A stone figurine was discovered in a 16500-year-old votive pit belonging to the Epi-paleolithic period, the transition phase from the Paleolithic Age to the Neolithic Age, during the archaeological excavation carried out in the Gedikkaya Cave in the İnhisar district of Bilecik in northwest Turkey.
With the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums, the rescue excavation started by the Bilecik Museum Directorate in the cave 1 kilometer away from İnhisar continues.
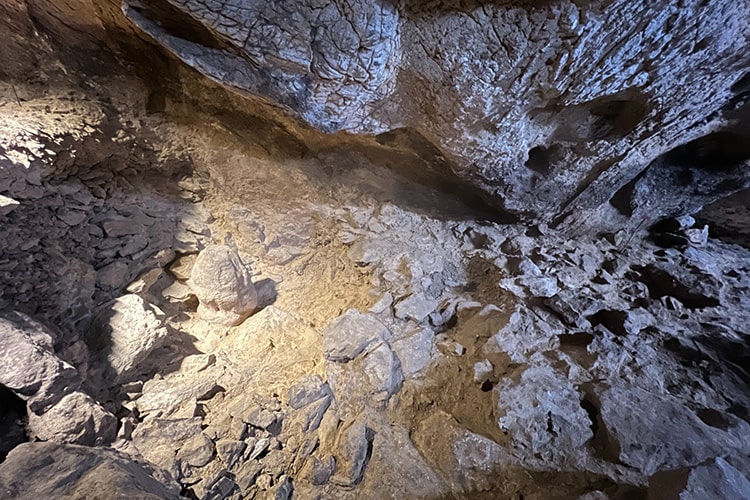
Traces of life were found in the cave at a depth of 180 meters, a height of about 20 meters, and a width of 30 meters, in two sections, the lower and the upper.
Bilecik Şeyh Edebali University (BŞEU) Faculty of Arts and Sciences Archeology Department Lecturer Assoc. Dr. Deniz Sarı, an ongoing study under the scientific consultancy of sheds light on the archeology of the region.
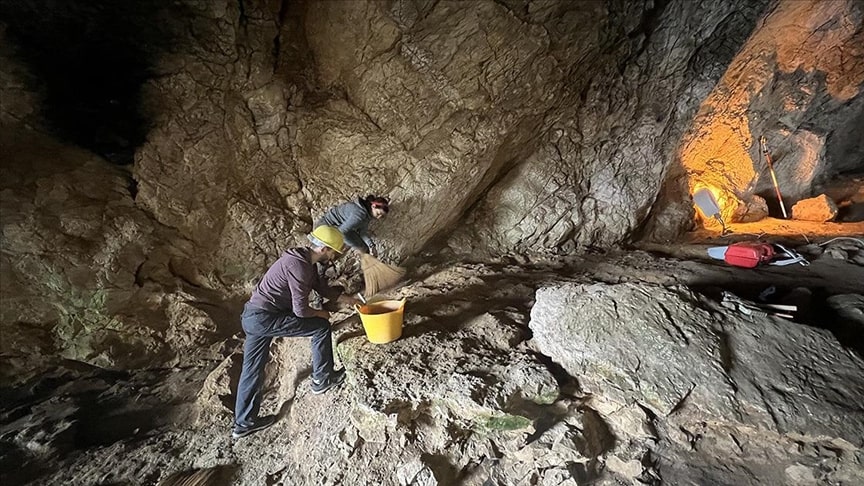

In the excavation, a flat ax made of diorite (rock type), grinding and hand stones, blades (stone chips), scraper, arrow and spearhead, ocher, spindle whorls, perforated ceramics (pottery), awl, a malachite ingot, and beads were unearthed.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In addition, important information was obtained about the craft branches such as stone and woodworking, mining and weaving carried out in the cave.
Finally, a votive pit dated to the Epipalaeolithic Period, 14500 BC was found in the cave.
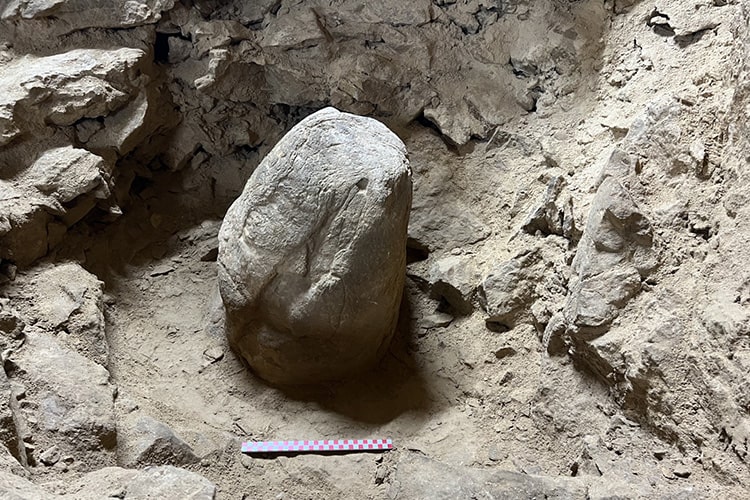

