In a newly published study, archaeologists from the Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Paleoenvironment at the University of Tübingen show that early humans of the Middle Paleolithic had a more varied diet than previously assumed.
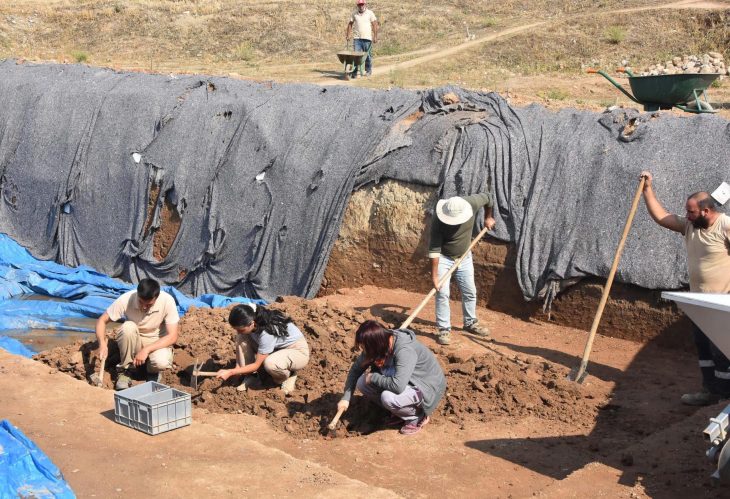
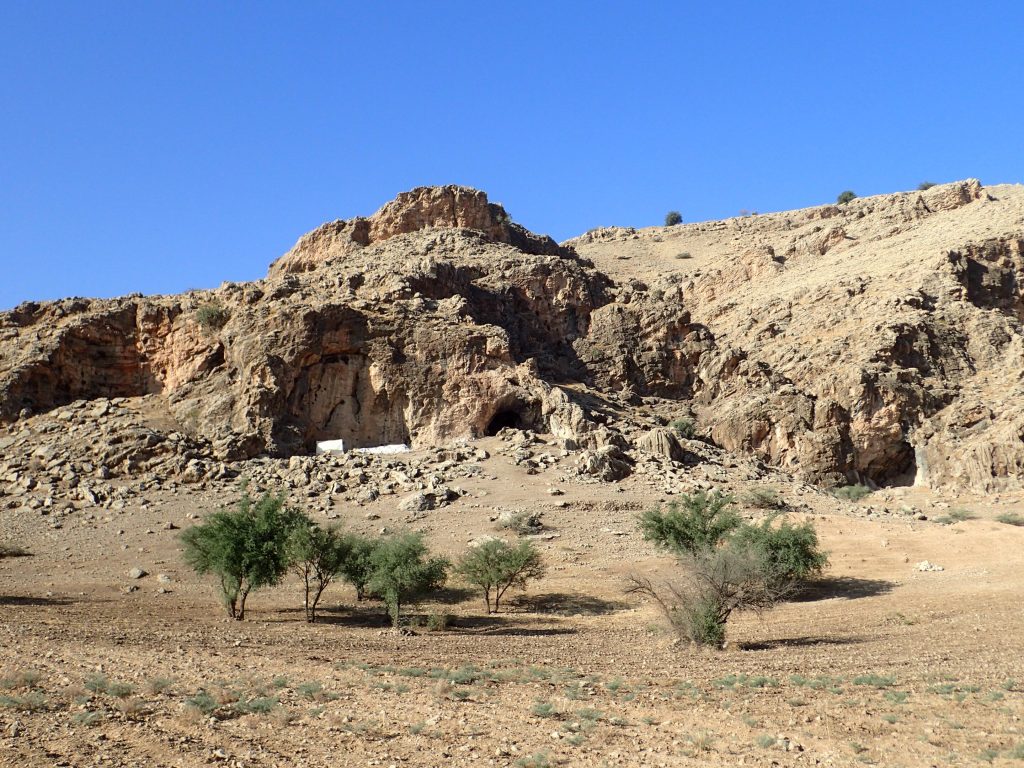
Researchers have analyzed the ancient animal remains from Ghar-e Boof, a Middle Paleolithic site in the southern Zagros of Iran that was occupied between 81,000 to 45,000 years ago.
