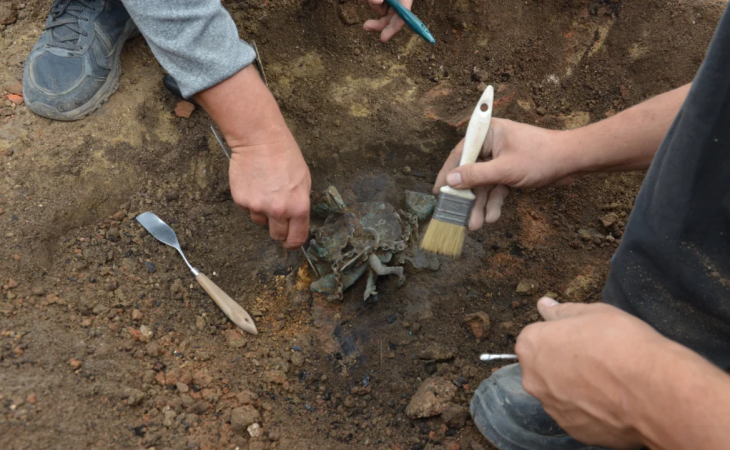
An individual bedecked in copper jewelry was discovered during the excavation of a protohistoric necropolis in Aubagne, southeastern France.
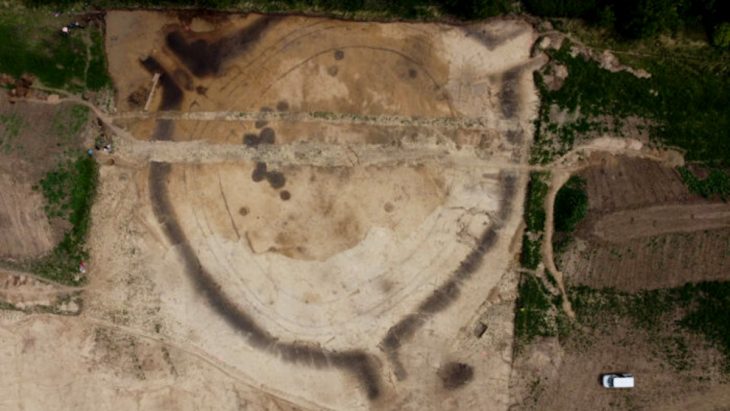
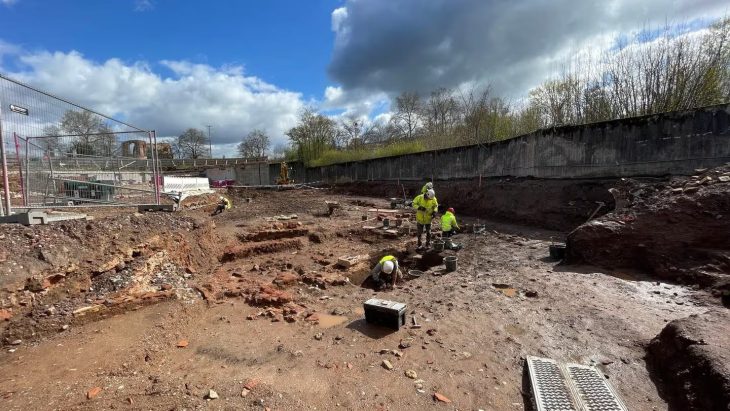
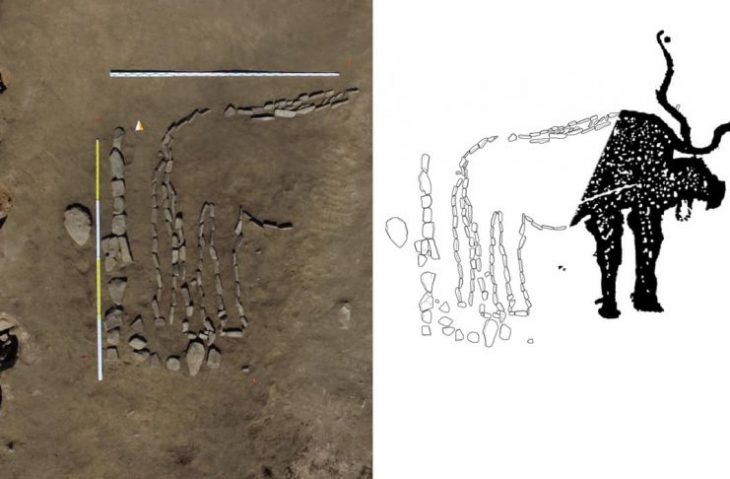
The necropolis, which served as a transitional site between the late Bronze and early Iron ages from roughly 900 to 600 B.C., was first unearthed in 2021. Ten burials, including three cremation deposits and eight burials buried beneath a tumulus, were discovered at that time. Three additional burials were found during this year’s excavation, one of which was hidden beneath a 33-foot-diameter tumulus. The tumulus is noteworthy because a deep ditch surrounded it, and it probably used to be marked by a ring of stones. However, the burial inside was not furnished.
