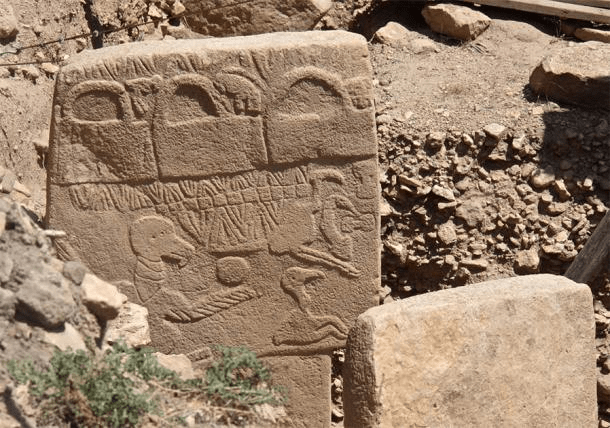
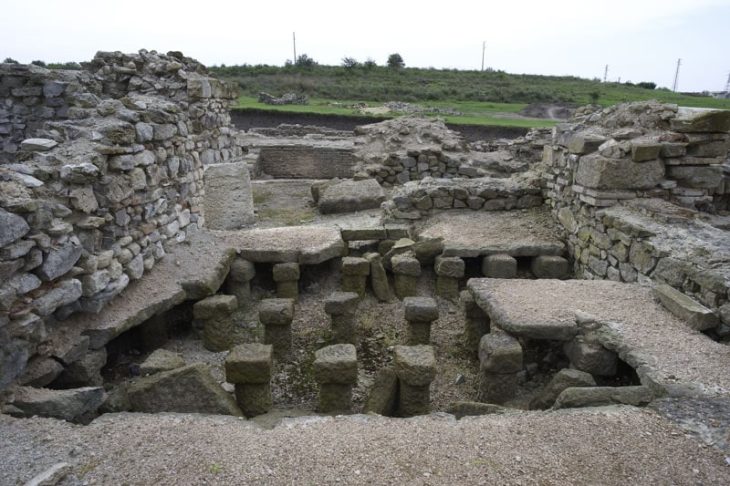
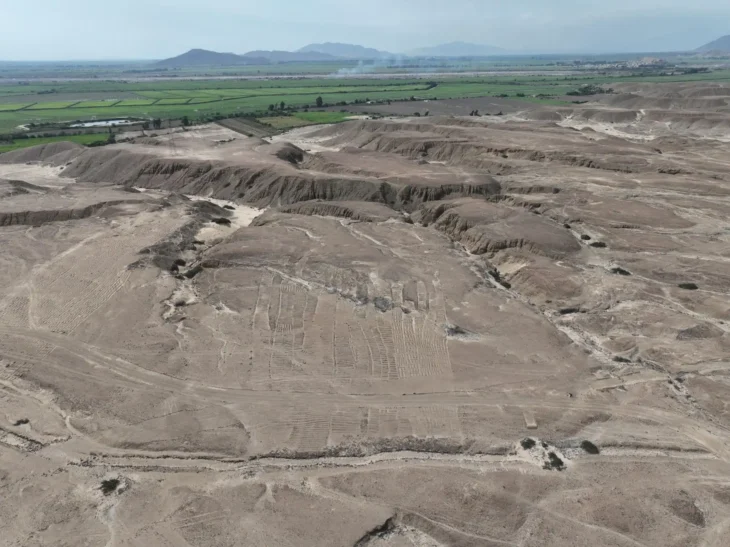
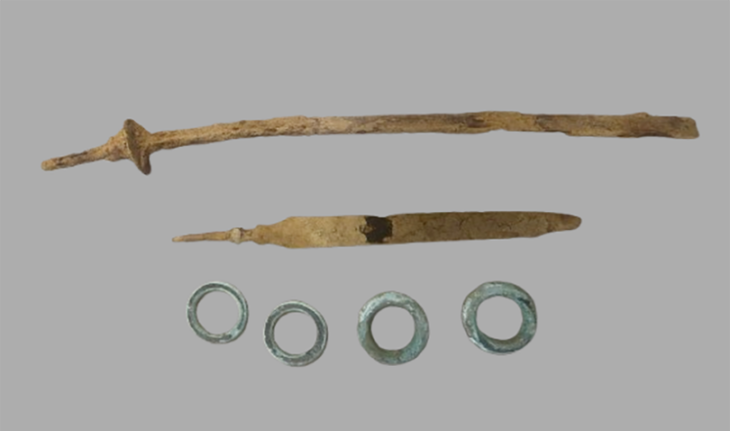
Karahantepe’s ancient site, which is home to Neolithic-era T-shaped obelisks similar to the ones in the world-famous Göbeklitepe, will reveal the mysteries of the period.