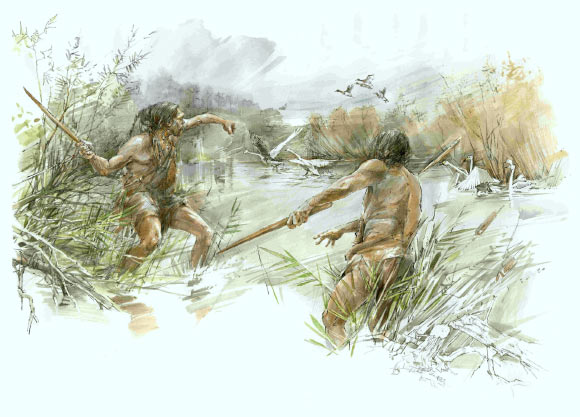
Their results suggest that tortoises constituted important dietary supplements for Middle Paleolithic hominins, and the occupants of Ghar-e Boof also exploited carnivores and possibly birds on occasion.
As early as the Upper Paleolithic, the earliest period of the Paleolithic, the ancestors of modern humans effectively hunted small and large mammals. “According to various studies, the hominins of the subsequent Middle Paleolithic—the period between 300,000 and 45,000 years ago—fed primarily on ungulates.
However, there is increasing evidence that, at least occasionally, tortoises, birds, hares, fish, and carnivorous mammals were also on the menu of Neanderthals and their relatives,” explains Mario Mata-González, first author of the new study and a doctoral student at the University of Tübingen.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

“Reconstructing the dietary habits of early hominins is one of the main objectives of archeozoological studies, which shed light on the way our ancestors adapted to and interacted with different environments,” he states.
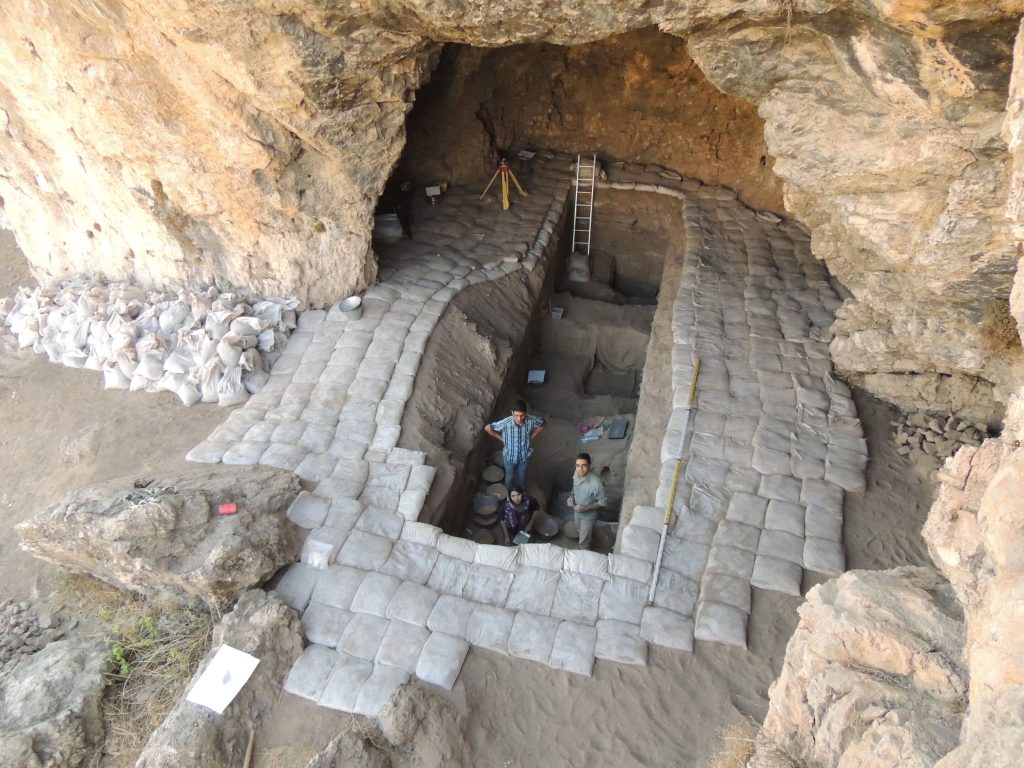
Together with other SHEP researchers, Mata-González has carried out the first comprehensive and systematic dietary analysis at a Late Pleistocene site in the southern Zagros Mountains with an age around 81,000 to 45,000 years.
