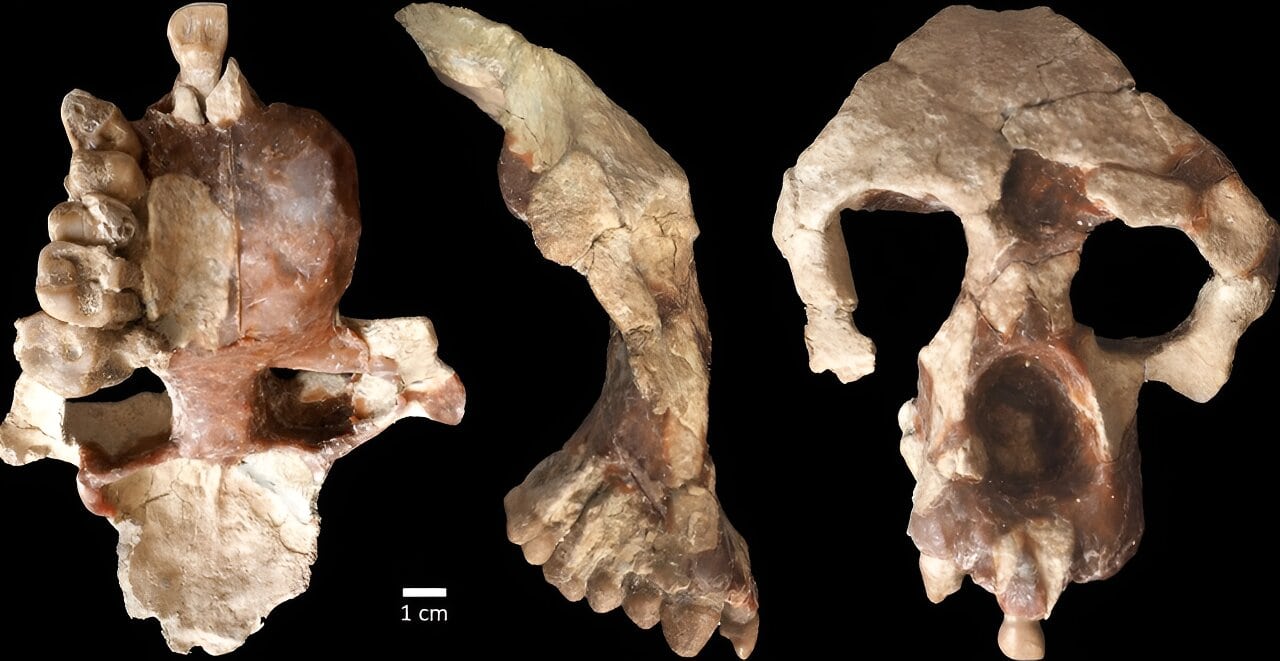
A recently discovered fossilized ape from a site in Turkey that is 8.7 million years old is inspiring scientists to reevaluate long-held theories about human evolution.
The study published in Communications on August 23 proposes that the ancestors of African apes and humans may have evolved in Europe before migrating to Africa between nine and seven million years ago.
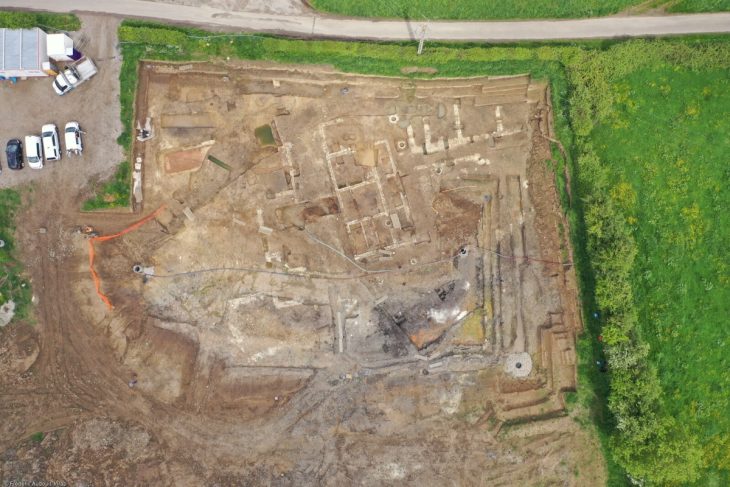
Analysis of a newly identified ape named Anadoluvius turkae recovered from the Çorakyerler fossil locality near Çankırı with the support of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism in Türkiye, shows Mediterranean fossil apes are diverse and part of the first known radiation of early hominines — the group that includes African apes (chimpanzees, bonobos and gorillas), humans and their fossil ancestors.
The findings are described in a new study published in Communications Biology co-authored by an international team of researchers led by Professor David Begun at the University of Toronto and Professor Ayla Sevim Erol at Ankara University.
