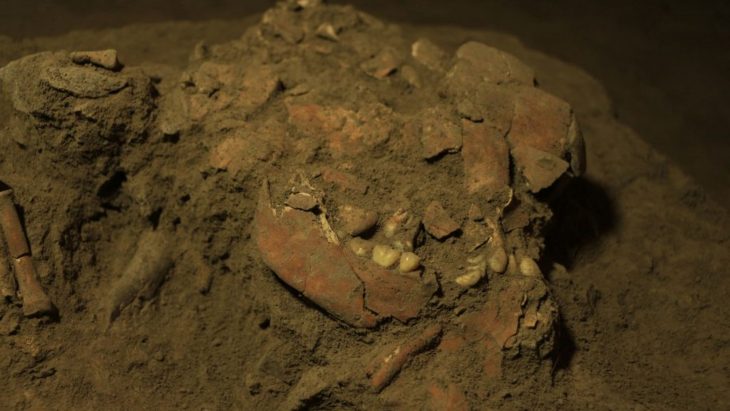
Researchers from the Federal University of São Paulo have managed to uncover the oldest known human viruses in a set of Neanderthal bones dating from over 50,000 years and they could soon recreate them.
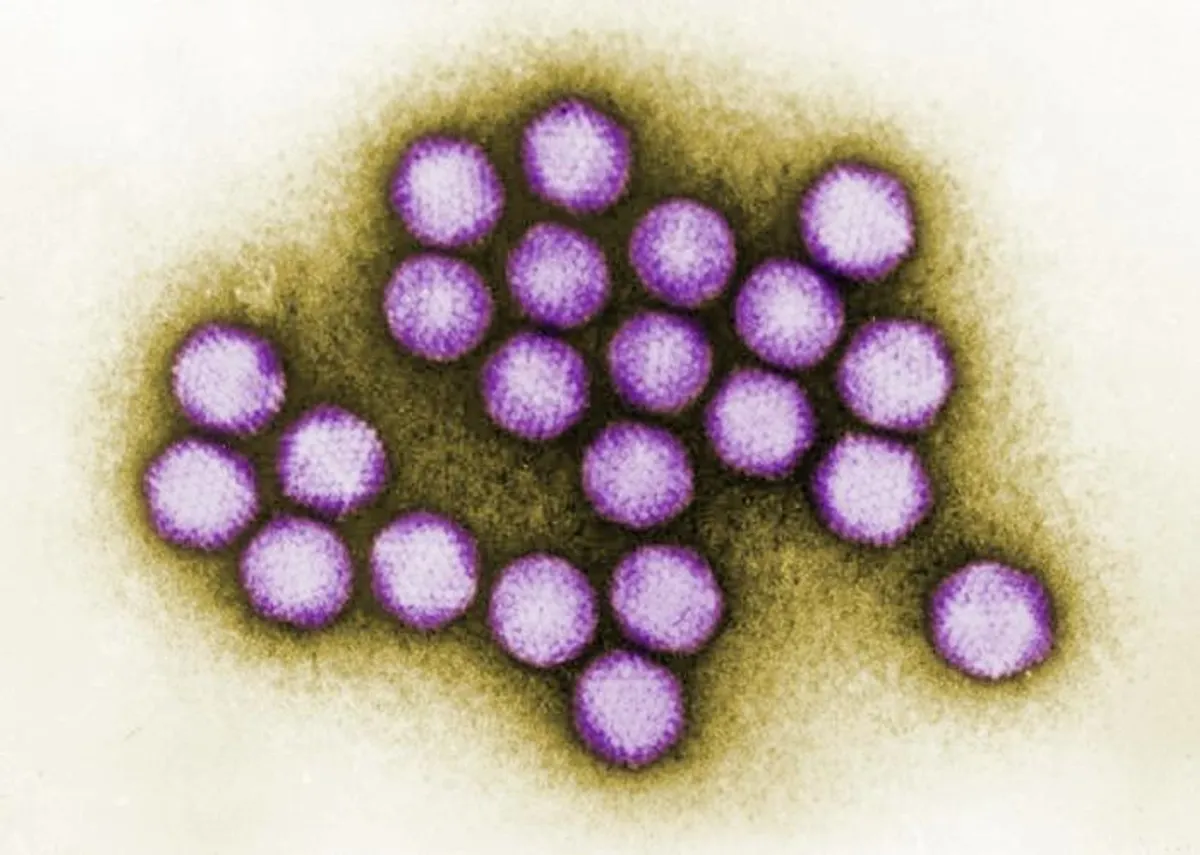
Two Neanderthals had their DNA tested, and the results showed traces of the papillomavirus (a sexually transmitted virus) and the adenovirus (adenovirus, which causes cold sores), as well as other viruses. The two prehistoric humans were male and their remains were found in a cave in Russia. Experts have long speculated that viruses may have caused the extinction of Neanderthals, and this most recent discovery could support that theory.