While we have detailed information on Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages, the Prehistoric era still remains a mystery in some aspects as we have little or no records of human history from this period.
Therefore, Turkey’s prehistoric marvel of Göbeklitepe, located near Örencik village – 15 kilometers (10 miles) northeast the city of Şanlıurfa in the south of the country – comes to the fore as one of the important centers providing some information from this foundational era.
Dating back to nearly 12,000 years ago, the archaeological site was a settlement belonging to the Neolithic period. It was home to communities that made the transition from the hunter-gatherer lifestyle to sedentism.
The T-shaped limestone pillars found in Göbeklitepe are older than the invention of agriculture and are one of the first manifestations of human-made monumental architecture. The monuments, decorated with depictions of wild animals, geometrical figures, and a few abstract depictions of humans, are believed to have been used in social events and rituals.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
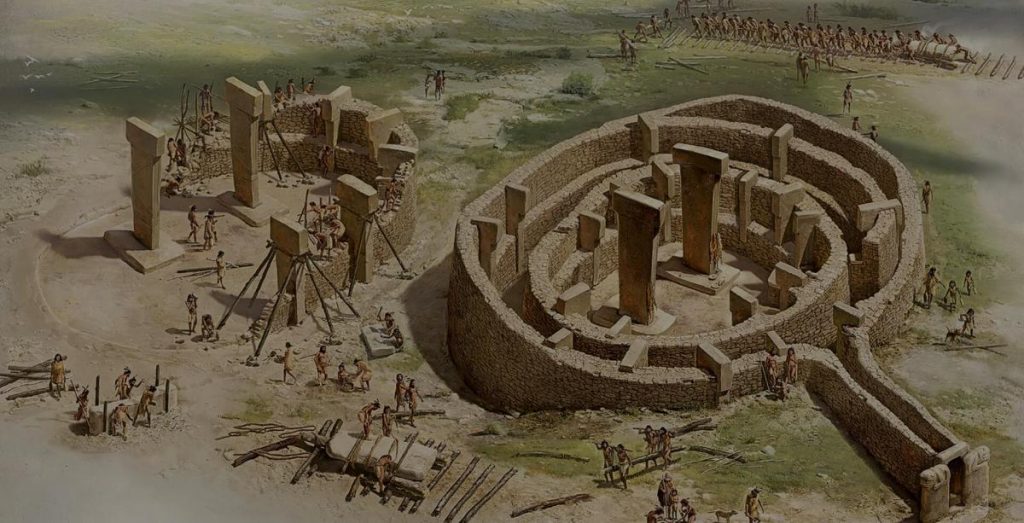

After Göbeklitepe showed a striking example of the first Neolithic settlements, the archaeology world understood that the lands of Şanlıurfa are vast and hold many mysteries yet to be revealed. So, Turkey launched works to unearth other significant Neolithic settlements around Göbeklitepe.
