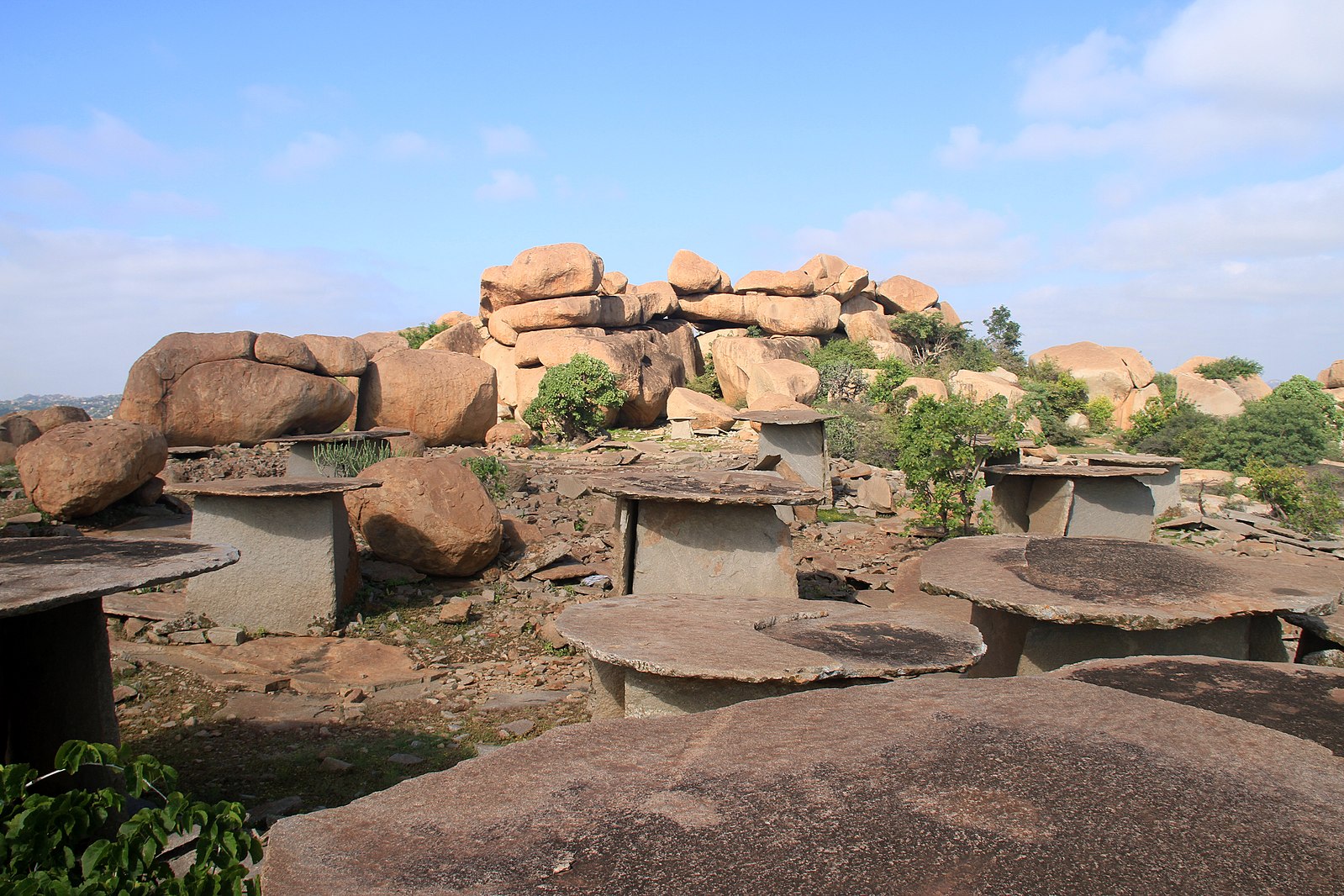
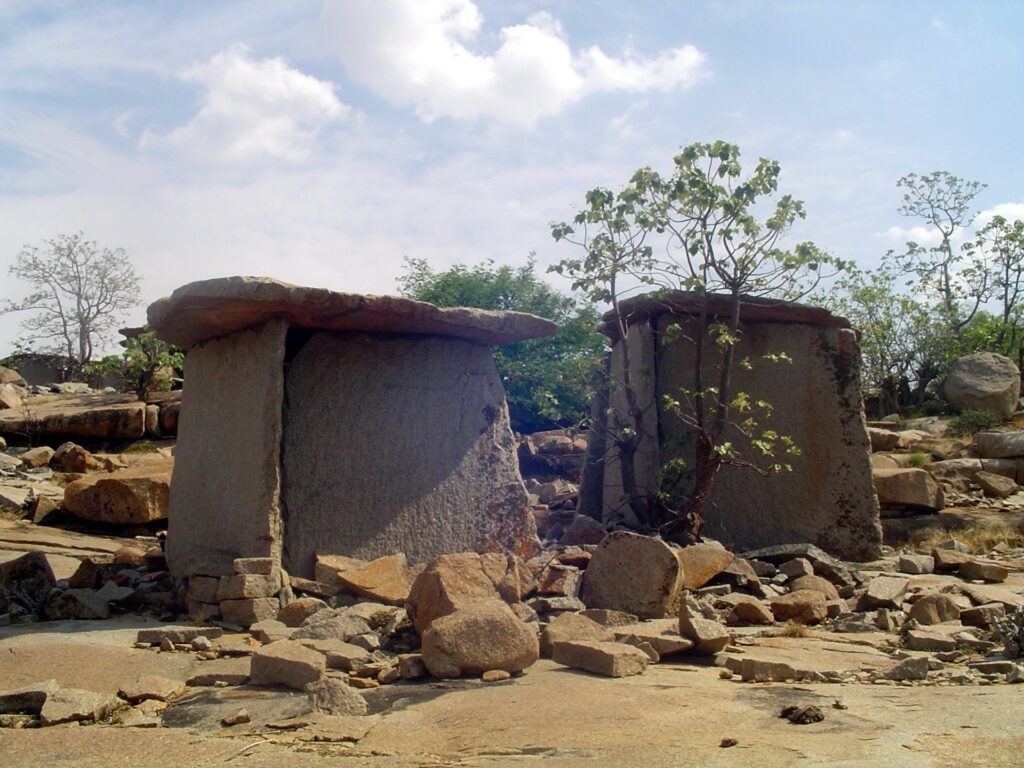
Tucked away in the rugged granite hills of Karnataka lies Hire Benkal, a vast prehistoric necropolis that silently guards the mysteries of India’s megalithic past. Scattered across this windswept landscape are nearly a thousand enigmatic stone chambers—known locally as the “Dwarf Chambers”—whose origins remain shrouded in legend, archaeology, and time.
Hidden in the hills of Karnataka, the prehistoric necropolis of Hire Benkal reveals a forgotten chapter of India’s ancient past. But who built these ‘dwarf’ chambers – and why?
An Archaeological Gem in Karnataka’s Heartland
