Cahokia is the largest and most significant urban settlement of the Mississippian culture, known for creating massive earthen platform mounds throughout the southeast, east, and Midwest of the United States approximately 500 years before European contact.
These were not the Mexican Maya or Aztec people. About 700 A.D., this culture emerged in the Mississippi Valley, in what is now Illinois, and it vanished roughly a century before Columbus arrived in America. The ancient civilization’s massive remains stand as one of the best-kept archaeological secrets in the country.
Without a doubt, Cahokia was one of North America’s most sophisticated societies. Nevertheless, a lot remains to be discovered about its mysterious past, especially about its fall, which has been the subject of continuous discussion. This pre-Columbian city had 20,000 residents spread over six square miles at its height, receiving the moniker “City of the Sun.”
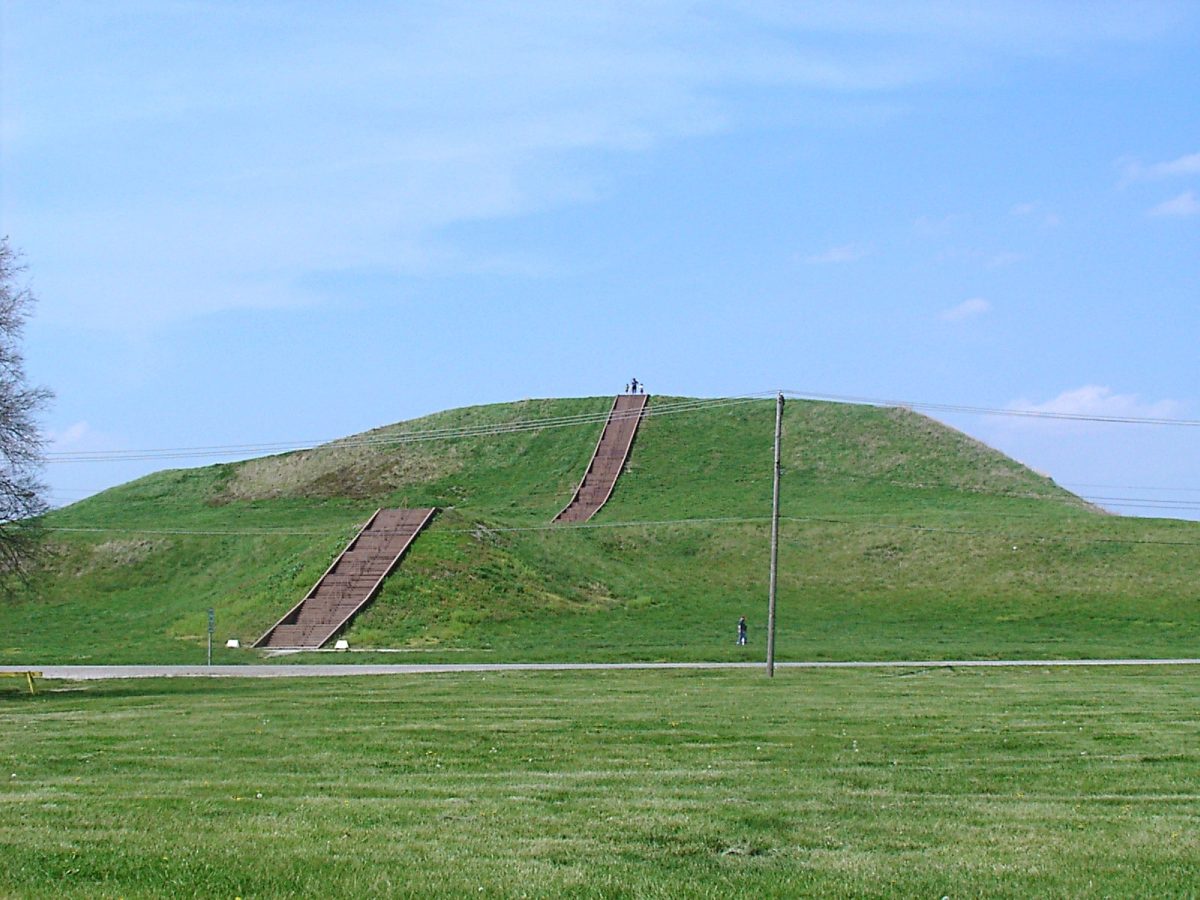
With 120 earthen mounds, Cahokia was the largest city ever built north of Mexico prior to the arrival of Columbus. Numerous of them were massive pyramids with square bottoms and flat tops that served as enormous pedestals for the residence of civic leaders. The largest earthwork in the Americas, the 100-foot Monk Mound, rose at the large plaza in the city’s center.
