A recent archaeological breakthrough on Japan’s sacred Okinoshima Island has unveiled an ornately decorated iron spear from the late Kofun period, offering a rare glimpse into the spiritual and political rituals of the ancient Yamato Dynasty. Hidden beneath rust and time for over a millennium, the spear has now been confirmed to contain intricate phoenix and vine motifs, inlaid with what is likely pure gold—using an advanced metalworking technique known as kinzogan.
A Sacred Relic from a Sacred Island
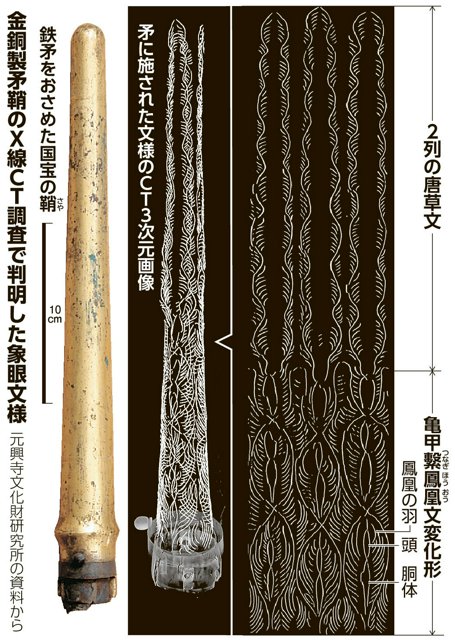
Discovered in 1954 but only recently scanned with high-resolution X-ray CT and X-ray fluorescence technology, the 30.5 cm-long spear had been sealed inside a gilt bronze sheath and found under a boulder on Okinoshima—an island long revered as a sacred space dedicated to marine rituals. The spear is now recognized as one of the finest examples of ritual weaponry from East Asia, with experts calling it “unparalleled in beauty and symbolic craftsmanship.”
According to Toshinori Mizuno, head of materials at the Archaeological Institute of Kashihara, “This spear demonstrates the Yamato state’s extraordinary dedication to the spiritual rites held on Okinoshima. Its complexity reflects both technical mastery and religious reverence.”
Okinoshima: Japan’s Island of the Gods
Located in the Genkai Sea, Okinoshima Island has been considered off-limits to the general public for centuries, and is still maintained under strict ritual purity by the Munakata Taisha Shrine, which manages the sacred island. Even today, women are not allowed to enter the island, and male visitors must undergo purification rituals before setting foot on its shores.
From the 4th to the 9th century, Okinoshima served as a central ritual site for the Yamato polity, Japan’s early imperial state, which performed elaborate ceremonies to pray for safe maritime voyages, particularly those involving diplomatic and trade missions to the Korean Peninsula. Offerings, known as hōnōhin, were dedicated to the sea deities believed to protect these journeys.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
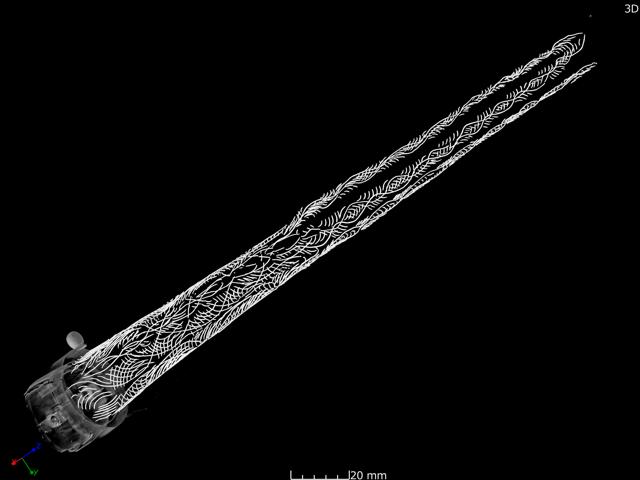
These rituals left behind a vast legacy: over 80,000 artifacts, including bronze mirrors, swords, glass beads, and now this ornate spear—all designated National Treasures of Japan.
Rediscovering Ancient Innovation
What makes this spear unique is not just its historical context, but the artistry itself. The embedded patterns, featuring phoenixes (hōō)—mythical creatures symbolizing peace and divine protection—are believed to represent an appeal for celestial favor. Experts suggest that the combination of gold inlay and arabesque patterns may indicate influences from continental Asia, possibly via the Korean Peninsula, while the construction remains distinctly Japanese.
The kinzogan technique seen in the spear involves carving intricate designs into metal and embedding gold wire or foil into the grooves—a process requiring extreme precision and often reserved for royal or sacred items.
According to Tadashi Nishitani, professor emeritus of archaeology at Kyushu University, “This discovery is without precedent in Japan. It confirms the scale and sophistication of state-level ritualism during the Kofun period, centered on Okinoshima’s sanctity.”
Continuing Efforts to Preserve Japan’s Spiritual Heritage
The Cultural Affairs Agency of Japan has allocated significant funding to scan and analyze over 4,200 metal artifacts from Okinoshima, as part of a long-term preservation project coordinated by the “Sacred Island of Okinoshima and Associated Sites in the Munakata Region” Preservation and Utilization Council.

This council includes Munakata Taisha, local government authorities, and cultural researchers, all working to protect and promote Okinoshima’s global cultural significance, recognized by UNESCO in 2017 as a World Heritage Site.
A Living Connection to the Past
Okinoshima continues to represent a rare, living connection to ancient Japan’s religious and political history. This latest discovery not only enhances our understanding of Kofun-period craftsmanship but also reaffirms the sacred island’s role as a spiritual epicenter of early Japanese statehood.
As the spear rests once again in protective storage, it stands as a shining symbol—both literally and historically—of a time when gods, rulers, and artisans converged on an island where the sea met the divine.
Cover Image Credit: The gilt bronze sheath containing the ancient spear tip was preserved at Munakata Taisha Shrine in Munakata, Fukuoka Prefecture, as of June 10. Photo: Kengo Hiyoshi
