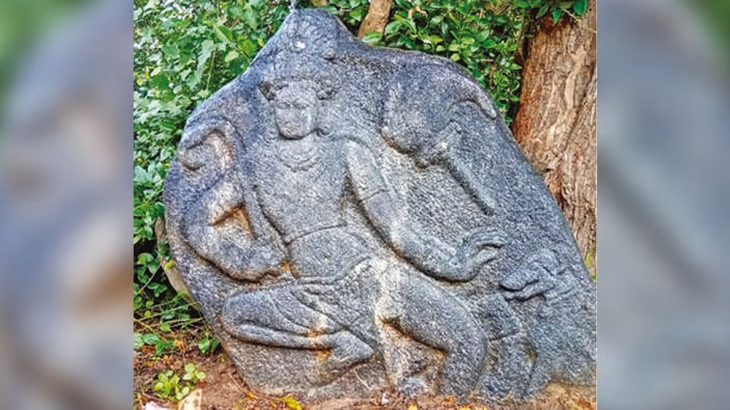
In the quiet village of Hire Benkal, located in Karnataka’s Koppal district, nearly 1,000 megalithic dolmens—mysterious stone burial chambers—dot the landscape of Moryar Gudda, or the “Hill of the Dwarfs”. These ancient structures, dating back more than 2,500 years, form one of India’s largest and best-preserved necropolises, yet remain largely unknown to the wider world.
Surrounded by mango orchards, sparse shrubland, and dramatic boulder formations, the region exudes a timeless, almost mystical atmosphere—making it not only a site of archaeological importance but also one of India’s most visually striking prehistoric landscapes.