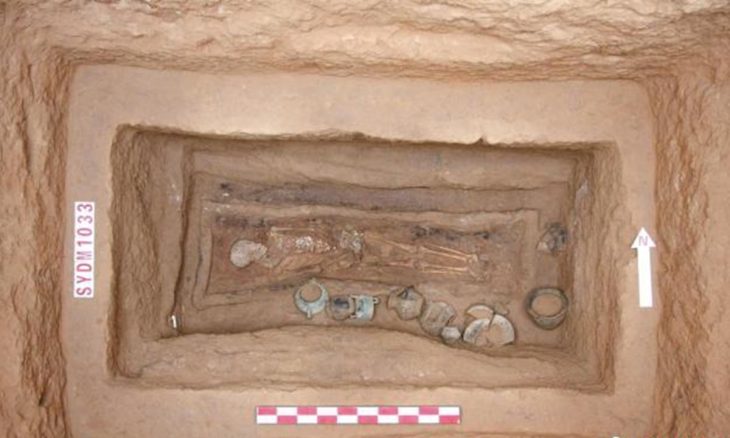
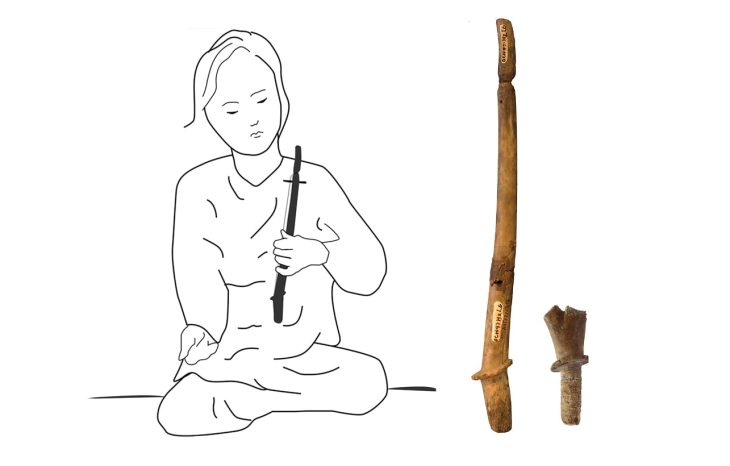
The two additional graves discovered this season were: The first contained the skeletal remains of a person who was wearing a twisted copper alloy bracelet and a pearl and stone jewel on the left shoulder. Near the deceased’s head, two ceramic pots were buried.