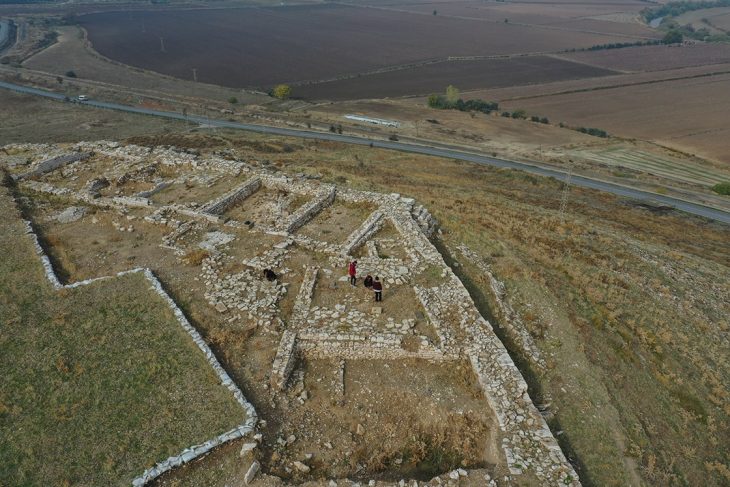
As part of the “Göbeklitepe Culture and Karahantepe Excavations” project, surface surveys were initiated two years ago by Istanbul University in the area, known as “Keçilitepe” by the people of the region. The works are headed by Professor Necmi Karul.
Taş Tepeler
The region of these settlements is named “Taş Tepeler,” literally meaning Stone Hills. Covering an area of 200 kilometers from one end to the other, Taş Tepeler is an Anatolian and Upper Mesopotamian territory that hosted the earliest settled communities.
Taş Tepeler features 12 main sites including Göbeklitepe. Some seven of these big and small sites are now excavation sites that will shed light on a crucial yet little-known period of history.
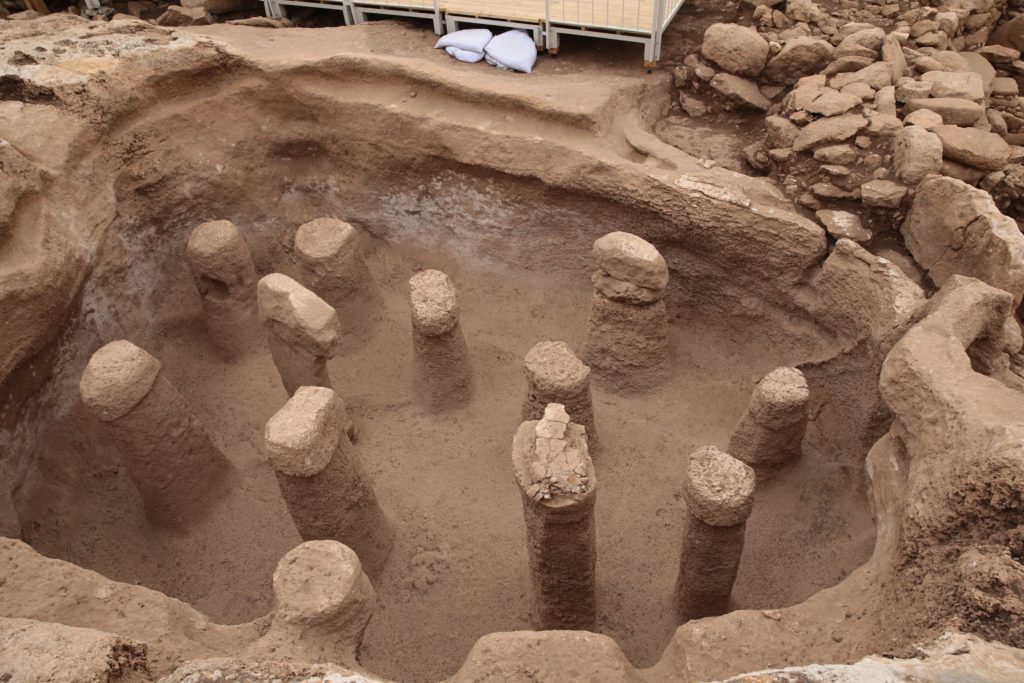

Among the sites of Taş Tepeler are Karahantepe, Harbetsuvan, Gürcütepe, Kurttepesi, Taşlıtepe, Sefertepe, Ayanlar, Yoğunburç, Sayburç, Çakmaktepe and Yenimahalle. As far as we know, Taş Tepeler is the first example of sedentism and social union on earth. In Taş Tepeler, human beings experimented with examples of organized labor and specialization for the first time.
Taş Tepeler is a crucially important region that proves to us the existence of other areas similar and contemporary to Göbeklitepe. Recent archaeological finds at the immediate surroundings of these locations support this significance. However, what we know is minimal when compared to what we will learn with excavations in the region.