Spanning over 20 hectares, the site is a rare, open-air museum of prehistoric mortuary architecture. The dolmens—large stone slabs supported by vertical stones—are believed to be burial monuments or commemorative structures, crafted by Iron Age communities. Yet, their purpose remains only partly understood.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Megalithic Marvels: More than Just Stone
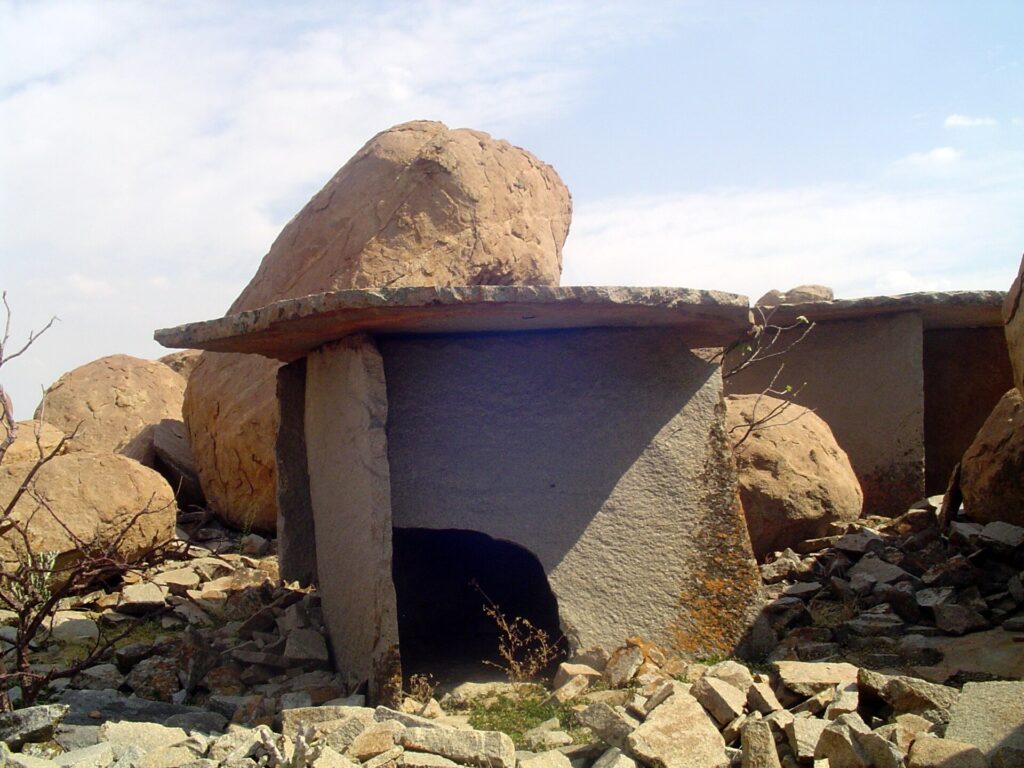
Some dolmens feature perfectly carved circular portholes, stone circles, and capstones weighing several tons—an engineering feat that has captivated both archaeologists and locals alike. The east-west orientation of many structures suggests astronomical or ceremonial significance, aligning with solar events like equinoxes or solstices, similar to theories surrounding Stonehenge.
According to Dr. Srikumar Menon, an expert on Indian megaliths at the National Institute of Advanced Studies, “The precision in design, and the fact that such a large number of structures are concentrated in one place, indicates this site was important for centuries.”
The Legend of the Moriyars: Ancient Builders or Mythical Dwarfs?