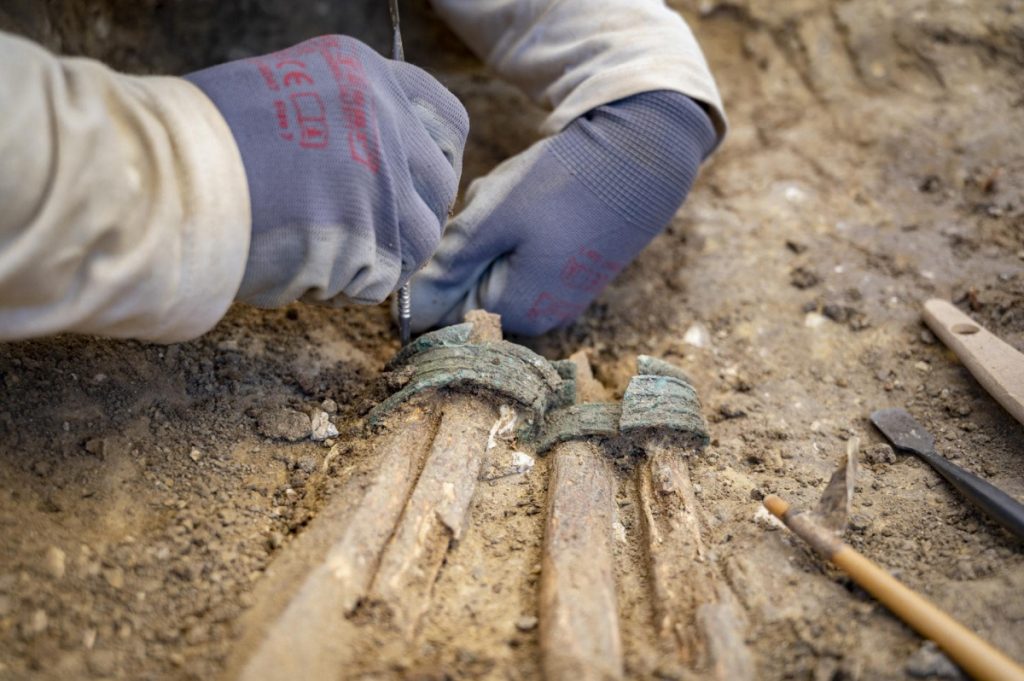

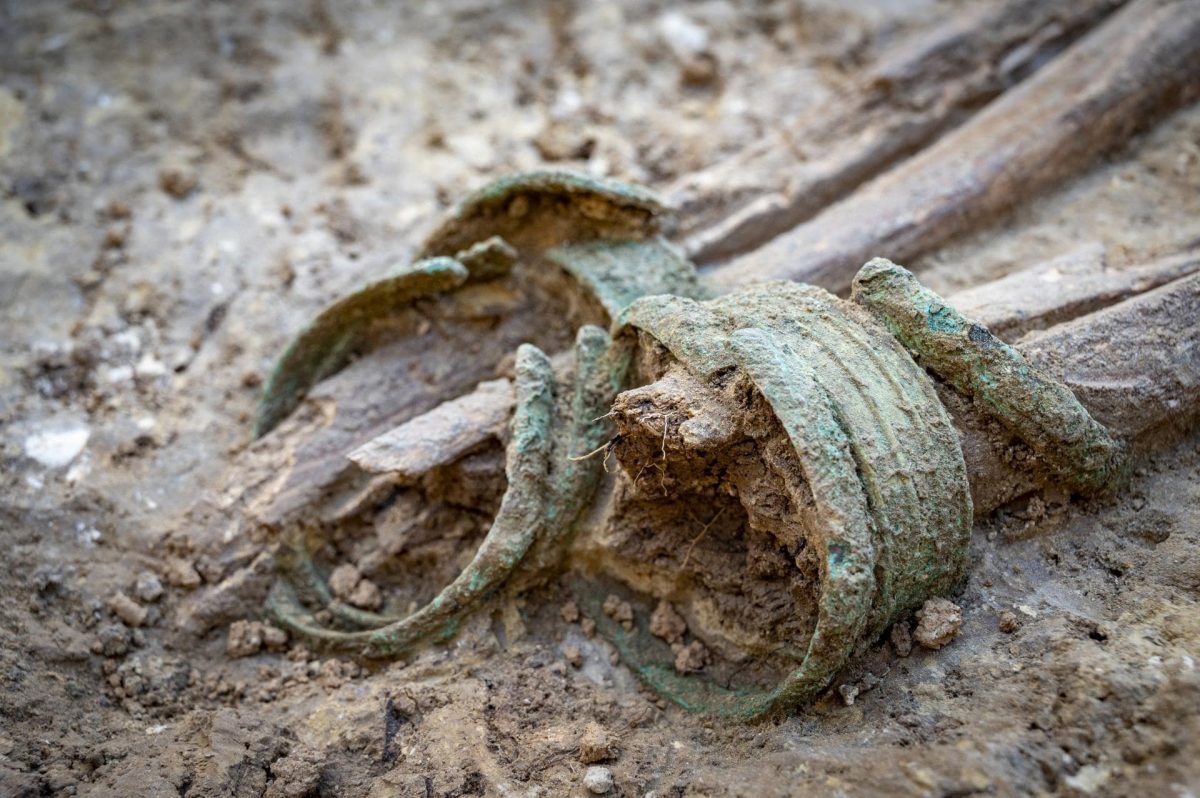
The second non-tumulus burial is the richest found in this necropolis thus far. The individual was buried wearing a tubular torc with rolled terminals around their neck, three ankle bangles, and three toe rings. A brooch and a large ceramic urn were placed next to the deceased.