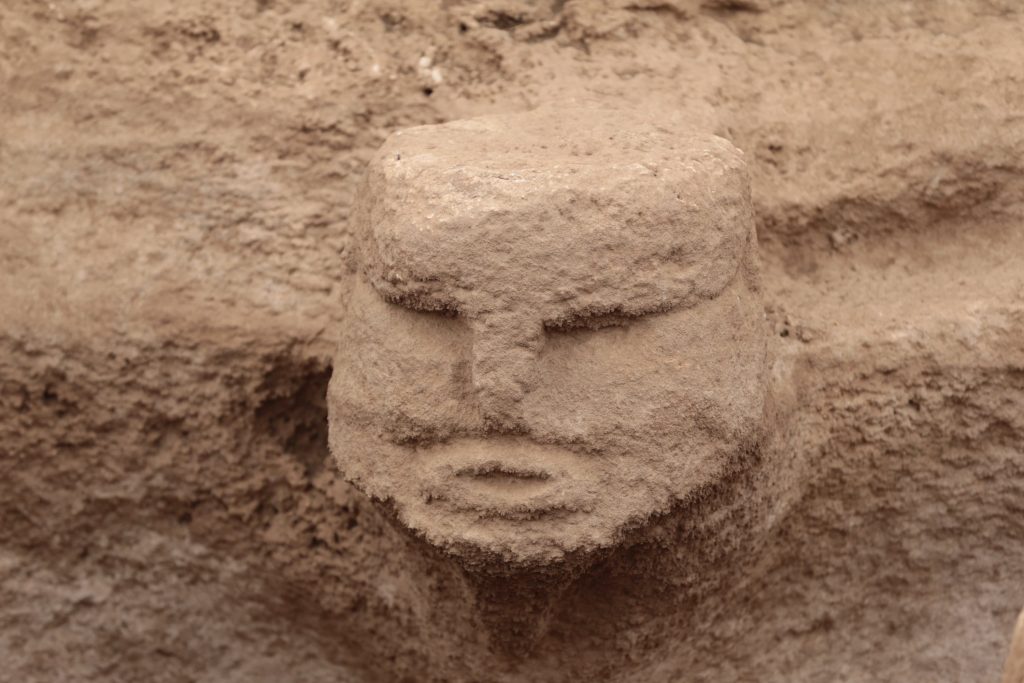

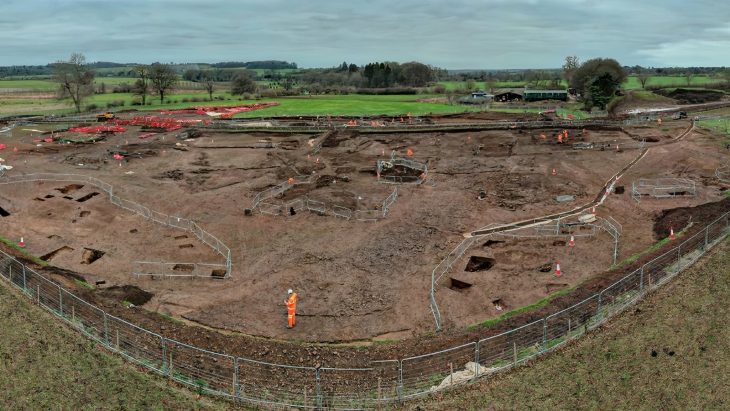
Karahantepe, which is a 46-kilometer drive from the city center in Şanlıurfa, was discovered in 1997. The first excavations were launched on the site in 2019. Karahantepe houses more than 250 T-shaped megaliths featuring animal depictions. Stelae with human depictions and three-dimensional human sculptures were also found in the site, which distinguishes it from Göbeklitepe.
An exhibition featuring these stelae and sculptures has been opened at the Şanlıurfa Archaeological Museum.
Excavations are carried out by scientific delegations and the Şanlıurfa Museum Directorate under the leadership of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums. Turkey will provide more financial support and staff to these seven sites and also will launch excavations in the rest soon. The Ministry of Culture of Tourism has also invited foreign experts from many countries to join the works in the sites.