Bilecik Museum Director Harun Küçükaydın told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the earliest human traces known in the cave date back to 16,500 years ago, and that a large number of finds dating from 7000 to 5000 BC were found in the radiocarbon analysis.
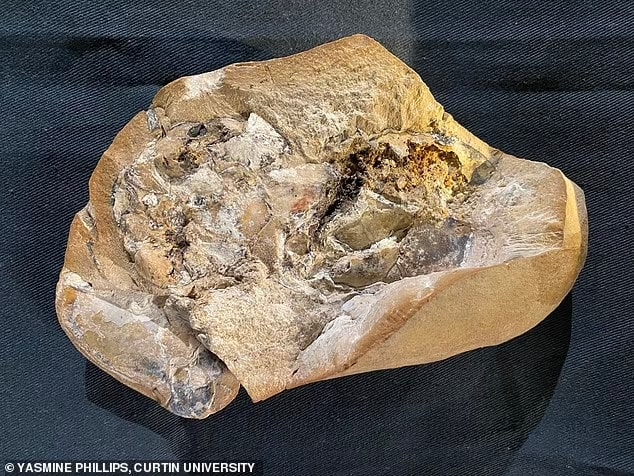
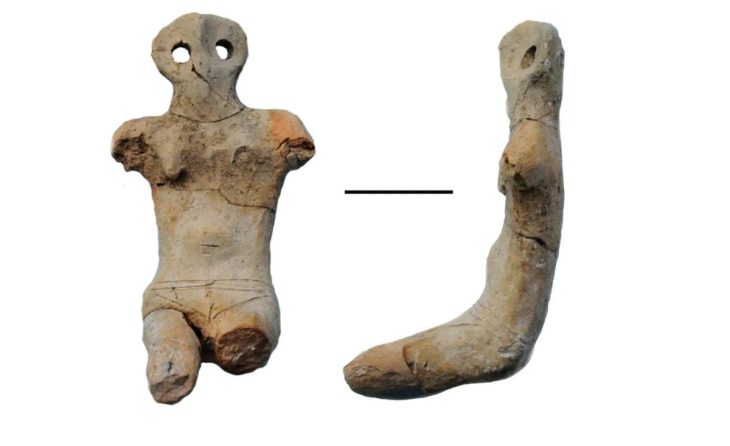
Küçükaydın continued as follows: ” A partially worked stalagmite was unearthed in this votive pit. We can associate the stalagmite with the Neolithic cultures of the Near East.”
“The seated human figurine carved from this stone can be considered a link between Venus figurines from the European Upper Paleolithic period and mother goddess figurines from Anatolian Neolithic cultures.”
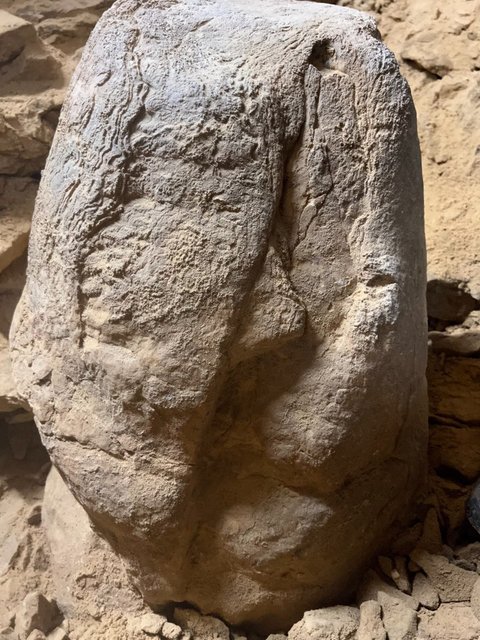

Explaining that they determined that the earliest of the finds obtained during the studies in Gedikkaya Cave dates back to 16,500 years ago, Associate Professor Deniz Sarı said: “This period, of which we know very little, is a process by which European Upper Paleolithic cultures spread to the Balkans, the Caucasus, and the Mediterranean. Excavations in the larger area will provide more concrete data about the location of Gedikkaya in this extension and the pre-human activity at the end of the Ice Ages. However, in 2022, we uncovered a votive pit in the cave in relation to the process in question.”
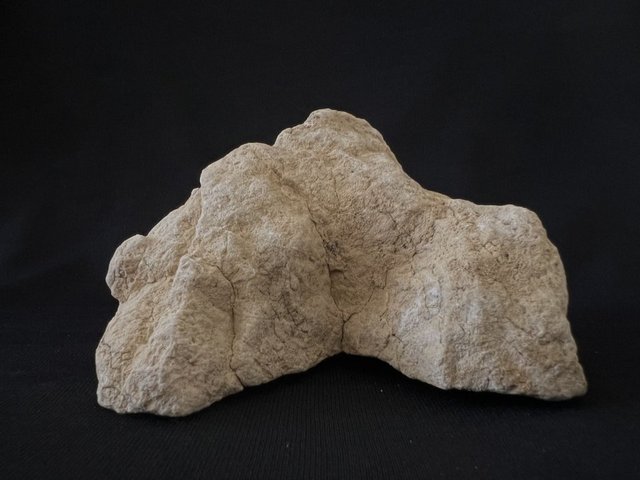

“We unearthed a naturally formed stalagmite inside the pit surrounded by rows of crescent-shaped stones. The stalagmite is partially embroidered, giving the appearance of a stele. The pit was probably closed later. The finds inside the pit are extremely important and contain very new and extraordinary data in terms of prehistoric archeology. One of them is this a stone figurine. The stylized figurine in a sitting position is depicted with its legs spread out to the sides. It is a stone and stylized example of a mother goddess figurine characteristic of the Neolithic cultures of the Near East. In this context, the studies in the cave will make new contributions to the literature in the context of Anatolian prehistoric archeology.”