This suggests that Neanderthals may have been infected with the same viruses that affect humans today, according to the authors of a preprint that has not yet undergone peer review. It also shows that it was possible to identify portions of viral genomes in archaeological samples.
Adenoviruses, for example, can cause a wide range of illnesses from the pain in the butt that is the common cold, to a nasty bout of acute gastroenteritis. The overwhelmingly prevalent Epstein-Barr virus that can trigger mononucleosis and multiple sclerosis belongs to the herpesviruses. Papillomaviruses are perhaps best known for their association with cervical cancer.
The team who made the discovery now plan to try and synthesise the “Jurassic Park-like viruses” to see how they compare to modern ones. “These Jurassic Park-like viruses could then be studied for their reproductive and pathogenic traits and compared to present-day counterparts,’ Marcelo Briones, the study’s lead author told NewScientist.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
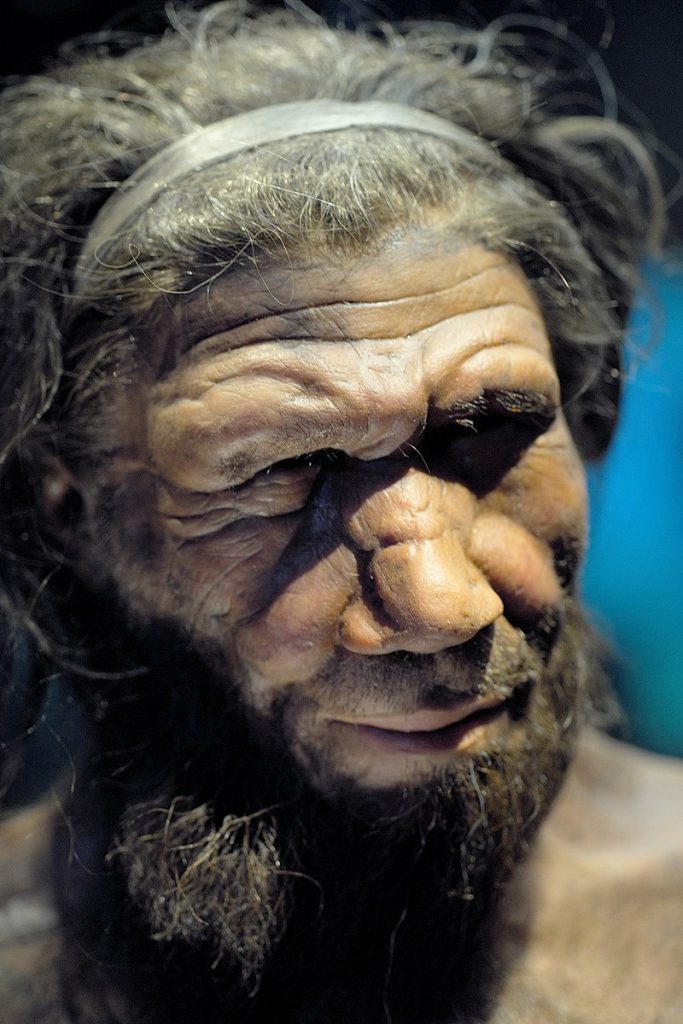

“I am sceptical that this could be achieved given the lack of full understanding of how the viruses’ DNA is damaged and how to reconstruct the recovered pieces into a full viral genome,” he added. “’Also, the host-virus interaction, especially in a completely different environment, is something to consider.” The remains were found in Russia’s Altai mountains in Siberia, in the Chagyrskaya cave. The remains were among a group of nine, found in 2022, who all shared DNA, meaning they were related.
Researchers were able to sequence genome data from the Neanderthals giving an astonishing glimpse into their DNA. They were able to ascertain that the viral traces in the remains did not get there from animals or modern humans contaminating them.
“Taken together, our data indicate that these viruses might represent viruses that really infected Neanderthals,” study author Marcelo Briones told New Scientist.
That is not to say that viruses alone could have led to the extinction of the Neanderthals—as the authors make clear in the paper—but it does lend support to the theory put forth by some scientists that viruses could have been involved in some way.
“To support their provocative and interesting hypothesis, it would be necessary to prove that at least the genomes of these viruses can be found in Neanderthal remains,” said Briones. “That is what we did.”
The study is available as a preprint on bioRxiv.
Cover Photo: Adenovirus is one of three viruses isolated from Neanderthal remains. CDC/ Dr. G. William Gary, Jr. / Public Domain