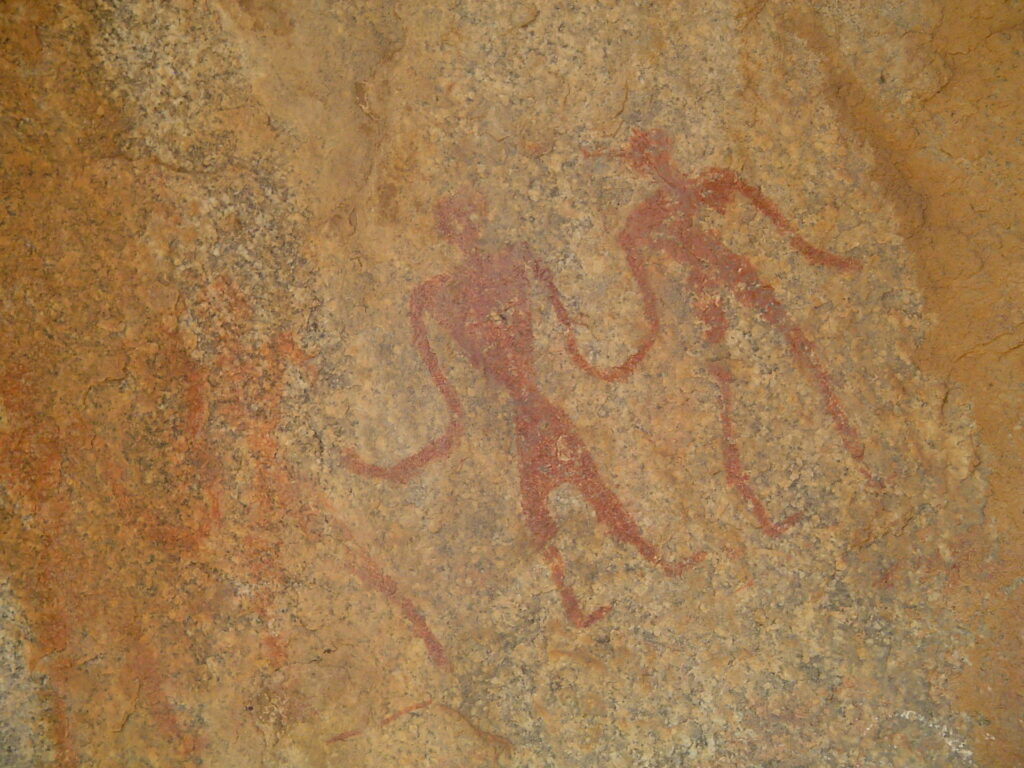
Local folklore attributes the dolmens to a supernatural race of tiny, powerful beings known as moriyars, believed to have been wiped out in a “rain of fire.” This belief is rooted in the unusual size and symmetry of the chambers—considered too sophisticated to be the work of early humans.
However, researchers point to similar legends from other nearby sites like Moribetta, Morikallu, and Sanna Moriyara Thatte, suggesting a widespread cultural memory.
“We know the megalith builders were humans like us,” said Menon, “but these enduring stories may reflect ancient memories passed down through generations.”

A Site in Peril: Neglect, Vandalism, and the Race Against Time
Despite its historical importance, Hire Benkal remains unprotected under India’s Archaeological Survey and lacks UNESCO World Heritage status—unlike its famous neighbor, Hampi, located just 42km away.
Vandalism, cattle grazing, and illegal excavations by treasure hunters have damaged several dolmens. Overgrowth and lack of conservation measures further threaten the site. According to Meera Iyer, convener at INTACH Bengaluru, “People often vandalize what they don’t understand. Interpretation, education, and controlled tourism are critical.”
Efforts are ongoing to have Hire Benkal included on UNESCO’s Tentative List, a move that could bring vital funding and global recognition. But progress remains slow.
Tourism Potential: A Hidden Jewel Awaiting Discovery
Currently, Hire Benkal sees only 20 to 100 visitors per month, mostly during the cooler season between October and February. In comparison, Stonehenge in the UK attracts over 1 million tourists annually.
Disha Ahluwalia, an archaeologist and scholar at MSU Baroda, believes public awareness is key: “Even people in Bengaluru often haven’t heard of it. This is a rare piece of Indian heritage that demands documentation and preservation.”
For travelers seeking off-the-beaten-path destinations, Hire Benkal offers raw natural beauty, mystical legends, and a glimpse into India’s prehistoric past. Its scenic hike, wildlife, and tranquil plateau make it an ideal eco-tourism site—if managed sustainably.

Conclusion: India’s Forgotten Stone Puzzle
Hire Benkal stands as a poignant reminder of India’s rich but underexplored prehistoric heritage. As the wind rustles through golden amaltas trees and monsoon clouds gather above the Deccan plateau, the stone chambers whisper stories of a people long forgotten—but not entirely lost.
With increased attention, better conservation, and community involvement, this ancient site could finally earn the recognition it deserves—transforming from a fragile mystery into a proud symbol of India’s archaeological wealth.
Sources:
Agrawal, D. P. (1979). Indian Society for Prehistoric and Quaternary Studies. B.R. Publishing Corporation.
National Institute of Advanced Studies, Bangalore
BBC Travel, 2024 Feature on Hire Benkal
Cover Image Credit: Wikipedia