner, a zooarchaeologist. “This bright, eagle-eyed researcher looked at them and said, actually these aren’t just fish bones, they’ve been modified and turned into something,” he said.
During the 2021 dig season, the beads were discovered on the neck of an adult guy who was most likely a monk. The holes in the vertebrae through which the spinal column runs were enlarged, either during the making of the necklace and/or over time as the bones wore against the threading. Fish were one of the earliest recognized Christian emblems, therefore fish bones are both a thematically fitting material and a readily available local supply for devotional jewelry.
Cover photo: The tidal island of Lindisfarne or Holy Island in Northumberland, the U.K (Photo: AwesomeBritain YouTube screencap)