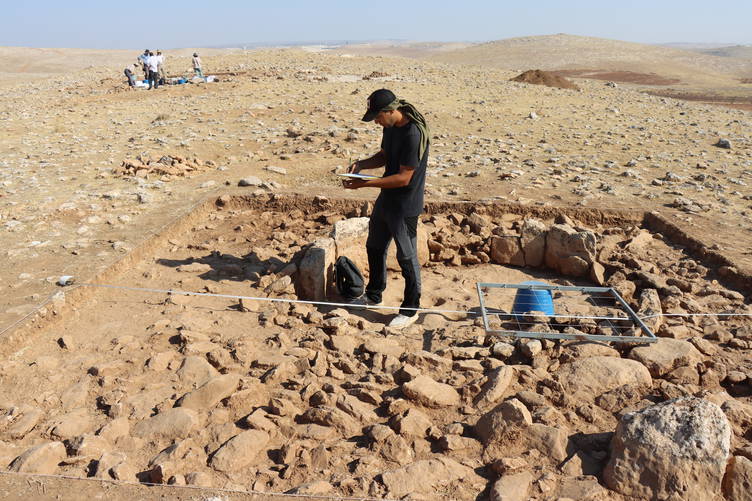
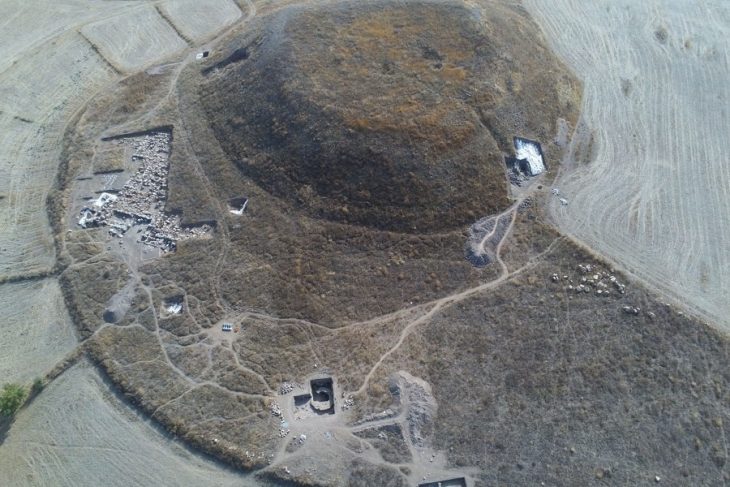
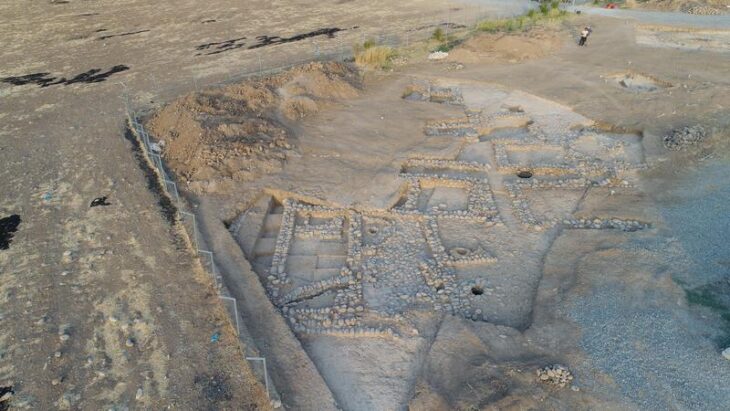
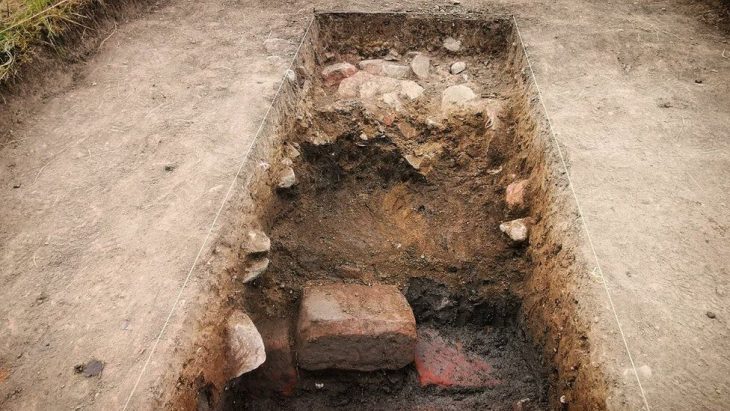
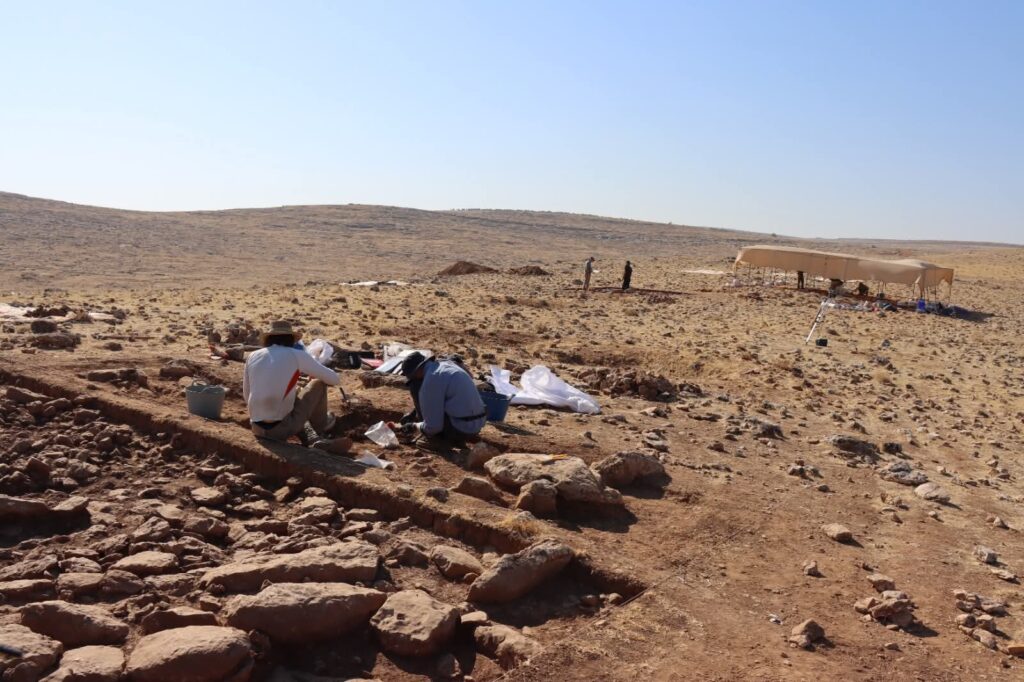
Archaeologists working at Mendik Tepe, a prehistoric mound in southeastern Türkiye, are unearthing evidence that may date earlier than the world-famous Göbekli Tepe, often hailed as the “zero point of history.” The excavation, part of the wider Taş Tepeler Project, is already reshaping our understanding of the Neolithic Revolution and humanity’s transition from hunter-gatherers to settled communities.