“Not only are the Zagros Mountains the largest mountain range in Iran, but they are also considered a key geographical region for the study of human evolution in Southwest Asia during the Middle Paleolithic, in particular due to their heterogeneous topography and great environmental diversity,” he adds.
To date, archeozoological finds from the mountains have been almost exclusively limited to ungulates. However, the results from the Ghar-e Boof site show that the diet of the local hominins also included carnivorous mammals and turtles.
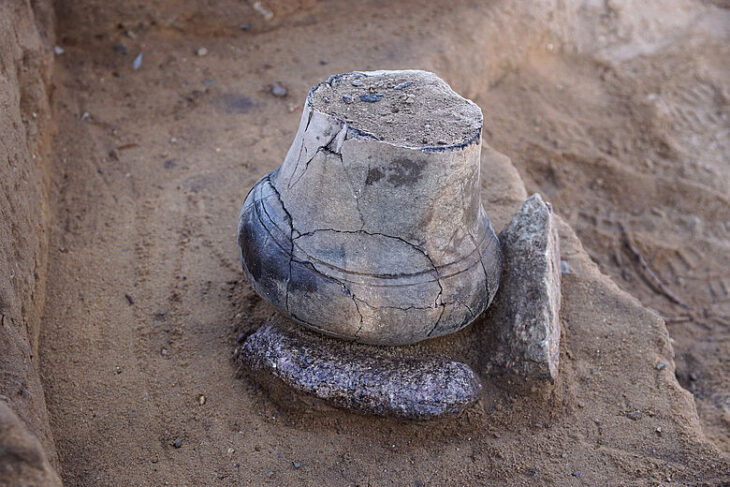
“More than 75% of the fauna at Ghar-e Boof consists of ungulates—from small to very large species. We mainly found remains of wild goats (Capra aegagrus) and gazelles (Gazella sp.). But we were also able to document smaller numbers of wild boar (Sus scrofa), red deer (Cervus elaphus), horses (Equus sp.), and wild cattle (Bos primigenius),” explains Mata-González. “In addition to ungulates, tortoises (Testudo sp.) are the most frequent species whose fossils we were able to recover from the approximately 18-square-meter large excavation area.”

The research team was also able to identify bones of various bird species and a few remains of carnivores, such as a red fox (Vulpes vulpes) and a large predatory cat—probably a leopard (Panthera cf. pardus). Cuts and traces of processing on some of the fossil bones point to early humans as the originators. According to the study, the tortoises were roasted in their shells before being eaten—this is how the researchers interpret the scorch marks on the external surfaces of the fossil tortoise shells.
The study’s last author, Prof. Nicholas J. Conard of SHEP, concludes, “The faunal remains from Ghar-e Boof are the first evidence that small game animals such as tortoises and birds as well as carnivores were utilized by hominins in the southern Zagros Mountains. Even if some of these species were consumed only sporadically, our findings show that the hominins of the Zagros region in the Middle Paleolithic had a more varied diet than previously assumed. This is consistent with findings in other parts of Eurasia.”
The study was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-45974-8
Cover image: An artist’s impression of Homo heidelbergensis hunting birds. Image credit: Benoit Clarys.