No one knows the Cahokians’ ethnicity, language, songs, or even what they called themselves. The name “Cahokia” is a misnomer. Cahokia was multi-ethnic, metropolitan, and connected to numerous distant societies through trade and exchange. Now, Cahokia is a UNESCO World Heritage site managed by the Illinois Department of Natural Resources.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
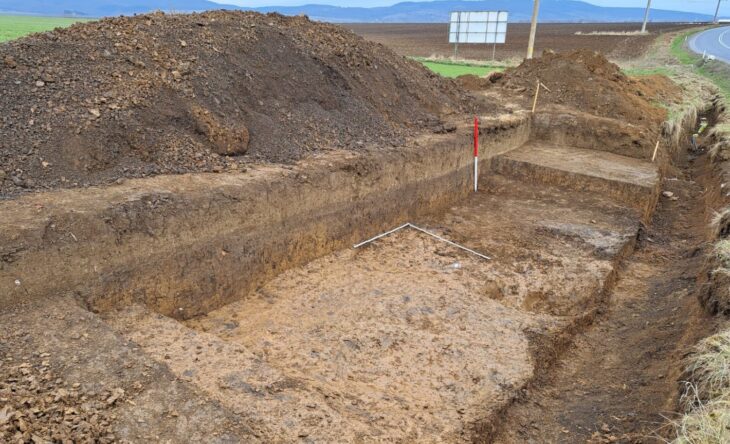
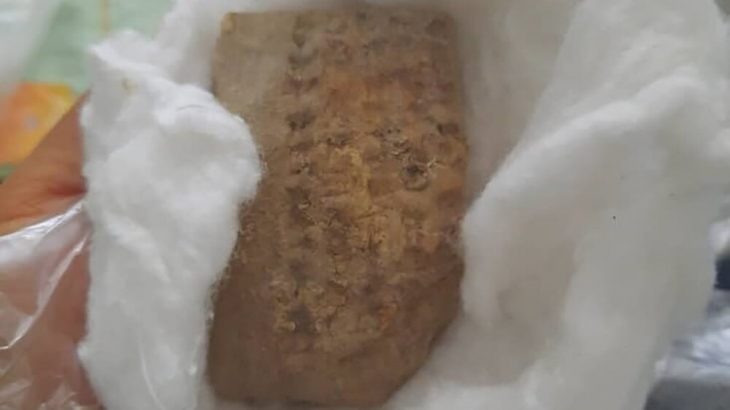
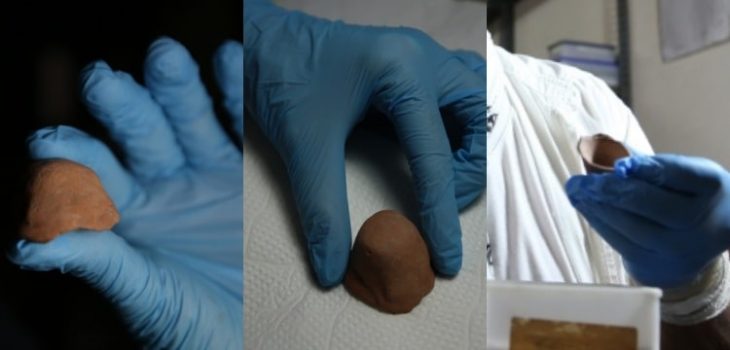
Archaeologists and students from Saint Louis University (SLU) have recently conducted a series of excavations on the western periphery of the Cahokia Mounds and made some surprising discoveries.
“I’m not interested in destroying features, just documenting them,” said Mary Vermilion, associate professor of anthropology and archaeology at Saint Louis University.
Amidst the Sterling Phase of the Mississippian Period, approximately AD 1100–1200, the team discovered wall trenches, microdrills, ceramics, and structures that date back 900 years. According to the archaeologists, the discoveries shed new light on a critical period in the chiefdom’s history, coinciding with Cahokia’s rapid population growth.
To find out if there are any more mounds or archaeological features within the acres of dense forests and marshy land close to the site’s main complex, St. Louis University and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency conducted an aerial survey using Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) and Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR).
Researchers from St. Louis University and the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency will soon embark on an ambitious project to create the most comprehensive and reliable 3D map of the Cahokia Mounds. This endeavor aims to provide a detailed and accurate representation of the famed prehistoric site, which will serve as a valuable resource for future studies and research.
LiDAR, a remote sensing method that uses laser light to measure distances, will enable the team to identify and map previously undocumented portions of the 2,200-acre National Historical Landmark with unprecedented precision.
Cover Photo: Monks Mound