International Excavation Brings New Clues to Light
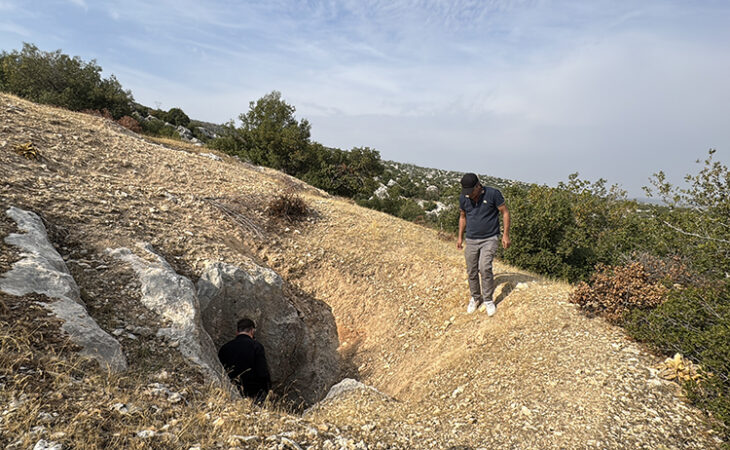
Mendik Tepe is located in the Eyyübiye district of Şanlıurfa, near Payamlı village, at the heart of the Fertile Crescent. The site was first identified by archaeologist Fatma Şahin and is now being excavated under the direction of Professor Douglas Baird of the University of Liverpool, in collaboration with the Şanlıurfa Archaeology Museum and the British Institute of Archaeology.
Baird emphasizes the importance of this new site:
“The finds suggest Mendik Tepe belongs to the very beginnings of the Neolithic. While connected to Göbekli Tepe and Karahantepe, its structures show unique forms and may even predate them.”
This makes Mendik Tepe a crucial piece in understanding how Neolithic culture emerged and spread across the Taş Tepeler region.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
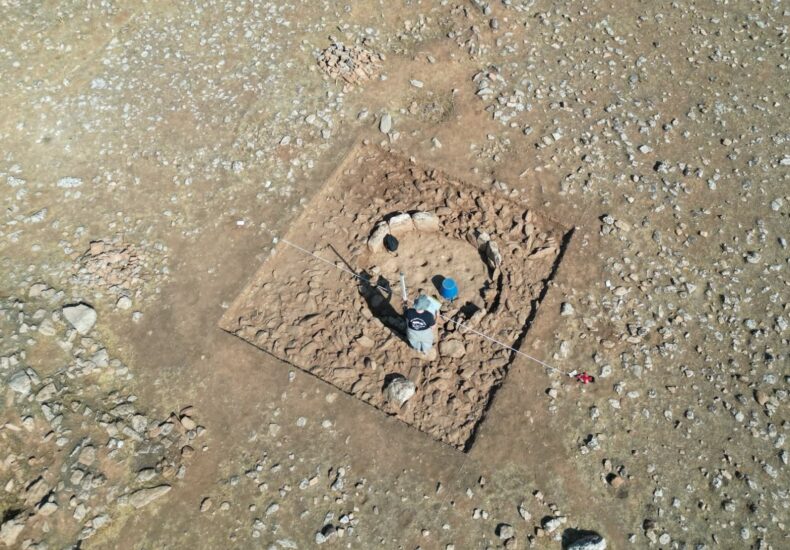

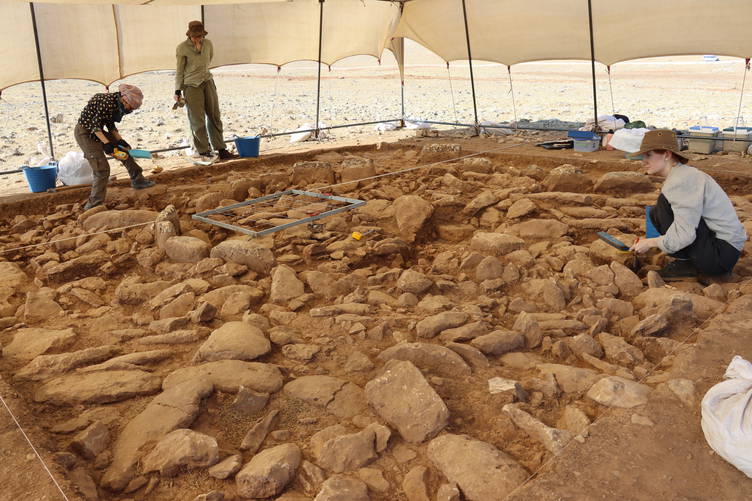
Different Building Sizes, Different Purposes
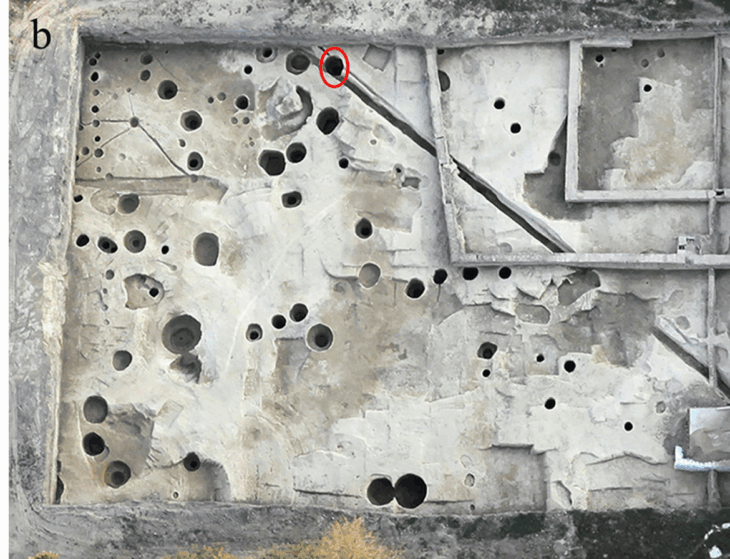
Excavations have revealed a variety of structures in terms of size and function:
Small buildings appear to have been used for storage or food preparation.
Medium-sized structures (about 4–5 meters wide) likely functioned as houses or communal dwellings.
Large structures, built with meticulous stonework, are believed to have had ritual or ceremonial significance.
This diversity suggests that Mendik Tepe was not merely a ritual center like Göbekli Tepe, but also a multi-purpose settlement where everyday life and spiritual practices coexisted.
Older Than Göbekli Tepe?
What excites archaeologists most is the possibility that Mendik Tepe could be older than Göbekli Tepe (c. 9600 BCE). Recent dating evidence from nearby Çakmak Tepe, another site under the Taş Tepeler Project, shows striking similarities in age. If confirmed, these findings could push back the timeline of monumental architecture in human history.