“Our findings further suggest that hominines not only evolved in western and central Europe but spent over five million years evolving there and spreading to the eastern Mediterranean before eventually dispersing into Africa, probably as a consequence of changing environments and diminishing forests,” said Begun, professor in the Department of Anthropology in the Faculty of Arts & Science. “The members of this radiation to which Anadoluvius belongs are currently only identified in Europe and Anatolia.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The conclusion is based on an analysis of a significantly well-preserved partial cranium uncovered at the site in 2015, which includes most of the facial structure and the front part of the brain case.

“The completeness of the fossil allowed us to do a broader and more detailed analysis using many characters and attributes that are coded into a program designed to calculate evolutionary relationships,” said Begun. “The face is mostly complete, after applying mirror imaging. The new part is the forehead, with bone preserved to about the crown of the cranium. Previously described fossils do not have this much of the braincase.”
The researchers say Anadoluvius was about the size of a large male chimpanzee (50-60 kg) — very large for a chimp and close to the average size of a female gorilla (75-80 kg) — lived in a dry forest setting, and probably spent a great deal of time on the ground.
“We have no limb bones but judging from its jaws and teeth, the animals found alongside it, and the geological indicators of the environment, Anadoluvius probably lived in relatively open conditions, unlike the forest settings of living great apes,” said Sevim Erol. “More like what we think the environments of early humans in Africa were like. The powerful jaws and large, thickly enameled teeth suggest a diet including hard or tough food items from terrestrial sources such as roots and rhizomes.”
The animals that lived with Anadoluvius are those commonly associated with African grasslands and dry forests today, such as giraffes, wart hogs, rhinos, diverse antelopes, zebras, elephants, porcupines, hyaenas and lion-like carnivores. Research shows that the ecological community appears to have dispersed into Africa from the eastern Mediterranean sometime after about eight million years ago.
“The founding of the modern African open country fauna from the eastern Mediterranean has long been known and now we can add to the list of entrants the ancestors of the African apes and humans,” said Sevim Erol.
The findings establish Anadoluvius turkea as a branch of the part of the evolutionary tree that gave rise to chimpanzees, bonobos, gorillas and humans. Although African apes today are only known from Africa, as are the earliest known humans, the study’s authors — which also include colleagues at Ege University and Pamukkale University in Türkiye and the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in The Netherlands — conclude that the ancestors of both came from Europe and the eastern Mediterranean.
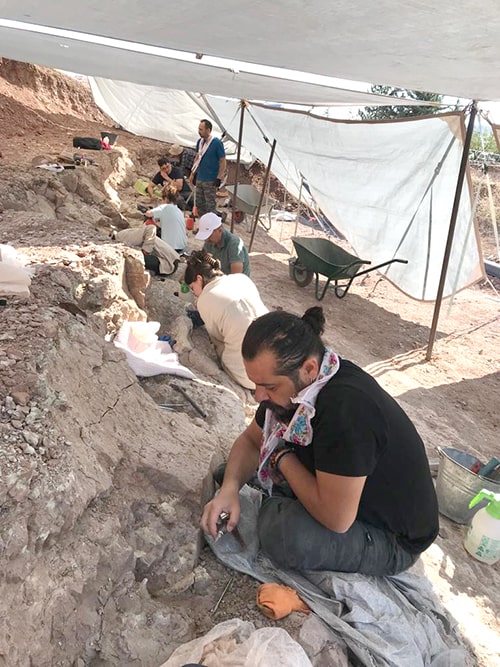

Anadoluvius and other fossil apes from nearby Greece (Ouranopithecus) and Bulgaria (Graecopithecus) form a group that come closest in many details of anatomy and ecology to the earliest known hominins, or humans. The new fossils are the best-preserved specimens of this group of early hominines and provide the strongest evidence to date that the group originated in Europe and later dispersed into Africa.
The study’s detailed analysis also reveals that the Balkan and Anatolian apes evolved from ancestors in western and central Europe. With its more comprehensive data, the research provides evidence that these other apes were also hominines and means that it is more likely that the whole group evolved and diversified in Europe, rather than the alternative scenario in which separate branches of apes earlier moved independently into Europe from Africa over the course of several million years, and then went extinct without issue.
“There is no evidence of the latter, though it remains a favorite proposal among those who do not accept a European origin hypothesis,” said Begun. “These findings contrast with the long-held view that African apes and humans evolved exclusively in Africa. While the remains of early hominines are abundant in Europe and Anatolia, they are completely absent from Africa until the first hominin appeared there about seven million years ago.
“This new evidence supports the hypothesis that hominines originated in Europe and dispersed into Africa along with many other mammals between nine and seven million years ago, though it does not definitively prove it. For that, we need to find more fossils from Europe and Africa between eight and seven million years old to establish a definitive connection between the two groups.”
Cover Photo: A new face and partial brain case of Anadoluvius turkae, a fossil hominine — the group that includes African apes and humans – from the Çorakyerler fossil site located in Central Anatolia, Türkiye.
Photo credit: Sevim-Erol, A., Begun, D.R., Sözer, Ç.S. et al.