The tumulus and the first burial are close together. The third was separated from the first two. Each space was clearly and purposefully delimited by structures that are now long gone. A line of postholes separates the tumulus and the first inhumation, indicating a linear structure that once formed the boundary line of space reserved for the dead. The second burial was defined by a six-foot-long alignment of stone blocks.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
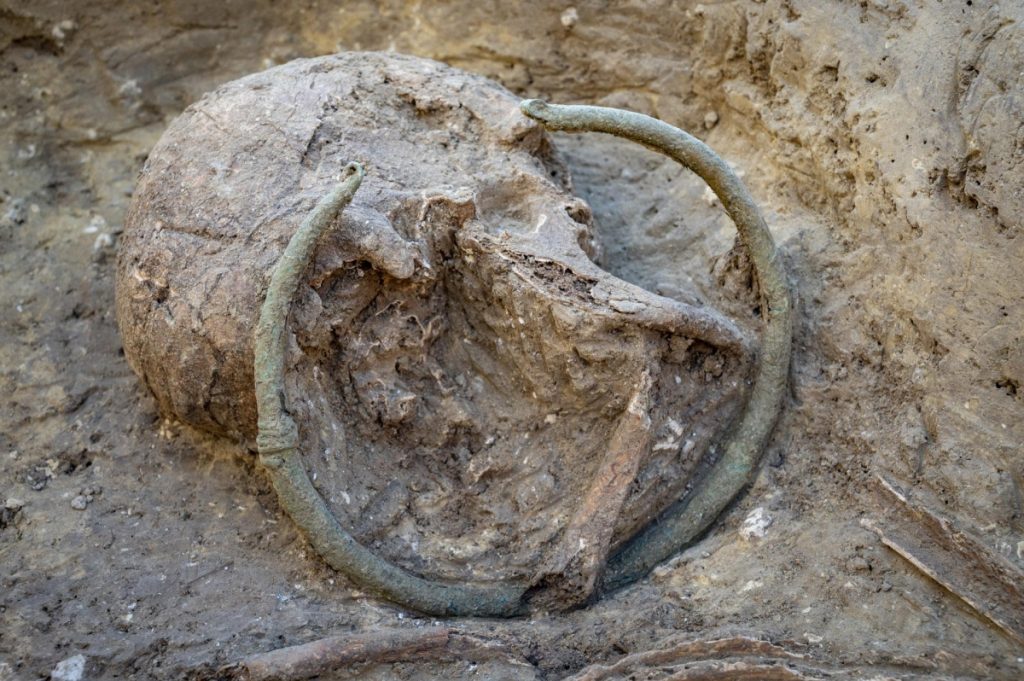

The discovery of these three graves has significantly increased our knowledge of protohistoric southern French funerary customs. They also show that the necropolis was much larger than what early archaeologists had thought it to be. The necropolis is estimated to have covered at least 1.3 hectares and probably even more, according to the new data.
Cover Photo: © Denis Dubesset, Inrap