Unlike Göbekli Tepe and Karahantepe, known for their iconic T-shaped pillars, Mendik Tepe features upright stones in different forms, marking a distinctive architectural identity. This difference may point to a transitional phase in early human construction methods.

Part of the Taş Tepeler Network
Mendik Tepe is one of more than 12 Neolithic mound sites in the Şanlıurfa region, collectively known as Taş Tepeler (Stone Hills). Together, they form one of the most significant prehistoric landscapes in the world.
These interconnected sites reveal how early farming communities experimented with architecture, ritual, and social organization. Sites like Sayburç with its reliefs and Çayönü Tepesi with non-T-shaped pillars share parallels with Mendik Tepe, strengthening the idea of a diverse but interconnected Neolithic culture.
A Window Into the Birth of Civilization
Archaeologists believe the discoveries at Mendik Tepe could transform our understanding of the Neolithic Revolution – the period when humans shifted from mobile hunting groups to permanent settlements and farming societies.
This transformation, which began in southeastern Türkiye over 11,000 years ago, laid the foundations for modern civilization. With Mendik Tepe now entering the spotlight, scholars anticipate new insights into:
How early humans organized communal and ritual spaces.
The role of food storage and production in the rise of permanent settlements.
The spread of architectural traditions across the Fertile Crescent.

Looking Ahead
The Mendik Tepe excavations are still in their early stages, but findings already suggest the site could be one of the most significant archaeological discoveries of the 21st century. As Prof. Baird notes, ongoing research will reveal whether this little-known mound truly predates Göbekli Tepe and reshapes the history of the Neolithic world.
For now, one thing is certain: Mendik Tepe is not just another dig site, but a key to unlocking humanity’s first steps into civilization.